How the India-Bangladesh Enclaves Problem Was Jump-Started in 2007 Towards its 2015 Solution: A Case Study of Academic Impact on Policy
June 8, 2015 — drsubrotoroy“Haksar, Manmohan and Sonia” (2014)
August 7, 2014 — drsubrotoroyMy article “Haksar, Manmohan and Sonia” appeared today as an op-ed with the New Indian Express http://t.co/bRnQI1hrwy

In the summer of 1973, my father, then with India’s embassy in Paris, brought home two visiting colleagues separately, to advise me before I headed to undergraduate studies at the LSE. One was G Parthasarathi, India’s envoy in Karachi during the 1965 war [CORRECTION Nov 2015: Parthasarathi had left shortly before the war; Kewal Singh arrived as the war started] when my father had been acting head in Dhaka; G P was marvelous, strictly advising I do the hardest things I could find at LSE, namely mathematical economics. The other visitor was Manmohan Singh.
Manmohan, then in his early 40s, asked to meet me alone, and we plunged quickly into a heated debate about the demerits (as I saw them) and merits (as he saw them) of the USSR and its “planning”. He was taken aback by the lad, and at the end of his 40-minute visit said he would write to his friend Amartya Sen at LSE about me. An ambiguous, hardly laudatory letter of introduction to Amartya arrived, which I duly but reluctantly carried; I wish I had kept a copy but xeroxing was not yet a word back then.
When I told my father about the debate, he to my surprise said Manmohan was extremely highly thought of in government circles, had degrees from both Cambridge and Oxford, and was expected to become prime minister of India some day!
That prediction, more than 30 years before Manmohan did become India’s PM, was almost certainly a reflection of the opinion of P N Haksar, still at the height of his power as Indira Gandhi’s right-hand man. In a 2005 interview with Mark Tully, Manmohan acknowledged Haksar being his mentor in politics who brought him into government in early 1971. My father himself was sent by Haksar to the Paris embassy in anticipation of Indira’s November 1971 visit on her diplomatic tour before the Bangladesh War.
Fast forward to the afternoon of March 22, 1991, at Delhi’s Andhra Bhavan. I had met Rajiv Gandhi through S S Ray on September 18, 1990, and given him results of a perestroika-for-India project I had led at the University of Hawaii since 1986.On September 25, 1990, Rajiv formed a group consisting of Gen K V Krishna Rao, M K Rasgotra, V Krishnamurthy, S Pitroda and myself to write a modern agenda and manifesto for elections Rajiv said he expected by April 1991. Krishnamurthy later brought in A M Khusro to the group, and all these persons were present at the March 22 meeting—when I was unexpectedly challenged by Rasgotra demanding to know what Manmohan Singh would say about all this liberalisation and efficiency (and public goods, etc.) I had proposed.
That was the first mention of Manmohan in post-Indira politics. I replied I did not know what he would say but knew he had been on a project for Julius Nyerere, that the main thing was to get the world to see the Congress at least knew its economics and wanted to improve India’s woeful credit-standing.
The next day, on the lawns of 10 Jan Path, Rajiv launched Krishna Rao’s book titled Prepare or Perish. Rajiv was introduced on the occasion by none other than P N Haksar. I talked to Haksar briefly, mentioning his sending my father to Paris in 1971 and my father’s old friends the Kaul brothers, the elder being Haksar’s brother-in-law and the younger being Manmohan’s first boss in government. Haksar seemed unwell but was clearly delighted to have returned to favour after falling out with Indira during Sanjay’s regime.
The March 22, 1991, meeting was also one of several occasions when I, a complete layman on security issues and new to Delhi and in my 30s, warned as vehemently as I could that Rajiv seemed to my layman’s eyes extremely vulnerable to assassination. Absolutely nothing was done in response by anyone, other than saying I should probably speak to “Madame”!
One man’s response, in 2007 and 2014 publications, has been to deny he knew me at all and claim the group came to exist without me—when in fact it was created by Rajiv as a sounding board one week after I gave him the academic project results I had led since 1986. This same man had excitedly revealed to me on September 25, 1990, that his claim to a doctoral degree originated in the USSR in the 1970s; he has always concealed his experiences in that country. After Rajiv’s assassination, he rose to much background influence with Sonia, and one of his protégés is now apparently influential with Mr Modi too.
Sonia Gandhi I met only once to convey my condolences in December 1991, and give her a copy of a tape of conversations between Rajiv and myself during the Gulf war in January that year. She seemed a taciturn figure in deep grief, and apparently continued with the seven-year period of mourning traditional in her culture of origin.
Natwar Singh and Sanjaya Baru, in their recent publications, may have allowed basic misinterpretations of events to distract from what may be informative in their experience.
Natwar has said Haksar was central in May 1991 in the move (purportedly on behalf of Rajiv’s newly bereaved widow) to first ask S D Sharma to take the PM’s job, which Sharma declined. If so, this was a failed attempt by the “Haksar axis” of unelected non-politicians to maintain control of events. Natwar claims it was only then Sonia chose P V N Rao. In reality, P V N R was a highly respected leader who, though due to retire, was the acknowledged senior member in a group of regional leaders including S S Ray, Sharad Pawar and others. The Haksar axis failed to stop P V N R’s rise to the top job, though it managed to get Haksar’s protégé to become finance minister. Sonia was hardly involved.
As for Manmohan becoming Sonia’s PM, a senior Lok Sabha Congress leader with PM ambitions himself told me of his own accord in December 2001 that it was certain she would not take the top job herself and it was generally presumed Manmohan would get one term—the denouement of the Haksarian prediction my father made to me in 1973 in Paris. Contrary to Baru’s claim or even Manmohan’s own self-knowledge, it was never any “accident” that he became PM of India.
Finally on the issue of files being shown, the man named as the conduit is someone I became related to in law back in 1981. He and Manmohan, too, would have been sticklers for the rules. The real issue is this: given the 1970s brand of Soviet influence on the Congress, would anyone have said it was Kosygin as PM who did or could ever wield more power than Brezhnev the party boss? Of course not. The same with Manmohan and Sonia in India.
One of the men Rajiv introduced me to on 25-9-1990 at 10 JanPath (No, Rajiv did not realize who he was…) 2023
July 3, 2014 — drsubrotoroyMuch as I might love Russia, England, France, America, I despise their spies & local agents affecting poor India’s policies: Memo to PM Modi, Mr Jaitley, Mr Doval & the new Govt. of India: Beware of Delhi’s sleeper agents, lobbyists & other dalals (2014)
1 July 2014
Dear Bibek,
The very elderly man I refer to as “Sonia’s Lying Courtier” herein
https://independentindian.com/2007/11/25/sonias-lying-courtier/
is someone who has known you, leading up to your appointment as Director at Sonia’s “Rajiv Gandhi Institute” and later. He has now published a purported memoir whose main aim is to conceal his Soviet connections during the Brezhnev era 1960s-1970s, besides trying to rub my name out from my role with Rajiv in 1990-1991. The woman journalist in Delhi who is named as having ghost-written his new book is someone you know quite well too.
The man was someone whom I worked with and who was introduced to me by Rajiv Gandhi on 25/9/1990, a Soviet trained “technocrat” who had inveigled himself into Rajiv’s circle as he had been a favoured one of Indira (presumably via PN Haksar) when he returned from the USSR. He was also the link explaining, again via PN Haksar, how Manmohan first became FM in 1991 after Rajiv’s assassination, then how Manmohan came to Sonia’s notice and attention, and was later crucial in the so-called Rajiv Gandhi Foundation and in the formation of Sonia’s so-called National Advisory Council.
His mandate was to keep INC policies predictable and agreeable in the areas of Soviet/Russian interest, in which he seems to have succeeded during the Sonia-Manmohan regime.
He found me an unknown force, and worked to edge me out, despite the fact the 25/9/90 group was formed by Rajiv as a sounding-board for the perestroika-for-India project I led in America since 1986 and which I brought to Rajiv the week before on 18/9/90…
I send this to you as a word of caution as you are clearly close to Mr Modi and Mr Doval, yet none of you may know the man’s background and intent, even in his dotage. Certainly the purported memoir written by the woman journalist is something whose main aim is to conceal the man’s Soviet/Russian background. Had it been an honest intent, he would have had no need to conceal any of this but would have addressed his own Russian experience openly and squarely. He may have had his impact already with the new Government, I do not know.
For myself, I have been openly rather pro-Russia on the merits of the current Ukraine issue, but, as you will appreciate, I despise any kind of deep foreign agent seeking to control Indian policy in long-term concealment.
Cordially
Suby Roy
Sonia’s Lying Courtier with Postscript 25 Nov 2007, & Addendum 30 June 2014
30th June 2014
“Sonia’s Lying Courtier” (see below) has now lied again! In a ghost-written 2014 book published by a prominent publisher in Delhi!
He has so skilfully lied about himself the ghost writer was probably left in the dark too about the truth.
**The largest concealment has to do with his Soviet connection: he is fluent in Russian, lived as a privileged guest of the state there, and before returning to the Indian public sector was awarded in the early 1970s a Soviet degree, supposedly an earned doctorate in Soviet style management!**
How do I know? He told me so personally! His Soviet degree is what allowed himself to pass off as a “Dr” in Delhi power-circles for decades, as did many others who were planted in that era. He has also lied about himself and Rajiv Gandhi in 1990-1991, and hence he has lied about me indirectly.
In 2007 I was gentle in my exposure of his mendacity because of his advanced age. Now it is more and more clear to me that exposing this directly may be the one way for Sonia and her son to realise how they, and hence the Congress party, were themselves influenced without knowing it for years…
25 November 2007
Two Sundays ago in an English-language Indian newspaper, an elderly man in his 80s, advertised as being “the Gandhi family’s favourite technocrat” published some deliberate falsehoods about events in Delhi 17 years ago surrounding Rajiv Gandhi’s last months. I wrote at once to the man, let me call him Mr C, asking him to correct the falsehoods since, after all, it was possible he had stated them inadvertently or thoughtlessly or through faulty memory. He did not do so. I then wrote to a friend of his, a Congress Party MP from his State, who should be expected to know the truth, and I suggested to him that he intercede with his friend to make the corrections, since I did not wish, if at all possible, to be compelled to call an elderly man a liar in public.
That did not happen either and hence I am, with sadness and regret, compelled to call Mr C a liar.
The newspaper article reported that Mr C’s “relationship with Rajiv (Gandhi) would become closer when (Rajiv) was out of power” and that Mr C “was part of a group that brainstormed with Rajiv every day on a different subject”. Mr C has reportedly said Rajiv’s “learning period came after he left his job” as PM, and “the others (in the group)” were Mr A, Mr B, Mr D, Mr E “and Manmohan Singh” (italics added).
In reality, Mr C was a retired pro-USSR bureaucrat aged in his late 60s in September 1990 when Rajiv Gandhi was Leader of the Opposition and Congress President. Manmohan Singh was an about-to-retire bureaucrat who in September 1990 was not physically present in India, having been working for Julius Nyerere of Tanzania for several years.
On 18 September 1990, upon recommendation of Siddhartha Shankar Ray, Rajiv Gandhi met me at 10 Janpath, where I handed him a copy of the unpublished results of an academic “perestroika-for-India” project I had led at the University of Hawaii since 1986. The story of that encounter has been told first on July 31-August 2 1991 in The Statesman, then in the October 2001 issue of Freedom First, then in January 6-8 2006, September 23-24 2007 in The Statesman, and most recently in The Statesman Festival Volume 2007. The last of these speaks most fully yet of my warnings against Rajiv’s vulnerability to assassination; this document in unpublished form was sent by me to Rajiv’s friend, Mr Suman Dubey in July 2005, who forwarded it with my permission to the family of Rajiv Gandhi.
It was at the 18 September 1990 meeting that I suggested to Rajiv that he should plan to have a modern election manifesto written. The next day, 19 September, I was asked by Rajiv’s assistant V George to stay in Delhi for a few days as Mr Gandhi wished me to meet some people. I was not told whom I was to meet but that there would be a meeting on Monday, 24th September. On Saturday, the Monday meeting was postponed to Tuesday 25th September because one of the persons had not been able to get a flight into Delhi. I pressed to know what was going on, and was told I would meet Mr A, Mr B, Mr C and Mr D. It turned out later Mr A was the person who could not fly in from Hyderabad.
The group (excluding Mr B who failed to turn up because his servant had failed to give him the right message) met Rajiv at 10 Janpath in the afternoon of 25th September. We were asked by Rajiv to draft technical aspects of a modern manifesto for an election that was to be expected in April 1991. The documents I had given Rajiv a week earlier were distributed to the group. The full story of what transpired has been told in my previous publications.
Mr C was ingratiating towards me after that first meeting with Rajiv and insisted on giving me a ride in his car which he told me was the very first Maruti ever manufactured. He flattered me needlessly by saying that my PhD (in economics from Cambridge University) was real whereas his own doctoral degree had been from a dubious management institute of the USSR. (Handling out such doctoral degrees was apparently a standard Soviet way of gaining influence.) Mr C has not stated in public how his claim to the title of “Dr” arises.
Following that 25 September 1990 meeting, Mr C did absolutely nothing for several months towards the purpose Rajiv had set us, stating he was very busy with private business in his home-state where he flew to immediately. Mr D went abroad and was later hit by severe illness. Mr B, Mr A and I met for luncheon at New Delhi’s Andhra Bhavan where the former explained how he had missed the initial meeting. Then Mr B said he was very busy with his house-construction, and Mr A said he was very busy with finishing a book for his publishers on Indian defence, and both begged off, like Mr C and Mr D, from any of the work that Rajiv had explicitly set our group. My work and meeting with Rajiv in October 1990 has been reported previously.
Mr C has not merely suppressed my name from the group in what he has published in the newspaper article two Sundays ago, he has stated he met Rajiv as part of such a group “every day on a different subject”, another falsehood. The next meeting of the group with Rajiv was in fact only in December 1990, when the Chandrashekhar Government was discussed. I was called by telephone in the USA by Rajiv’s assistant V George but I was unable to attend, and was briefed later about it by Mr A.
When new elections were finally announced in March 1991, Mr C brought in Mr E into the group in my absence (so he told me), perhaps in the hope I would remain absent. But I returned to Delhi and between March 18 1991 and March 22 1991, our group, including Mr E (who did have a genuine PhD), produced an agreed-upon document. That document was handed over by us together in a group to Rajiv Gandhi at 10 Janpath the next day, and also went to the official political manifesto committee of Narasimha Rao, Pranab Mukherjee and M. Solanki.
Our group, as appointed by Rajiv on 25 September 1990, came to an end with the submission of the desired document to Rajiv on 23 March 1991.
As for Manmohan Singh, contrary to Mr C’s falsehood, Manmohan Singh has himself truthfully said he was with the Nyerere project until November 1990, then joined Chandrashekhar’s PMO in December 1990 which he left in March 1991, that he had no meeting with Rajiv Gandhi prior to Rajiv’s assassination but rather did not in fact enter Indian politics at all until invited by Narasimha Rao several weeks later to be Finance Minister. In other words, Manmohan Singh himself is on record stating facts that demonstrate Mr C’s falsehood.
The economic policy sections of the document submitted to Rajiv on 23 March 1991 had been drafted largely by myself with support of Mr E and Mr D and Mr C as well. It was done over the objections of Mr B, who had challenged me by asking what Manmohan Singh would think of it. I had replied I had no idea what Manmohan Singh would think of it, saying I knew he had been out of the country on the Nyerere project for some years.
Mr C has deliberately excluded my name from the group and deliberately added Manmohan Singh’s instead. What explains this attempted falsification of facts – reminiscent of totalitarian practices in communist countries? Manmohan Singh was not involved by his own admission, and as Finance Minister told me so directly when he and I were introduced in Washington DC in September 1993 by Siddhartha Shankar Ray, then Indian Ambassador to the USA.
A possible explanation for Mr C’s mendacity is as follows: I have been recently publishing the fact that I repeatedly pleaded warnings that I (even as a layman on security issues) perceived Rajiv Gandhi to have been insecure and vulnerable to assassination. Mr C, Mr B and Mr A were among the main recipients of my warnings and my advice as to what we as a group, appointed by Rajiv, should have done towards protecting Rajiv better. They did nothing — though each of them was a senior man then aged in his late 60s at the time and fully familiar with Delhi’s workings while I was a 35 year old newcomer. After Rajiv was assassinated, I was disgusted with what I had seen of the Congress Party and Delhi, and did not return except to meet Rajiv’s widow once in December 1991 to give her a copy of a tape in which her late husband’s voice was recorded in conversations with me during the Gulf War.
Mr C has inveigled himself into Sonia Gandhi’s coterie – while Manmohan Singh went from being mentioned in our group by Mr B to becoming Narasimha Rao’s Finance Minister and Sonia Gandhi’s Prime Minister. If Rajiv had not been assassinated, Sonia Gandhi would have been merely a happy grandmother today and not India’s purported ruler. India would also have likely not have been the macroeconomic and political mess that the mendacious people around Sonia Gandhi like Mr C have now led it towards.
POSTSCRIPT: The Congress MP was kind enough to write in shortly afterwards; he confirmed he “recognize(d) that Rajivji did indeed consult you in 1990-1991 about the future direction of economic policy.” A truth is told and, furthermore, the set of genuine Rajivists in the present Congress Party is identified as non-null.
Did Jagdish Bhagwati “originate”, “pioneer”, “intellectually father” India’s 1991 economic reform? Did Manmohan Singh? Or did I, through my encounter with Rajiv Gandhi, just as Siddhartha Shankar Ray told Manmohan & his aides in Sep 1993 in Washington? Judge the evidence for yourself. And why has Amartya Sen misdescribed his work? India’s right path forward today remains what I said in my 3 Dec 2012 Delhi lecture!
August 23, 2013 — drsubrotoroyDid Jagdish Bhagwati “originate”, “pioneer”, “intellectually father” India’s 1991 economic reform? Did Manmohan Singh? Or did I, through my encounter with Rajiv Gandhi, just as Siddhartha Shankar Ray told Manmohan & his aides in Sep 1993 in Washington? Judge the evidence for yourself. And why has Amartya Sen misdescribed his work? India’s right path forward today remains what I said in my 3 Dec 2012 Delhi lecture!
[See also “I’m on my way out”: Siddhartha Shankar Ray (1920-2010)…An Economist’s Tribute”; “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform”; “Three Memoranda to Rajiv Gandhi 1990-1991″
Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s edited by Subroto Roy & William E James, 1986-1992… pdf copy uploaded 2021
Foundations of Pakistan’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s, edited by William E James & Subroto Roy, 1986-1993… pdf copy uploaded 2021
Critique of Amartya Sen: A Tragedy of Plagiarism, Fake News, Dissimulation
Contents
Part I: Facts vs Fiction, Flattery, Falsification, etc
1. Problem
2. Rajiv Gandhi, Siddhartha Shankar Ray, Milton Friedman & Myself
3. Jagdish Bhagwati & Manmohan Singh? That just don’t fly!
4. Amartya Sen’s Half-Baked Communism: “To each according to his need”?
Part II: India’s Right Road Forward Now: Some Thoughtful Analysis for Grown Ups
5. Transcending a Left-Right/Congress-BJP Divide in Indian Politics
6. Budgeting Military & Foreign Policy
7. Solving the Kashmir Problem & Relations with Pakistan
8. Dealing with Communist China
9. Towards Coherence in Public Accounting, Public Finance & Public Decision-Making
10. India’s Money: Towards Currency Integrity at Home & Abroad
Part I: Facts vs Fiction, Flattery, Falsification, etc
1. Problem
Arvind Panagariya says in the Times of India of 27 July 2013
“…if in 1991 India embraced many of the Track-I reforms, writings by Sen played no role in it… The intellectual origins of the reforms are to be found instead in the writings of Bhagwati, both solely and jointly with Padma Desai and T N Srinivasan….”
Now Amartya Sen has not claimed involvement in the 1991 economic reforms so we are left with Panagariya claiming
“The intellectual origins of the reforms are to be found instead in the writings of Bhagwati…”
Should we suppose Professor Panagariya’s master and co-author Jagdish Bhagwati himself substantially believes and claims the same? Three recent statements from Professor Bhagwati suffice by way of evidence:
(A) Bhagwati said to parliamentarians in the Lok Sabha on 2 December 2010 about the pre-1991 situation:
“This policy framework had been questioned, and its total overhaul advocated, by me and Padma Desai in writings through the late 1960s which culminated in our book, India: Planning for Industrialization (Oxford University Press: 1970) with a huge blowback at the time from virtually all the other leading economists and policymakers who were unable to think outside the box. In the end, our views prevailed and the changes which would transform the economy began, after an external payments crisis in 1991, under the forceful leadership of Prime Minister Manmohan Singh who was the Finance Minister at the time….”
(B) Bhagwati said to Economic Times on 28 July 2013:
“When finance minister Manmohan Singh was in New York in 1992, he had a lunch for many big CEOs whom he was trying to seduce to come to India. He also invited me and my wife, Padma Desai, to the lunch. As we came in, the FM introduced us to the invitees and said: ‘These friends of mine wrote almost a quarter century ago [India: Planning for Industrialisation was published in 1970 by Oxford] recommending all the reforms we are now undertaking. If we had accepted the advice then, we would not be having this lunch as you would already be in India’.”
(C) And Bhagwati said in Business Standard of 9 August 2013:
“… I was among the intellectual pioneers of the Track I reforms that transformed our economy and reduced poverty, and witness to that is provided by the Prime Minister’s many pronouncements and by noted economists like Deena Khatkhate.. I believe no one has accused Mr. Sen of being the intellectual father of these reforms. So, the fact is that this huge event in the economic life of India passed him by…”
From these pronouncements it seems fair to conclude Professors Bhagwati and Panagariya are claiming Bhagwati has been the principal author of “the intellectual origins” of India’s 1991 reforms, has been their “intellectual father” or at the very least has been “among the intellectual pioneers” of the reform (“among” his own collaborators and friends, since none else is mentioned). Bhagwati has said too his friend Manmohan Singh as Finance Minister participated in the process while quoting Manmohan as having said Bhagwati was the principal author.
Bhagwati’s opponent in current debate, Amartya Sen, has been in agreement with him that Manmohan, their common friend during college days at Cambridge in the 1950s, was a principal originating the 1991 reforms, saying to Forbes in 2006:
“When Manmohan Singh came to office in the early 1990s as the newly appointed finance minister, in a government led by the Congress Party, he knew these problems well enough, as someone who had been strongly involved in government administration for a long time.”
In my experience, such sorts of claims, even in their weakest form, have been, at best, scientifically sloppy and unscholarly, at worst mendacious suppressio veri/suggestio falsi, and in between these best and worst interpretations, examples of academic self-delusion and mutual flattery. We shall see Bhagwati’s opponent, Amartya Sen, has denied academic paternity of recent policies he has spawned while appearing to claim academic paternity of things he has not! Everyone may have reasonably expected greater self-knowledge, wisdom and scholarly values of such eminent academics. Their current spat has instead seemed to reveal something rather dismal and self-serving.
You can decide for yourself where the truth, ever such an elusive and fragile thing, happens to be and what is best done about it. Here is some evidence.
2. Rajiv Gandhi, Siddhartha Shankar Ray, Milton Friedman & Myself
Professor Arvind Panagariya is evidently an American economics professor of Indian national origin who holds the Jagdish Bhagwati Chair of Indian Political Economy at Columbia University. I am afraid I had not known his name until he mentioned my name in Economic Times of 24 October 2001. He said
In mentioning the volume “edited by Subroto Roy and William E James”, Professor Panagariya did not appear to find the normal scientific civility to identify our work by name, date or publisher. So here that is now:
This was a book published in 1992 by the late Tejeshwar Singh for Sage. It resulted from the University of Hawaii Manoa perestroika-for-India project, that I and Ted James created and led between 1986 and 1992/93. (Yes, Hawaii — not Stanford, Harvard, Yale, Columbia or even Penn, whose India-policy programs were Johnny-come-latelies a decade or more later…) There is a sister-volume too on Pakistan, created by a parallel project Ted and I had led at the same time (both now in pdf):
In 2004 from Britain, I wrote to the 9/11 Commission saying if our plan to study Afghanistan after India and Pakistan had not been thwarted by malign local forces among our sponsors themselves, we, a decade before the September 11 2001 attacks on the USA, may just have come up with a pre-emptive academic analysis. It was not to be.
Milton Friedman’s chapter that we published for the first time was a memorandum he wrote in November 1955 for the Government of India which the GoI had effectively suppressed. I came to know of it while a doctoral student at Cambridge under Frank Hahn, when at a conference at Oxford about 1979-1980, Peter Tamas Bauer sat me down beside him and told me the story. Later in Blacksburg about 1981, N. Georgescu-Roegen on a visit from Vanderbilt University told me the same thing. Specifically, Georgescu-Roegen told me that leading Indian academics had almost insulted Milton in public which Milton had borne gamely; that after Milton had given a talk in Delhi to VKRV Rao’s graduate-students, a talk Georgescu-Roegen had been present at, VKRV Rao had addressed the students and told them in all seriousness “You have heard what Professor Friedman has to say, if you repeat what he has said in your exams, you will fail”.
In 1981-1982 my doctoral thesis emerged, titled “On liberty & economic growth: preface to a philosophy for India”,
My late great master in economic theory, Frank Hahn (1925-2013), found what I had written to be a “good thesis” bringing “a good knowledge of economics and of philosophy to bear on the literature on economic planning”, saying I had shown “a good knowledge of economic theory” and my “critique of Development Economics was powerful not only on methodological but also on economic theory grounds”.
I myself said about it decades later “My original doctoral topic in 1976 ‘A monetary theory for India’ had to be altered not only due to paucity of monetary data at the time but because the problems of India’s political economy and allocation of resources in the real economy were far more pressing. The thesis that emerged in 1982 … was a full frontal assault from the point of view of microeconomic theory on the “development planning” to which everyone routinely declared their fidelity, from New Delhi’s bureaucrats and Oxford’s “development” school to McNamara’s World Bank with its Indian staffers. Frank Hahn protected my inchoate liberal arguments for India; and when no internal examiner could be found, Cambridge showed its greatness by appointing two externals, Bliss at Oxford and Hutchison at Birmingham, both Cambridge men. “Economic Theory and Development Economics” was presented to the American Economic Association in December 1982 in company of Solow, Chenery, Streeten, and other eminences…” How I landed on that eminent AEA panel in December 1982 was because its convener Professor George Rosen of the University of Illinois recruited me overnight — as a replacement for Jagdish Bhagwati, who had had to return to India suddenly because of a parental death. The results were published in 1983 in World Development.
Soon afterwards, London’s Institute of Economic Affairs published Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India. This slim work (now in pdf) was the first classical liberal critique of post-Mahalonobis Indian economic thought since BR Shenoy’s original criticism decades earlier. It became the subject of The Times’ lead editorial on its day of publication 29 May 1984 — provoking the Indian High Commission in London to send copies to the Finance Ministry in Delhi where it apparently caused a stir, or so I was told years later by Amaresh Bagchi who was a recipient of it at the Ministry.
The Times had said
“When Mr. Dennis Healey in the Commons recently stated that Hongkong, with one per cent of the population of India has twice India’s trade, he was making an important point about Hongkong but an equally important point about India. If Hongkong with one per cent of its population and less than 0.03 per cert of India’s land area (without even water as a natural resource) can so outpace India, there must be something terribly wrong with the way Indian governments have managed their affairs, and there is. A paper by an Indian economist published today (Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India by Subroto Roy, IEA £1.80) shows how Asia’s largest democracy is gradually being stifled by the imposition of economic policies whose woeful effect and rhetorical unreality find their echo all over the Third World. As with many of Britain’s former imperial possessions, the rot set in long before independence. But as with most of the other former dependencies, the instrument of economic regulation and bureaucratic control set up by the British has been used decisively and expansively to consolidate a statist regime which inhibits free enterprise, minimizes economic success and consolidates the power of government in all spheres of the economy. We hear little of this side of things when India rattles the borrowing bowl or denigrates her creditors for want of further munificence. How could Indian officials explain their poor performance relative to Hongkong? Dr Roy has the answers for them. He lists the causes as a large and heavily subsidized public sector, labyrinthine control over private enterprise, forcibly depressed agricultural prices, massive import substitution, government monopoly of foreign exchange transactions, artificially overvalued currency and the extensive politicization of the labour market, not to mention the corruption which is an inevitable side effect of an economy which depends on the arbitrament of bureaucrats. The first Indian government under Nehru took its cue from Nehru’s admiration of the Soviet economy, which led him to believe that the only policy for India was socialism in which there would be “no private property except in a restricted sense and the replacement of the private profit system by a higher ideal of cooperative service.” Consequently, the Indian government has now either a full monopoly or is one of a few oligipolists in banking, insurance, railways, airlines, cement, steel, chemicals, fertilizers, ship-building, breweries, telephones and wrist-watches. No businessman can expand his operation while there is any surplus capacity anywhere in that sector. He needs government approval to modernize, alter his price-structure, or change his labour shift. It is not surprising that a recent study of those developing countries which account for most manufactured exports from the Third World shows that India’s share fell from 65 percent in 1953 to 10 per cent in 1973; nor, with the numerous restrictions on inter-state movement of grains, that India has over the years suffered more from an inability to cope with famine than during the Raj when famine drill was centrally organized and skillfully executed without restriction. Nehru’s attraction for the Soviet model has been inherited by his daughter, Mrs. Gandhi. Her policies have clearly positioned India more towards the Soviet Union than the West. The consequences of this, as Dr Roy states, is that a bias can be seen in “the antipathy and pessimism towards market institutions found among the urban public, and sympathy and optimism to be found for collectivist or statist ones.” All that India has to show for it is the delivery of thousands of tanks in exchange for bartered goods, and the erection of steel mills and other heavy industry which help to perpetuate the unfortunate obsession with industrial performance at the expense of agricultural growth and the relief of rural poverty.”…..
I felt there were inaccuracies in this and so replied dated 4 June which The Times published on 16 June 1984:
Milton and I met for the first time in the Fall of 1984 at the Mont Pelerin Society meetings at Cambridge when I gave him a copy of the IEA monograph, which he came to think extremely well of. I told him I had heard of his 1955 document and asked him for it; he sent me the original blue/purple version of this soon thereafter.
[That original document was, incidentally, in my professorial office among all my books, papers, theses and other academic items including my gown when I was attacked in 2003 by a corrupt gang at IIT Kharagpur — all yet to be returned to me by IIT despite a High Court order during my present ongoing battle against corruption there over a USD 1.9 million scam !… Without having ever wished to, I have had to battle India’s notorious corruption first hand for a decade!]
I published Milton’s document for the first time on 21 May 1989 at the conference of the Hawaii project over the loud objection of assorted leftists…
Amartya Sen, Jagdish Bhagwati, Manmohan Singh or any of their acolytes will not be seen in this group photograph dated 21 May 1989 at the UH President’s House, because they were not there. The Government of India was represented by the Ambassador to Washington, PK Kaul, as well as the Consul General in San Francisco, KS Rana (later Ambassador to Germany), besides the founding head of ICRIER who had invited himself.
Manmohan Singh was not there as he precisely represented the Indian economic policy establishment I had been determined to reform! In any case, he had left India about 1987 on his last assignment before retirement, with Julius Nyerere of Tanzania relating to the “South-South Commission”.
I have said over more than a half dozen years now that there is no evidence whatsoever of Manmohan Singh having been a liberal economist in any sense of that word at any time before 1991, and scant evidence that he originated any liberal economic ideas since. The widespread worldwide notion that he is to be credited for originating a sudden transformation of India from a path of pseudo-socialism to one of pseudo-liberalism has been without basis in evidence — almost entirely a political fiction, though an explicable one and one which has served, as such political fictions do, the purposes of those who invent them.
Jagdish Bhagwati and Amartya Sen were in their mid 50s and were two of the three senior-most Indians in US academic economics at the time. I and Ted James, both in our 30s, decided to invite both Bhagwati and Sen to the Hawaii project-conference as distinguished guests but to do so somewhat insincerely late in the day, predicting they would decline, which is what they did, yet they had come to be formally informed of what we were doing. We had a very serious attitude that was inspired a bit, I might say, by Oppenheimer’s secret “Manhattan project” and we wanted neither press-publicity nor anyone to become the star who ended up hogging the microphone or the limelight.
Besides, and most important of all, neither Bhagwati nor Sen had done work in the areas we were centrally interested in, namely, India’s macroeconomic and foreign trade framework and fiscal and monetary policies.
Bhagwati, after his excellent 1970 work with Padma Desai for the OECD on Indian industry and trade, also co-authored with TN Srinivasan a fine 1975 volume for the NBER Foreign Trade Regimes and Economic Development: India.
TN Srinivasan was the third of the three senior-most Indian economists at the time in US academia; his work made us want to invite him as one of our main economic authors, and we charged him with writing the excellent chapter in Foundations that he came to do titled “Planning and Foreign Trade Reconsidered”.
The other main economist author we had hoped for was Sukhamoy Chakravarty from Delhi University and the Government of India’s Planning Commission, whom I had known since 1977 when I had been given his office at the Delhi School of Economics as a Visiting Assistant Professor while he was on sabbatical; despite my pleading he would not come due to ill health; he strongly recommended C Rangarajan, telling me Rangarajan had been the main author with him of the crucial 1985 RBI report on monetary policy; and he signed and gave me his last personal copy of that report dating it 14 July 1987. Rangarajan said he could not come and recommended the head of the NIPFP, Amaresh Bagchi, promising to write jointly with him the chapter on monetary policy and public finance.
Along with Milton Friedman’s suppressed 1955 memorandum which I was publishing for the first time in 1989, TN Srinivasan and Amaresh Bagchi authored the three main economic policy chapters that we felt we wanted.
Other chapters we commissioned had to do with the state of governance (James Manor), federalism (Bhagwan Dua), Punjab and similar problems (PR Brass), agriculture (K Subbarao, as proposed by CH Hanumantha Rao), health (Anil Deolalikar, through open advertisement), and a historical assessment of the roots of economic policy (BR Tomlinson, as proposed by Anil Seal). On the vital subject of education we failed to agree with the expert we wanted very much (JBG Tilak, as proposed by George Psacharopolous) and so we had to cover the subject cursorily in our introduction mentioning his work. And decades later, I apologised to Professor Dietmar Rothermund of Heidelberg University for having been so blinkered in the Anglo-American tradition at the time as to not having obtained his participation in the project.
[The sister-volume we commissioned in parallel on Pakistan’s political economy had among its authors Francis Robinson, Akbar Ahmed, Shirin Tahir-Kehli, Robert La Porte, Shahid Javed Burki, Mohsin Khan, Mahmood Hasan Khan, Naved Hamid, John Adams and Shahrukh Khan; this book came to be published in Pakistan in 1993 to good reviews but apparently was then lost by its publisher and is yet to be found; the military and religious clergy had been deliberately not invited by us though the name of Pervez Musharraf had I think arisen, and the military and religious clergy in fact came to rule the roost through the 1990s in Pakistan; the volume, two decades old, takes on fresh relevance with the new civilian governments of recent years.] [Postscript 27 November 2015: See my strident critique at Twitter of KM Kasuri, P Musharraf et al e.g. at https://independentindian.com/2011/11/22/pakistans-point-of-view-or-points-of-view-on-kashmir-my-as-yet-undelivered-lahore-lecture-part-i/ passing off ideas they have taken from this volume without acknowledgement, ideas which have in any case become defunct to their author, myself.]
Milton himself said this about his experience with me in his memoirs:
And Milton wrote on my behalf when I came to be attacked, being Indian, at the very University that had sponsored us:
My obituary notice at his passing in 2006 said: “My association with Milton has been the zenith of my engagement with academic economics…. I was a doctoral student of his bitter enemy yet for over two decades he not only treated me with unfailing courtesy and affection, he supported me in lonely righteous battles: doing for me what he said he had never done before, which was to stand as an expert witness in a United States Federal Court. I will miss him much though I know that he, as a man of reason, would not have wished me to….”
In August 1990 in Delhi I came to tell Siddhartha Shankar Ray about the unpublished India-manuscript resulting from the Hawaii project that was in my possession as it headed to its publisher.
Ray was a family-friend whose maternal grandfather CR Das led the Congress Party before MK Gandhi and had been a friend and colleague of my great grandfather SN Roy in Bengal’s politics in the 1920s; Ray had also consented to stand on my behalf as Senior Counsel in a matter in the Supreme Court of India.
Ray was involved in daily political parlays at his Delhi home with other Congress Party personages led by PV Narasimha Rao. These senior regional figures seemed to me to be keeping their national leader, Rajiv Gandhi, aloof in splendid isolation at 10 Jan Path.
Ray told me he and his wife had been in London in May 1984 on the day The Times had written its lead editorial on my work and they had seen it with excitement. Upon hearing of the Hawaii project and the manuscript I had with me, Ray immediately insisted of his own accord that I must meet Rajiv Gandhi, and that he would be arranging a meeting.
Hence it came to be a month later that a copy of the manuscript of the completed Hawaii project was be given by my hand on 18 September 1990 to Rajiv Gandhi, then Leader of the Opposition and Congress President, an encounter I have quite fully described elsewhere. I offered to get a copy to the PM, VP Singh, too but a key aide of his showed no interest in receiving it.
Rajiv made me a senior adviser, and I have claimed principal authorship of the 22 March 1991 draft of the Congress manifesto that actually shook and changed the political thinking of the Congress on economic matters in the direction Rajiv had desired and as I had advised him at our initial 18 September 1990 meeting.
“… He began by talking about how important he felt panchayati raj was, and said he had been on the verge of passing major legislation on it but then lost the election. He asked me if I could spend some time thinking about it, and that he would get the papers sent to me. I said I would and remarked panchayati raj might be seen as decentralized provision of public goods, and gave the economist’s definition of public goods as those essential for the functioning of the market economy, like the Rule of Law, roads, fresh water, and sanitation, but which were unlikely to appear through competitive forces.
I distinguished between federal, state and local levels and said many of the most significant public goods were best provided locally. Rajiv had not heard the term “public goods” before, and he beamed a smile and his eyes lit up as he voiced the words slowly, seeming to like the concept immensely. It occurred to me he had been by choice a pilot of commercial aircraft. Now he seemed intrigued to find there could be systematic ways of thinking about navigating a country’s governance by common pursuit of reasonable judgement. I said the public sector’s wastefulness had drained scarce resources that should have gone instead to provide public goods. Since the public sector was owned by the public, it could be privatised by giving away its shares to the public, preferably to panchayats of the poorest villages. The shares would become tradable, drawing out black money, and inducing a historic redistribution of wealth while at the same time achieving greater efficiency by transferring the public sector to private hands. Rajiv seemed to like that idea too, and said he tried to follow a maxim of Indira Gandhi’s that every policy should be seen in terms of how it affected the common man. I wryly said the common man often spent away his money on alcohol, to which he said at once it might be better to think of the common woman instead. (This remark of Rajiv’s may have influenced the “aam admi” slogan of the 2004 election, as all Congress Lok Sabha MPs of the previous Parliament came to receive a previous version of the present narrative.)
Our project had identified the Congress’s lack of internal elections as a problem; when I raised it, Rajiv spoke of how he, as Congress President, had been trying to tackle the issue of bogus electoral rolls. I said the judiciary seemed to be in a mess due to the backlog of cases; many of which seemed related to land or rent control, and it may be risky to move towards a free economy without a properly functioning judicial system or at least a viable system of contractual enforcement. I said a lot of problems which should be handled by the law in the courts in India were instead getting politicised and decided on the streets. Rajiv had seen the problems of the judiciary and said he had good relations with the Chief Justice’s office, which could be put to use to improve the working of the judiciary.
The project had worked on Pakistan as well, and I went on to say we should solve the problem with Pakistan in a definitive manner. Rajiv spoke of how close his government had been in 1988 to a mutual withdrawal from Siachen. But Zia-ul-Haq was then killed and it became more difficult to implement the same thing with Benazir Bhutto, because, he said, as a democrat, she was playing to anti-Indian sentiments while he had found it somewhat easier to deal with the military. I pressed him on the long-term future relationship between the countries and he agreed a common market was the only real long-term solution. I wondered if he could find himself in a position to make a bold move like offering to go to Pakistan and addressing their Parliament to break the impasse. He did not say anything but seemed to think about the idea. Rajiv mentioned a recent Time magazine cover of Indian naval potential, which had caused an excessive stir in Delhi. He then talked about his visit to China, which seemed to him an important step towards normalization. He said he had not seen (or been shown) any absolute poverty in China of the sort we have in India. He talked about the Gulf situation, saying he did not disagree with the embargo of Iraq except he wished the ships enforcing the embargo had been under the U.N. flag. The meeting seemed to go on and on, and I was embarrassed at perhaps having taken too much time and that he was being too polite to get me to go. V. George had interrupted with news that Sheila Dixit (as I recall) had just been arrested by the U. P. Government, and there were evidently people waiting. Just before we finally stood up I expressed a hope that he was looking to the future of India with an eye to a modern political and economic agenda for the next election, rather than getting bogged down with domestic political events of the moment. That was the kind of hopefulness that had attracted many of my generation in 1985. I said I would happily work in any way to help define a long-term agenda. His eyes lit up and as we shook hands to say goodbye, he said he would be in touch with me again…. The next day I was called and asked to stay in Delhi for a few days, as Mr. Gandhi wanted me to meet some people…..
… That night Krishna Rao dropped me at Tughlak Road where I used to stay with friends. In the car I told him, as he was a military man with heavy security cover for himself as a former Governor of J&K, that it seemed to me Rajiv’s security was being unprofessionally handled, that he was vulnerable to a professional assassin. Krishna Rao asked me if I had seen anything specific by way of vulnerability. With John Kennedy and De Gaulle in mind, I said I feared Rajiv was open to a long-distance sniper, especially when he was on his campaign trips around the country. This was one of several attempts I made since October 1990 to convey my clear impression to whomever I thought might have an effect that Rajiv seemed to me extremely vulnerable. Rajiv had been on sadhbhavana journeys, back and forth into and out of Delhi. I had heard he was fed up with his security apparatus, and I was not surprised given it seemed at the time rather bureaucratized. It would not have been appropriate for me to tell him directly that he seemed to me to be vulnerable, since I was a newcomer and a complete amateur about security issues, and besides if he agreed he might seem to himself to be cowardly or have to get even closer to his security apparatus. Instead I pressed the subject relentlessly with whomever I could. I suggested specifically two things: (a) that the system in place at Rajiv’s residence and on his itineraries be tested, preferably by some internationally recognized specialists in counter-terrorism; (b) that Rajiv be encouraged to announce a shadow-cabinet. The first would increase the cost of terrorism, the second would reduce the potential political benefit expected by terrorists out to kill him. On the former, it was pleaded that security was a matter being run by the V. P. Singh and then Chandrashekhar Governments at the time. On the latter, it was said that appointing a shadow cabinet might give the appointees the wrong idea, and lead to a challenge to Rajiv’s leadership. This seemed to me wrong, as there was nothing to fear from healthy internal contests for power so long as they were conducted in a structured democratic framework. I pressed to know how public Rajiv’s itinerary was when he travelled. I was told it was known to everyone and that was the only way it could be since Rajiv wanted to be close to the people waiting to see him and had been criticized for being too aloof. This seemed to me totally wrong and I suggested that if Rajiv wanted to be seen as meeting the crowds waiting for him then that should be done by planning to make random stops on the road that his entourage would take. This would at least add some confusion to the planning of potential terrorists out to kill him. When I pressed relentlessly, it was said I should probably speak to “Madame”, i.e. to Mrs. Rajiv Gandhi. That seemed to me highly inappropriate, as I could not be said to be known to her and I should not want to unduly concern her in the event it was I who was completely wrong in my assessment of the danger. The response that it was not in Congress’s hands, that it was the responsibility of the VP Singh and later the Chandrashekhar Governments, seemed to me completely irrelevant since Congress in its own interests had a grave responsibility to protect Rajiv Gandhi irrespective of what the Government’s security people were doing or not doing. Rajiv was at the apex of the power structure of the party, and a key symbol of secularism and progress for the entire country. Losing him would be quite irreparable to the party and the country. It shocked me that the assumption was not being made that there were almost certainly professional killers actively out to kill Rajiv Gandhi — this loving family man and hapless pilot of India’s ship of state who did not seem to have wished to make enemies among India’s terrorists but whom the fates had conspired to make a target. The most bizarre and frustrating response I got from several respondents was that I should not mention the matter at all as otherwise the threat would become enlarged and the prospect made more likely! This I later realized was a primitive superstitious response of the same sort as wearing amulets and believing in Ptolemaic astrological charts that assume the Sun goes around the Earth — centuries after Kepler and Copernicus. Perhaps the entry of scientific causality and rationality is where we must begin in the reform of India’s governance and economy. What was especially repugnant after Rajiv’s assassination was to hear it said by his enemies that it marked an end to “dynastic” politics in India. This struck me as being devoid of all sense because the unanswerable reason for protecting Rajiv Gandhi was that we in India, if we are to have any pretensions at all to being a civilized and open democratic society, cannot tolerate terrorism and assassination as means of political change. Either we are constitutional democrats willing to fight for the privileges of a liberal social order, or ours is truly a primitive and savage anarchy concealed beneath a veneer of fake Westernization….. Proceedings began when Rajiv arrived. This elite audience mobbed him just as the farmers had mobbed him earlier. He saw me and beamed a smile in recognition, and I smiled back but made no attempt to draw near him in the crush. He gave a short very apt speech on the role the United Nations might have in the new post-Gulf War world. Then he launched the book, and left for an investiture at Rashtrapati Bhavan. We waited for our meeting with him, which finally happened in the afternoon. Rajiv was plainly at the point of exhaustion and still hard-pressed for time. He seemed pleased to see me and apologized for not talking in the morning. Regarding the March 22 draft, he said he had not read it but that he would be doing so. He said he expected the central focus of the manifesto to be on economic reform, and an economic point of view in foreign policy, and in addition an emphasis on justice and the law courts. I remembered our September 18 conversation and had tried to put in justice and the courts into our draft but had been over-ruled by others. I now said the social returns of investment in the judiciary were high but was drowned out again. Rajiv was clearly agitated that day by the BJP and blurted out he did not really feel he understood what on earth they were on about. He said about his own family, “We’re not religious or anything like that, we don’t pray every day.” I felt again what I had felt before, that here was a tragic hero of India who had not really wished to be more than a happy family man until he reluctantly was made into a national leader against his will. We were with him for an hour or so. As we were leaving, he said quickly at the end of the meeting he wished to see me on my own and would be arranging a meeting. One of our group was staying back to ask him a favour. Just before we left, I managed to say to him what I felt was imperative: “The Iraq situation isn’t as it seems, it’s a lot deeper than it’s been made out to be.” He looked at me with a serious look and said “Yes I know, I know.” It was decided Pitroda would be in touch with each of us in the next 24 hours. During this time Narasimha Rao’s manifesto committee would read the draft and any questions they had would be sent to us. We were supposed to be on call for 24 hours. The call never came. Given the near total lack of system and organization I had seen over the months, I was not surprised. Krishna Rao and I waited another 48 hours, and then each of us left Delhi. Before going I dropped by to see Krishnamurty, and we talked at length. He talked especially about the lack of the idea of teamwork in India. Krishnamurty said he had read everything I had written for the group and learned a lot. I said that managing the economic reform would be a critical job and the difference between success and failure was thin….”
“… I got the afternoon train to Calcutta and before long left for America to bring my son home for his summer holidays with me. In Singapore, the news suddenly said Rajiv Gandhi had been killed. All India wept. What killed him was not merely a singular act of criminal terrorism, but the system of humbug, incompetence and sycophancy that surrounds politics in India and elsewhere. I was numbed by rage and sorrow, and did not return to Delhi….”
In December 1991, I visited Rajiv’s widow at 10 Jan Path to express my condolences, the only time I have met her, and I gave her for her records a taped copy of Rajiv’s long-distance telephone conversations with me during the Gulf War earlier that year. She seemed an extremely shy taciturn figure in deep mourning, and I do not think the little I said to her about her late husband’s relationship with me was comprehended. Nor was it the time or place for more to be said.
In September 1993, at a special luncheon at the Indian Ambassador’s Residence in Washington, Siddhartha Shankar Ray, then the Ambassador to Washington, pointed at me and declared to Manmohan Singh, then Finance Minister, in presence of Manmohan’s key aides accompanying him including MS Ahluwalia, NK Singh, C Rangarajan and others,
“Congress manifesto was written on his computer”.
This was accurate enough to the extent that the 22 March 1991 draft as asked for by Rajiv and that came to explicitly affect policy had been and remains on my then-new NEC laptop.
At the Ambassador’s luncheon, I gave Manmohan Singh a copy of the Foundations book as a gift. My father who knew him in the early 1970s through MG Kaul, ICS, had sent him a copy of my 1984 IEA monograph which Manmohan had acknowledged. And back in 1973, he had visited our then-home at 14 Rue Eugene Manuel in Paris to advise me about economics at my father’s request, and he and I had ended up in a fierce private debate for about forty minutes over the demerits (as I saw them) and merits (as he saw them) of the Soviet influence on Indian economic policy-making. But in 1993 we had both forgotten the 1973 meeting.
In May 2002, the Congress passed an official party resolution moved by Digvijay Singh in presence of PV Narasimha Rao and Manmohan Singh that the 1991 reforms had originated with Rajiv Gandhi and not with either Narasimha Rao or Manmohan; no one dissented. It was intended to flatter Sonia Gandhi as the Congress President, but there was truth in it too which all Congress MPs of the 13th Lok Sabha had come to know in a publication of mine they had received from me at IIT Kharagpur where since 1996 I had become Professor.
Manmohan Singh himself, to his credit, has not at any point, except once during his failed Lok Sabha bid, claimed the reforms as his own invention and has said always he had followed what his Prime Minister had told him. However, he has not been averse to being attributed with all the credit by his flatterers, by the media, by businessmen and many many others around the world, and certainly he did not respond to Ambassador Siddhartha Shankar Ray telling him and his key aides how the Congress-led reform had come about through my work except to tell me at the 1993 luncheon that when Arjun Singh criticised the reforms in Cabinet, he, Manmohan, would mention the manifesto.
On 28 December 2009, Rajiv’s widow in an official Congress Party statement finally declared her late husband
“left his personal imprint on the (Congress) party’s manifesto of 1991.″
How Sonia Gandhi, who has never had pretensions to knowledge of economics or political economy or political science or governance or history, came to place Manmohan Singh as her prime ministerial candidate and the font of economic and political wisdom along with Pranab Mukherjee, when both men hardly had been favourites of her late husband, would be a story in its own right. And how Amartya Sen’s European-origin naturalised Indian co-author Jean Drèze later came to have policy influence from a different direction upon Sonia Gandhi, also a naturalised Indian of European origin, may be yet another story in its own right, perhaps best told by themselves.
I would surmise the same elderly behind-the-scenes figure, now in his late 80s, had a hand in setting up both sets of influences — directly in the first case (from back in 1990-1991), and indirectly in the second case (starting in 2004) . This was a man who in a November 2007 newspaper article literally erased my name and inserted that of Manmohan Singh as part of the group that Rajiv created on 25 September following his 18 September meeting with me! Reluctantly, I had to call this very elderly man a liar; he has not denied it and knows he has not been libeled.
One should never forget the two traditional powers interested in the subcontinent, Russia and Britain, have been never far from influence in Delhi. In 1990-1991 what worried vested bureaucratic and business interests and foreign powers through their friends and agents was that they could see change was coming to India but they wanted to be able to control it themselves to their advantage, which they then broadly proceeded to do over the next two decades. The foreign weapons’ contracts had to be preserved, as did other big-ticket imports that India ends up buying needlessly on credit it hardly has in world markets. There are similarities to what happened in Russia and Eastern Europe where many apparatchiks and fellow-travellers became freedom-loving liberals overnight; in the Indian case more than one badly compromised pro-USSR senior bureaucrat promptly exported his children and savings to America and wrapped themselves in the American flag.
The stubborn unalterable fact remains that Manmohan Singh was not physically present in India and was still with the Nyerere project on 18 September 1990 when I met Rajiv for the first time and gave him the unpublished results of the UH-Manoa project. This simple straightforward fact is something the Congress Party, given its own myths and self-deception and disinformation, has not been able to cope with in its recently published history. For myself, I have remained loyal to my memory of my encounter with Rajiv Gandhi, and my understanding of him. The Rajiv Gandhi I knew had been enthused by me in 1990-1991 carrying the UH-Manoa perestroika-for-India project that I had led since 1986, and he had loved my advice to him on 18 September 1990 that he needed to modernise the party by preparing a coherent agenda (as other successful reformers had done) while still in Opposition waiting for elections, and to base that agenda on commitments to improving the judiciary and rule of law, stopping the debauching of money, and focusing on the provision of public goods instead. Rajiv I am sure wanted a modern and modern-minded Congress — not one which depended on him let aside his family, but one which reduced that dependence and let him and his family alone.
As for Manmohan Singh being a liberal or liberalising economist, there is no evidence publicly available of that being so from his years before or during the Nyerere project, or after he returned and joined the Chandrashekhar PMO and the UGC until becoming, to his own surprise as he told Mark Tully, PV Narasimha Rao’s Finance Minister. Some of his actions qua Finance Minister were liberalising in nature but he did not originate any basic idea of a change in a liberal direction of economic policy, and he has, with utmost honesty honestly, not claimed otherwise. Innumerable flatterers and other self-interested parties have made out differently, creating what they have found to be a politically useful fiction; he has yet to deny them.
Siddhartha Shankar Ray and I met last in July 2009, when I gave him a copy of this 2005 volume I had created, which pleased him much.
I said to him Bengal’s public finances were in abysmal condition, calling for emergency measures financially, and that Mamata Banerjee seemed to me to be someone who knew how to and would dislodge the Communists from their entrenched misgovernance of decades but she did not seem quite aware that dislodging a bad government politically was not the same thing as knowing how to govern properly oneself. He, again of his own accord, said immediately,
“I will call her and her people to a meeting here so you can meet them and tell them that directly”.
It never transpired. In our last phone conversation I mentioned to him my plans of creating a Public Policy Institute — an idea he immediately and fully endorsed as being essential though adding “I can’t be part of it, I’m on my way out”.
“I’m on my way out”. That was Siddhartha Shankar Ray — always intelligent, always good-humoured, always public-spirited, always a great Indian, my only friend among politicians other than the late Rajiv Gandhi himself.
In March February 2010, my father and I called upon the new Bengal Governor, MK Narayanan and gave him a copy of the Thatcher volume for the Raj Bhavan Library; I told him the story about my encounter with Rajiv Gandhi thanks to Siddhartha Shankar Ray and its result; Narayanan within a few days made a visit to Ray’s hospital-bed, and when he emerged after several hours he made a statement, which in substance he repeated again when Ray died in November 2010:
“There are few people in post-Independence India who could equal his magnificent contribution to India’s growth and progress”.
To what facts did MK Narayanan, a former Intelligence Bureau chief, mean to refer with this extravagant praise of Ray? Was Narayanan referring to Ray’s politics for Indira Gandhi? To Ray’s Chief Ministership of Bengal? To Ray’s Governorship of Punjab? You will have to ask him but I doubt that was what he meant: I surmise Narayanan’s eulogy could only have resulted after he confirmed with Ray on his hospital-bed the story I had told him, and that he was referring to the economic and political results that followed for the country once Ray had introduced me in September 1990 to Rajiv Gandhi. But I say again, you will have to ask MK Narayanan himself what he and Ray talked about in hospital and what was the factual basis of Narayanan’s precise words of praise. To what facts exactly was MK Narayanan, former intelligence chief, meaning to refer when he stated Siddhartha Shankar Ray had made a “magnificent contribution to India’s growth and progress”?
3. Jagdish Bhagwati & Manmohan Singh? That just don’t fly!
Now returning to the apparent desire of Professor Panagariya, the Jagdish Bhagwati Professor of Indian Political Economy at Columbia, to attribute to Jagdish Bhagwati momentous change for the better in India as of 1991, even if Panagariya had not the scientific curiosity to look into our 1992 book titled Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s or into Milton Friedman’s own 1998 memoirs, we may have expected him to at least turn to his co-author and Columbia colleague, Jagdish Bhagwati himself, and ask, “Master, have you heard of this fellow Subroto Roy by any chance?”
Jagdish would have had to say yes, since not only had he received a copy of the proofs of my 1984 IEA work Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India, he was kind enough to write in a letter dated 15 May 1984 that I had
“done an excellent job of setting out the problems afflicting our economic policies, unfortunately government-made problems!”
Also Jagdish may or may not have remembered our only meeting, when he and I had had a long conversation on the sofas in the foyer of the IMF in Washington when I was a consultant there in 1993 and he had come to meet someone; he was surprisingly knowledgeable about my personal 1990 matter in the Supreme Court of India which astonished me until he told me his brother the Supreme Court judge had mentioned the case to him!
Now my 1984 work was amply scientific and scholarly in fully crediting a large number of works in the necessary bibliography, including Bhagwati’s important work with his co-authors. Specifically, Footnote 1 listed the literature saying:
“The early studies notably include: B. R. Shenoy, `A note of dissent’, Papers relating to the formulation of the Second Five-Year Plan, Government of India Planning Commission, Delhi, 1955; Indian Planning and Economic Development, Asia Publishing, Bombay, 1963, especially pp. 17-53; P. T. Bauer, Indian Economic Policy and Development, George Allen & Unwin, London, 1961; M. Friedman, unpublished memorandum to the Government of India, November 1955 (referred to in Bauer, op. cit., p. 59 ff.); and, some years later, Sudha Shenoy, India : Progress or Poverty?, Research Monograph 27, Institute of Economic Affairs, London, 1971. Some of the most relevant contemporary studies are: B. Balassa, `Reforming the system of incentives in World Development, 3 (1975), pp. 365-82; `Export incentives and export performance in developing countries: a comparative analysis’, Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv, 114 (1978), pp. 24-61; The process of industrial development and alternative development strategies, Essays in International Finance No. 141, Princeton University, 1980; J. N. Bhagwati & P. Desai, India: Planning for Industrialisation, OECD, Paris : Oxford University Press, 1970; `Socialism and Indian Economic Policy’, World Development, 3 (1975), pp. 213-21; J. N. Bhagwati & T. N. Srinivasan, Foreign-trade Regimes and Economic Development: India, National Bureau of Economic Research, New York, 1975; Anne O. Krueger, `Indian planning experience’, in T. Morgan et al. (eds.), Readings in Economic Development, Wadsworth, California, 1963, pp. 403-20; `The political economy of the rent-seeking society, American Economic Review, 64 (June 1974); The Benefits and Costs of Import-Substitution in India: a Microeconomic Study, University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, 1975; Growth, distortions and patterns of trade among many countries, Studies in International Finance, Princeton University, 1977; Uma Lele, Food grain marketing in India : private performance and public policy, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1971; T. W. Schultz (ed.), Distortions in agricultural incentives, Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 1978; V. Sukhatme, “The utilization of high-yielding rice and wheat varieties in India: an economic assessment”, University of Chicago PhD thesis, 1977….”
There were two specific references to Bhagwati’s work with Srinivasan:
“Jagdish Bhagwati and T. N. Srinivasan put it as follows : `The allocation of foreign exchange among alternative claimants and users in a direct control system . . .would presumably be with reference to a well-defined set of principles and criteria based on a system of priorities. In point of fact, however, there seem to have been few such criteria, if any, followed in practice.’”
and
“But as Bhagwati and Srinivasan report, `. . . the sheer weight of numbers made any meaningful listing of priorities extremely difficult. The problem was Orwellian: all industries had priority and how was each sponsoring authority to argue that some industries had more priority than others? It is not surprising, therefore, that the agencies involved in determining allocations by industry fell back on vague notions of “fairness”, implying pro rata allocations with reference to capacity installed or employment, or shares defined by past import allocations or similar rules of thumb’”
and one to Bhagwati and Desai:
“The best descriptions of Indian industrial policy are still to be found in Bhagwati and Desai (1970)…”
Professors Bhagwati and Panagriya have not apparently referred to anything beyond these joint works of Bhagwati’s dated 1970 with Padma Desai and 1975 with TN Srinivasan. They have not claimed Bhagwati did anything by way of either publication or political activity in relation to India’s economic policy between May 1984, when he read my soon-to-be-published-work and found I had
“done an excellent job of setting out the problems afflicting our economic policies, unfortunately government-made problems”,
and September 1990 when I gave Rajiv the University of Hawaii perestroika-for-India project results developed since 1986, which came to politically spark the 1991 reform in the Congress’s highest echelons from months before Rajiv’s assassination.
There may have been no such claim made by Bhagwati and Panagariya because there may be no such evidence. Between 1984 and 1990, Professor Bhagwati’s research interests were away from Indian economic policy while his work on India through 1970 and 1975 had been fully and reasonably accounted for as of 1984 by myself.
What is left remaining is Bhagwati’s statement :
“When finance minister Manmohan Singh was in New York in 1992, he had a lunch for many big CEOs whom he was trying to seduce to come to India. He also invited me and my wife, Padma Desai, to the lunch. As we came in, the FM introduced us to the invitees and said: ‘These friends of mine wrote almost a quarter century ago [India: Planning for Industrialisation was published in 1970 by Oxford] recommending all the reforms we are now undertaking. If we had accepted the advice then, we would not be having this lunch as you would already be in India’
Now this light self-deprecating reference by Manmohan at an investors’ lunch in New York “for many big CEOs” was an evident attempt at political humour written by his speech-writer. It was clearly, on its face, not serious history. If we test it as serious history, it falls flat so we may only hope Manmohan Singh, unlike Jagdish Bhagwati, has not himself come to believe his own reported joke as anything more than that.
The Bhagwati-Desai volume being referred to was developed from 1966-1970. India saw critical economic and political events in 1969, in 1970, in 1971, in 1972, in 1975, in 1977, etc.
Those were precisely years during which Manmohan Singh himself moved from being an academic to becoming a Government of India official, working first for MG Kaul, ICS, and then in 1971 coming to the attention of PN Haksar, Indira Gandhi’s most powerful bureaucrat between 1967 and 1974: Haksar himself was Manmohan Singh’s acknowledged mentor in the Government, as Manmohan told Mark Tully in an interview.
After Manmohan visited our Paris home in 1973 to talk to me about economics, my father — who had been himself sent to the Paris Embassy by Haksar in preparation for Indira Gandhi’s visit in November 1971 before the Bangladesh war —
had told me Manmohan was very highly regarded in government circles with economics degrees from both Cambridge and Oxford, and my father had added, to my surprise, what was probably a Haksarian governmental view that Manmohan was expected to be India’s Prime Minister some day. That was 1973.
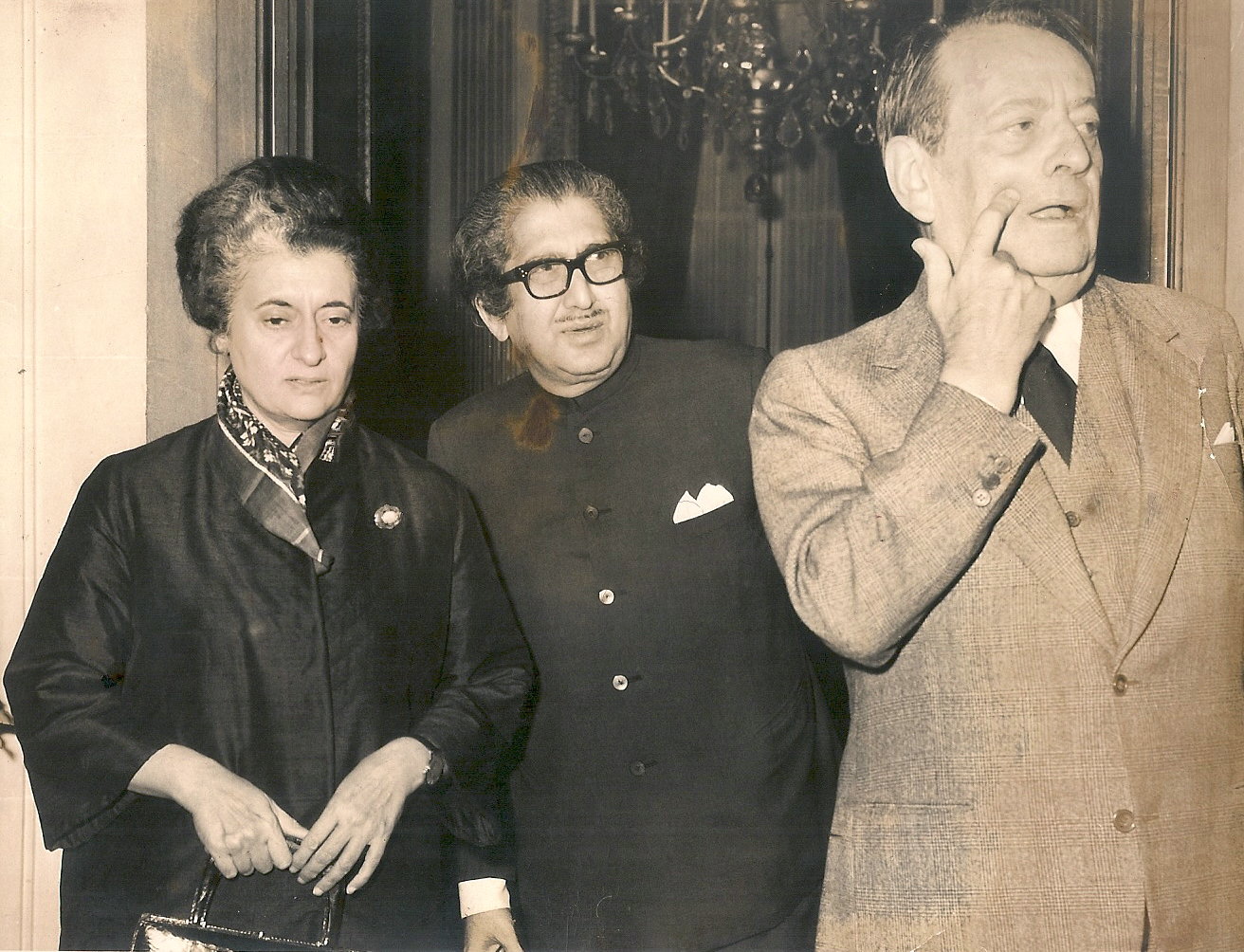
PN Haksar had been the archetypal Nehruvian Delhi intellectual of a certain era, being both a fierce nationalist and a fierce pro-USSR leftist from long before Independence. I met him once on 23 March 1991, on the lawns of 10 Jan Path at the launch of General V Krishna Rao’s book on Indian defence which Rajiv was releasing, and Haksar gave a speech to introduce Rajiv (as if Rajiv needed introduction on the lawns of his own residence); Haksar was in poor health but he seemed completely delighted to be back in favour with Rajiv, after years of having been treated badly by Indira and her younger son.
Had Manmohan Singh in the early 1970s gone to Haksar — the architect of the nationalisation of India’s banking going on right then — and said “Sir, this OECD study by my friend Bhagwati and his wife says we should be liberalising foreign trade and domestic industry”, Haksar would have been astonished and sent him packing.
There was a war on, plus a massive problem of 10 million refugees, a new country to support called Bangladesh, a railway strike, a bad crop, repressed inflation, shortages, and heaven knows what more, besides Nixon having backed Yahya Khan, Tikka Khan et al.
Then after Bangladesh and the railway strike etc, came the rise of the politically odious younger son of Indira Gandhi and his friends (at least one of whom is today Sonia Gandhi’s gatekeeper) followed by the internal political Emergency, the grave foreign-fueled problem of Sikh separatism and its control, the assassination of Indira Gandhi by her own Sikh bodyguards, and the Rajiv Gandhi years as Prime Minister.
Certainly it was Rajiv’s arrival in office and Benazir’s initial return to Pakistan, along with the rise of Michael Gorbachev in the changing USSR, that inspired me in far away Hawaii in 1986 to design with Ted James the perestroika-projects for India and Pakistan which led to our two volumes, and which, thanks to Siddhartha Shankar Ray, came to reach Rajiv Gandhi in Opposition in September 1990 as he sat somewhat forlornly at 10 Jan Path after losing office. “There is a tide in the affairs of men, Which taken at the flood, leads on to fortune….
My friend and collaborator Ted James died of cancer in Manila in May 2010; earlier that year he came to say publicly
“Seldom are significant reforms imposed successfully by international bureaucracies. Most often they are the result of indigenous actors motivated by domestic imperatives. I believe this was the case in India in 1991. It may have been fortuitous that Dr. Roy gained an audience with a receptive Rajiv Gandhi in 1990 but it was not luck that he was prepared with a well-thought out program; this arose from years of careful thought and debate on the matter.”
Changing the direction of a ship of state is very hard, knowing in which direction it should change and to what degree is even harder; it has rarely been something that can be done without random shocks arising let aside the power of vested interests. Had Rajiv Gandhi lived to form a new Government, I have little doubt I would have led the reform that I had chalked out for him and that he had approved of; Sonia Gandhi would have remained the housewife, mother and grandmother that she had preferred to be and not been made into the Queen of India by the Congress Party; Manmohan Singh had left India in 1987 for the Nyerere project and it had been rumoured at the time that had been slightly to do with him protesting, to the extent that he ever has protested anything, the anti-Sikh pogrom that some of Rajiv’s friends had apparently unleashed after Indira’s killing; he returned in November 1990, joined Chandrashekhar in December 1990, left Chandrashekhar in March 1991 when elections were announced and was biding his time as head of the UGC; had Rajiv Gandhi lived, Manmohan Singh would have had a governor’s career path, becoming the governor of one state after another; he would not have been brought into the economic reform process which he had had nothing to do with originating; and finally Pranab Mukherjee, who left the Congress Party and formed his own when Rajiv took over, would have been likely rehabilitated slowly but would not have come to control the working of the party as he did. I said in my Lok Sabha TV interview on 5 9 December 2012 that there have been many microeconomic improvements arising from technological progress in the last 22 years but the macroeconomic and monetary situation is grim, because at root the fiscal situation remains incoherent and confused. I do not see anyone in Manmohan Singh’s entourage among all his many acolytes and flatterers and apologists who is able to get to these root problems. We shall address these issues in Part II.
What Manmohan Singh said in self-deprecating humour at an investors’ lunch in New York in 1992 is hardly serious history as Jagdish Bhagwati has seemed to wish it to be. Besides, it would have been unlike Manmohan, being the devoted student of Joan Robinson and Nicholas Kaldor as he told Mark Tully, to have taken such a liberalising initiative at all. Furthermore, the 1969 American Economic Review published asurvey of Indian economic policy authored by his Delhi University colleagues Jagdish Bhagwati and Sukhamoy Chakravarty which made little mention of his work, and it would have been unreasonable to expect him to have been won over greatly by theirs. Perhaps there is a generous review from the 1970s by Manmohan Singh of the Bhagwati-Desai volume hidden somewhere but if so we should be told where it is. A list of Manmohan Singh’s publications as an economist do not seem easily available anywhere.
Lastly and perhaps most decisively, the 1970 Bhagwati-Desai volume, excellent study that it was, was hardly the first of its genre by way of liberal criticism of modern Indian economic policy! Bhagwati declared in his 2010 speech to the Lok Sabha
“This policy framework had been questioned, and its total overhaul advocated, by me and Padma Desai in writings through the late 1960s…”
But why has Bhagwati been forever silent about the equally if not more forceful and fundamental criticism of “the policy framework”, and advocacy of its “total overhaul”, by scholars in the 1950s, a decade and more earlier than him, when he and Manmohan and Amartya were still students? Specifically, by BR Shenoy, Milton Friedman, and Peter Bauer? The relevant bibliography from the mid 1950s is given in Footnote 1 of my 1984 work.
Peter Tamas Bauer (1915-2002) played a vital role in all this as had he himself not brought the Friedman 1955 document to my attention I would not have known of it.
As undergraduates at the LSE, we had been petrified of him and I never spoke to him while there, having believed the propaganda that floated around about him; then while a Research Student at Cambridge, I happened to be a speaker with him at a conference at Oxford; he made me sit next to him at a meal and told me for the first time about Milton Friedman’s 1955 memorandum to the Government of India which had been suppressed. I am privileged to say Peter from then on became a friend, and wrote, at my request, what became I am sure the kiss of death for me at the World Bank of 1982:
Later he may have been responsible for the London Times writing its lead editorial of 29 May 1984 on my work.
Now Milton had sent me in 1984, besides the original of his November 1955 memorandum to the Government of India, a confidential 1956 document also which seemed to have been written for US Government consumption. I did not publish this in Hawaii in 1989 as I was having difficulty enough publishing the 1955 memorandum. I gave it to be published on the Internet some years ago, and after Milton’s passing, I had it published in The Statesman on the same day as my obituary of him.
It makes fascinating reading, especially about Mahalanobis and Shenoy, of how what Bhagwati wishes to call “the policy framework” that, he claims, he and Desai called for a “total overhaul” of, came to be what it was in the decade earlier when he and Amartya and Manmohan were still students.
Friedman’s 1956 document said
“I met PC Mahalanobis in 1946 and again at a meeting of the International Statistical Institute in September 1947, and I know him well by reputation. He was absent during most of my stay in New Delhi, but I met him at a meeting of the Indian Planning Commission, of which he is one of the strongest and most able members. Mahalanobis began as a mathematician and is a very able one. Able mathematicians are usually recognized for their ability at a relatively early age. Realizing their own ability as they do and working in a field of absolutes, tends, in my opinion, to make them dangerous when they apply themselves to economic planning. They produce specific and detailed plans in which they have confidence, without perhaps realizing that economic planning is not the absolute science that mathematics is. This general characteristic of mathematicians is true of Mahalanobis but in spite of the tendency he is willing to discuss a problem and listen to a different point of view. Once his decision is reached, however, he has great confidence in it. Mahalanobis was unquestionably extremely influential in drafting the Indian five-year plan. There were four key steps in the plan. The first was the so-called “Plan Frame” drafted by Mahalanobis himself. The second was a tentative plan based on the “Plan Frame”. The third step was a report by a committee of economists on the first two steps, and the fourth was a minority report by BR Shenoy on the economists’ report. The economists had no intention of drafting a definitive proposal but merely meant to comment on certain aspects of the first two steps. Shenoy’s minority report, however, had the effect of making the economists’ report official. The scheme of the Five Year Plan attributed to Mahalanobis faces two problems; one, that India needs heavy industry for economic development; and two, that development of heavy industry uses up large amounts of capital while providing only small employment. Based on these facts, Mahalanobis proposed to concentrate on heavy industry development on the one hand and to subsidize the hand production cottage industries on the other. The latter course would discriminate against the smaller manufacturers. In my opinion, the plan wastes both capital and labour and the Indians get only the worst of both efforts. If left to their own devices under a free enterprise system I believe the Indians would gravitate naturally towards the production of such items as bicycles, sewing machines, and radios. This trend is already apparent without any subsidy. The Indian cottage industry is already cloaked in the same popular sort of mist as is rural life in the US. There is an idea in both places that this life is typical and the backbone of their respective countries. Politically, the Indian cottage industry problem is akin to the American farm problem. Mohandas Gandhi was a proponent of strengthening the cottage industry as a weapon against the British. This reason is now gone but the emotions engendered by Gandhi remain. Any move to strengthen the cottage industry has great political appeal and thus, Mahalanobis’ plan and its pseudo-scientific support for the industry also has great political appeal. I found many supporters for the heavy industry phase of the Plan but almost no one (among the technical Civil Servants) who really believes in the cottage industry aspects, aside from their political appeal. In its initial form, the plan was very large and ambitious with optimistic estimates. My impression is that there is a substantial trend away from this approach, however, and an attempt to cut down. The development of heavy industry has slowed except for steel and iron. I believe that the proposed development of a synthetic petroleum plant has been dropped and probably wisely so. In addition, I believe that the proposed five year plan may be extended to six years. Other than his work on the plan, I am uncertain of Mahalanobis’ influence. The gossip is that he has Nehru’s ear and potentially he could be very influential, simply because of his intellectual ability and powers of persuasion. The question that occurs to me is how much difference Mahalanobis’ plan makes. The plan does not seem the important thing to me. I believe that the new drive and enthusiasm of the Indian nation will surmount any plan, good or bad. Then too, I feel a wide diversity in what is said and what is done. I believe that much of Nehru’s socialistic talk is simply that, just talk. Nehru has been trying to undermine the Socialist Party by this means and apparently the Congress Party’s adoption of a socialistic idea for industry has been successful in this respect. One gets the impression, depending on whom one talks with, either that the Government runs business, or that two or three large businesses run the government. All that appears publicly indicates that the first is true, but a case can also be made for the latter interpretation. Favour and harassment are counterparts in the Indian economic scheme. There is no significant impairment of the willingness of Indian capitalists to invest in their industries, except in the specific industries where nationalization has been announced, but they are not always willing to invest and take the risks inherent in the free enterprise system. They want the Government to support their investment and when it refuses they back out and cry “Socialism”..”
I look forward to seeing a fundamental classical liberal critique from India’s distinguished American friends at Columbia University, Professors Jagdish Bhagwati and Padma Desai and Arvind Panagariya, if and when such a critique arises, of the “policy framework” in India as that evolved from the mid 1950s to become what exists across India in 2013 today. Specifically: Where is the criticism from Bhagwati of Mahalanobis and friends? And where is Bhagwati’s defence of Shenoy, leave aside of Milton Friedman or Peter Bauer? They seem not to exist. The most we get is a footnote again without the civility of any references, in the otherwise cogent 1975 Desai-Bhagwati paper “Socialism and Indian Economic Policy” alleging
” Of these three types of impact of the Soviet example, the Plan-formulation approach was to be enthusiastically received by most commentators and, indeed, to lead to demands on the part of aid agencies for similar efforts by other developing countries. However, the shift to heavy industry was seen as a definite mistake by economic opinion of the Chicago school variety, reflecting their basic unfamiliarity with the structural models of growth and development planning of the Feldman-Mahalanobis variety-an ignorance which probably still persists. The detailed regulation was not quite noticed at the time, except by conservative commentators whose position however was extreme and precluded governmental planning of industrial investments on any scale.”
Desai and Bhagwati naturally found no apparent desire to locate any possible scientific truth or reasonableness among
“conservative commentators”
nor among the unnamed and undescribed
“economic opinion of the Chicago school variety”.
Could Desai and Bhagwati have done anything different after all, even when talking about India to an American audience, without being at risk of losing their East Coast Limousine Liberal credentials? Bhagwati used to routinely declare his “socialist” credentials, and even the other day on Indian TV emphatically declared he was not a “conservative” and scornfully dismissed “Thatcher and Reagan” for their “trickle down economics”…
Jagdish Bhagwati has evidently wanted to have his cake and eat it too…
4. Amartya Sen’s Half-Baked Communism: “To each according to his need”?
If I have been candid or harsh in my assessments of Jagdish Bhagwati and Manmohan Singh as they relate to my personal experience with the change of direction in Indian economic policy originating in 1990-1991, I am afraid I must be equally so with Bhagwati’s current opponent in debate, Amartya Sen. Certainly I have found the current spat between Bhagwati and Sen over India’s political economy to be dismal, unscholarly, unscientific and misleading (or off-base) except for it having allowed a burst of domestic policy-discussion in circumstances when India needs it especially much.
None of this criticism is personal but based on objective experience and the record. My criticism of Professor Bhagwati and Dr Manmohan Singh does not diminish in the slightest my high personal regard for both of them.
Similarly, Amartya Sen and I go back, momentarily, to Hindustan Park in 1964 when there was a faint connection as family friends from World War II (as Naren Deb and Manindranath Roy were friends and neighbours, and we still have the signed copy of a book gifted by the former to the latter), and then he later knew me cursorily when I was an undergraduate at LSE and he was already a famous professor, and I greatly enjoyed his excellent lectures at the LSE on his fine book On Economic Inequality, and a few years later he wrote in tangential support of me at Cambridge for which he was thanked in the preface to my 1989 Philosophy of Economics — even though that book of mine also contained in its Chapter 10 the decisive criticism of his main contribution until that time to what used to be called “social choice theory”. Amartya Sen had also written some splendid handwritten letters, a few pages of which remain with me, which puzzled me at the time due to his expressing his aversion to what is normally called ‘price theory’, namely the Marshallian and/or Walrasian theory of value.
Professor Sen and I met briefly in 1978, and then again in 2006 when I was asked to talk to him in our philosophical conversation which came to be published nicely. In 2006 I told him of my experience with Rajiv Gandhi in initiating what became the 1991 reform on the basis of my giving Rajiv the results of the Hawaii project, and Amartya was kind enough to say that he knew I had been arguing all this “very early on”, referring presumably to the 1984 London Times editorial which he would have seen in his Oxford days before coming to Harvard.
This personal regard on my part or personal affection on his part aside, I have been appalled to find Professor Sen not taking moral and intellectual responsibility for and instead disclaiming paternity of the whole so-called “Food Security” policy which Sonia Gandhi has been prevailed upon over the years by him and his acolytes and friends and admirers to adopt, and she in her ignorance of all political economy and governance has now wished to impose upon the Congress Party and India as a whole:
“Questioner: You are being called the creator of the Food Security Bill.
Amartya Sen: Yes, I don’t know why. That is indeed a paternity suit I’m currently fighting. People are accusing me of being the father”.
Amartya Sen has repeatedly over the years gone on Indian prime-time television and declared things like
“If you don’t agree there’s hunger in the world, there’s something morally wrong with you”
besides over the decades publishing titles like Poverty and Famines: An Essay on Entitlement and Deprivation, Hunger and Public Action, The Political Economy of Hunger etc and ceaselessly using his immense power with the media, with book publishing houses, with US academic departments and the world development economics business, to promote his own and his acolytes’ opinions around the world, no matter how ill-considered or incoherent these may be. A passage from his latest book with Jean Drèze reportedly reads
“If development is about the expansion of freedom, it has to embrace the removal of poverty as well as paying attention to ecology as integral parts of a unified concern, aimed ultimately at the security and advancement of human freedom. Indeed, important components of human freedoms — and crucial ingredients of our quality of life — are thoroughly dependent on the integrity of the environment, involving the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the epidemiological surroundings in which we live….”
Had such a passage reached me in an undergraduate essay, I would have considered it incoherent waffle, and I am afraid I cannot see why merely because it is authored by an eminence at Harvard and his co-author, the evaluation should be any different. I am reminded of my encounter in 1976 with Joan Robinson, the great tutor in 1950s Cambridge of Amartya and Manmohan: “Joan Robinson cornered me once and took me into the office she shared with EAG… She came at me for an hour or so wishing to supervise me, I kept declining politely… saying I was with Frank Hahn and wished to work on money… “What does Frankie know about India?” she said… I said I did not know but he did know about monetary theory and that was what I needed for India; I also said I did not think much about the Indian Marxists she had supervised… and mentioned a prominent name… she said about him, “Yes most of what he does can go straight into the dustbin”…” The Indian Marxist whom I had referred to in this conversation with Joan was not Amartya but someone else much younger, yet her candid “can go straight into the dustbin” still applies to all incoherent waffle, whomsoever may produce it.
Indeed, Amartya Sen, if anyone, really should get down to writing his memoirs, and candidly so in order to explain his own thinking and deeds over the decades to himself and to the world in order that needless confusions do not arise.
Else it becomes impossible to explain how someone who was said to be proud to have been a Communist student on the run from the police in West Bengal, who was Joan Robinson’s star pupil at a time she was extolling Maoist China and who has seemingly nurtured a deep lifelong fascination and affection for Communist China despite all its misdeeds, who was feted by the Communist regime of West Bengal after winning the Bank of Sweden Prize (on the same day that same regime had tossed into jail one unfortunate young Mr Khemkha merely for having been rude to its leaders on the Internet), and who seemed to share some of those winnings on social causes like primary education at the behest of the Communist regime’s ministers, etc, how someone with that noble comradely leftist personal history as an economist allows a flattering interviewer with a Harvard connection to describe him in Business Standard of 25 July 2013 as having been all along really a
“neoclassical economist”
who also happens to be
“the greatest living scholar of the original philosopher of the free market, Adam Smith”!
Amartya Sen a neoclassical economist and a great scholar of Adam Smith? It is hilarious to suppose so. The question arises, Does Sen, having published about Adam Smith recently in a few newspapers and leftist periodicals, agree with such a description by his flattering admirer from Harvard at Business Standard? “Neoclassical” economics originated with men like Jevons, Menger, Walras, Pareto, Marshall, Wicksell, and was marked by the theory of value being explained by a demand-side too, and not, like classical economics, merely by the cost of production alone on the supply side. Indeed a striking thing about the list below published by the Scandinavian Journal of Economics of Amartya’s books following his 1998 Bank of Sweden Prize
 is how consistently these works display his avoidance of all neoclassical economics, and the absence of all of what is normally called ‘price theory’, namely the Marshallian and/or Walrasian theory of value. No “neoclassical economics” anywhere here for sure!
is how consistently these works display his avoidance of all neoclassical economics, and the absence of all of what is normally called ‘price theory’, namely the Marshallian and/or Walrasian theory of value. No “neoclassical economics” anywhere here for sure!
It would be fair enough if Professor Sen says he is hardly responsible for an admirer’s ignorant misdescription of his work — except the question still arises why he has himself also evidently misdescribed his own work! For example, in his 13 July 2013 letter to The Economist in response to the criticism of Jagdish Bhagwati and Arvind Panagariya, he says he had always been keenly interested in
“the importance of economic growth as a means— not an end”
and that this
“has been one of the themes even in my earliest writings (including “Choice of Techniques” in 1960 and “Growth Economics” in 1970)”.
This is a very peculiar opinion indeed to have been expressed by Professor Sen about his own work because the 1970 volume Growth Economics listed above among his books hardly can be said at all to be one of his own “earliest writings” as he now describes it to have been!
What had happened back then was that Sen, as someone considered a brilliant or promising young Indian economist at the time, had been asked by the editors of the famous Penguin Modern Economics Readings series to edit the specific issue devoted to growth-theory — a compendium of classic already-published essays including those of Roy Harrod, Evsey Domar, Robert Solow and many others, to which young Amartya was given a chance to write an editorial Introduction. Every economist familiar with that literature knows too that the growth-theory contained in that volume and others was considered highly abstract and notoriously divorced from actual historical processes of economic growth in different countries. Everyone also knew that the individual editors in that famous Penguin Modern Economics Series were of relative unimportance as they did not commission new papers but merely collected classics already published and wrote an introduction.
This is significant presently because neither Professor Sen nor Professor Bhagwati may be objectively considered on the evidence of his life’s work as an economist to have been a major scholar of economic growth, either in theory or in historical practice. As of December 1989, Amartya Sen himself described his own interests to the American Economic Association as
“social choice theory, welfare economics, economic development”
and Jagdish Bhagwati described his interests as
“theory of international trade and policy, economic development”.
Neither Sen nor Bhagwati mentioned growth economics or economic history or even general economic theory, microeconomics, macroeconomics, monetary economics, public finance, etc. Furthermore, Sen saying in his letter to The Economist that he has been always interested in economic growth seems to be baseless in light of the list of his books above, other than the Penguin compendium already discussed.
Incidentally in the same American Economic Association volume of 1989, Padma Desai had described her interests as
“Soviet economy and comparative economic systems”;
Arvind Panagariya had described his interests as
“economies of scale and trade; smuggling; parallel markets in planned economies”;
and one Suby Roy described his interests as
“foundations of monetary economics”.
Reflecting on Amartya Sen’s works over the 40 year period that I have known them
[and again, my personal copies of his books and those of Bhagwati and Desai, were all in my professorial office at IIT Kharagpur when I was attacked by a corrupt gang there in 2003; and IIT have been under a High Court order to return them but have not done so],
I wonder in fact if it might be fairly said that Sen has been on his own subjective journey over the decades around the world seeking to reinvent economics and political economy from scratch, and inventing his own terminology like “capabilities”, “functionings” and yes “entitlements” etc. to help him do so, while trying to assiduously avoid mention of canonical works of modern world economics like Marshall’s Principles, Hicks’s Value and Capital, Debreu’s Theory of Value, or Arrow and Hahn’s General Competitive Analysis, all defining the central neoclassical tradition of the modern theory of value.
But no contemporary science, economics and political economy included, is open to be re-invented from scratch, and what Amartya Sen has ended up doing instead is seeming to be continually trying to reinvent the wheel, possibly without having had the self-knowledge to realise this. Wittgenstein once made a paradoxical statement that one may know another’s mind better than one knows one’s own…
Here is a current example. Professor Sen says
“First, unlike the process of development in Japan, China, Korea and other countries, which pursued what Jean Drèze and I have called “Asian economic development” in our book, India has not had enough focus on public spending on school education and basic healthcare, which these other countries have had….”
Does Sen really believes believe he and Drèze have now in 2013 discovered and christened an economic phenomenon named “Asian economic development”? Everyone, from Japan and Bangkok and Manila, to Hawaii and Stanford to the World Bank’s East Asia department, including especially my Hawaii colleague Ted James, and many many others including especially Gerald M Meier at Stanford, were was publishing about all that every month — in the mid 1980s! In fact, our project on India and Pakistan arose in the 1980s from precisely such a Hawaiian wave! Everyone knows all that from back then or even earlier when the Japanese were talking about the “flying geese” model. (And, incidentally, Communist China did not at the time belong in the list.) Where was Amartya Sen in the mid 1980s when all that was happening? Jean Drèze was still a student perhaps. Is Professor Sen seeking to reinvent the wheel again with “Asian Economic Development” being claimed to be invented in 2013 by him and Drèze now? Oh please! That just won’t fly either!
A second example may be taken from the year before Professor Sen was awarded the Bank of Sweden Prize when he gave a lecture on “human capital” theory which was published as a survey titled “Human Capital and Human Capability” in World Development 1997 Vol. 25, No. 12,
Can you see any reference in this 1997 survey to TW Schultz’s 1960 American Economic Association Presidential Address or to Schultz’s classic 1964 book Transforming Traditional Agriculture or to his 1979 Bank of Sweden Prize address? I could not. If one did not know better, one might have thought from Professor Sen’s 1997 survey that there was nothing done worth talking about on the subject of “human capital” from the time of Adam Smith and David Hume until Amartya Sen finally came to the subject himself.
Thirdly, one is told by Sen’s admirer and collaborator, Professor James Foster of George Washington University, that what Sen means by his notion of
“effective freedom”
is that this is something
“enhanced when a marginally nourished family now has the capability to be sufficiently nourished due to public action”…
Are Amartya and his acolytes claiming he has invented or reinvented welfare economics ab initio? That before Amartya Sen, we did not know the importance of the able-bodied members of a community assisting those who are not able-bodied?
Where have they been? Amartya needed merely to have read Marshall’s Principles evenslightly to find Marshall himself, the master of Maynard Keynes and all of Cambridge and modern world economics, declaring without any equivocation at the very start
“….the study of the causes of poverty is the study of the causes of the degradation of a large part of mankind…”
But Marshall was interested in study, serious study, of poverty and its causes and amelioration, which is not something as easy or trivial as pontification on modern television. My 1984 article “Considerations on Utility, Benevolence and Taxation” which also became a chapter of my 1989 Philosophy of Economics surveyed some of Marshall’s opinion.
“From each according to his ability, to each according to his need” was a utopian slogan around 1875 from Karl Marx, which generations of passionate undergraduates have found impressive. Amartya Sen deserves to tell us squarely about his engagement with Marx or Marxist thought from his earliest days until now. His commitment in recent decades to democracy and the open and free society is clear; but has he also at the same time all along been committed to a kind of half-baked communist utopia as represented by Marx’s 1875 slogan?
“To each according to his need” sounds to be the underlying premise that is seeing practical manifestation in the Sonia Congress’s imposition of a so-called “right to food”; “from each according to his ability” is its flip side in the so-called “rural employment guarantee”. Leave aside the limitless resource-allocation and incentive and public finance problems created by such naive ideas being made into government policy, there is a grave and fundamental issue that Amartya and other leftists have been too blinkered to see:
Do they suppose the organised business classes have been weakly cooperative and will just allow such massive redistribution to occur without getting the Indian political system to pay them off as well? And how do the organised business classes get paid off? By their getting to take the land of the inhabitants of rural India. And land in an environment of a debauching of money and other paper assets is as good as gold.
So the peasants will lose their land to the government’s businessman friends on the one hand while purportedly getting “guaranteed” employment and food from the government’s bureaucrats on the other! A landless, asset-less slave population, free to join the industrial proletariat! Is that what Amartya wants to see in India? It may become what results within a few decades from his and his acolytes’ words and deeds.
Rajiv Gandhi once gave me his private phone numbers at 10 Jan Path. I used them back in January 1991 during the Gulf war. But I cannot do so now as Rajiv is gone. Amartya can. Let him phone Sonia and prevail upon her to put the brakes on the wild food and employment schemes he and his friends have persuaded her about until he reads and reflects upon what I said in January 2007 in “On Land-Grabbing” and in my July 2007 open letter to him, reproduced below:
“At a business meet on 12 January 2005, Dr Manmohan Singh showered fulsome praise on Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee as “dynamic”, “the Nation’s Best Chief Minister”, whose “wit and wisdom”, “qualities of head and heart”, “courage of conviction and passionate commitment to the cause of the working people of India” he admired, saying “with Buddhadeb Babu at the helm of affairs it appears Bengal is once again forging ahead… If today there is a meeting of minds between Delhi and Kolkata, it is because the ideas that I and Buddhadebji represent have captured the minds of the people of India. This is the idea of growth with equity and social justice, the idea that economic liberalization and modernization have to be mindful of the needs of the poor and the marginalized.”…. Dr Singh returned to the “needs of the poor and the marginalized” at another business meet on 8 January 2007 promising to “unveil a new Rehabilitation Policy in three months to increase the pace of industrialisation” which would be “more progressive, humane and conducive to the long-term welfare of all stakeholders”, while his businessman host pointedly stated about Singur “land for industry must be made available to move the Indian manufacturing sector ahead”. The “meeting of minds between Delhi and Kolkata” seems to be that agriculture allegedly has become a relatively backward slow-growing sector deserving to yield in the purported larger national interest to industry and services: what the PM means by “long-term welfare of all stakeholders” is the same as the new CPI-M party-line that the sons of farmers should not remain farmers (but become automobile technicians or IT workers or restaurant waiters instead). It is a political viewpoint coinciding with interests of organised capital and industrial labour in India today, as represented by business lobbies like CII, FICCI and Assocham on one hand, and unions like CITU and INTUC on the other. Business Standard succinctly (and ominously) advocated this point of view in its lead editorial of 9 January as follows: “it has to be recognised that the world over capitalism has progressed only with the landed becoming landless and getting absorbed in the industrial/service sector labour force ~ indeed it is obvious that if people don’t get off the land, their incomes will rise only slowly”. Land is the first and ultimate means of production, and the attack of the powerful on land-holdings or land-rights of the unorganised or powerless has been a worldwide phenomenon ~ across both capitalism and communism. In the mid-19th Century, white North America decimated hundreds of thousands of natives in the most gargantuan land-grab of history. Defeated, Chief Red Cloud of the Sioux spoke in 1868 for the Apache, Navajo, Comanche, Cheyenne, Iroquois and hundreds of other tribes: “They made us many promises, more than I can remember, but they never kept any except one: they promised to take our land, and they took it.” Half a century later, while the collapse of grain prices contributed to the Great Depression and pauperisation of thousands of small farmers in capitalist America in the same lands that had been taken from the native tribes, Stalin’s Russia embarked on the most infamous state-sponsored land-grab in modern history: “The mass collectivisation of Soviet agriculture (was) probably the most warlike operation ever conducted by a state against its own citizens…. Hundreds of thousands and finally millions of peasants… were deported… desperate revolts in the villages were bloodily suppressed by the army and police, and the country sank into chaos, starvation and misery… The object of destroying the peasants’ independence…was to create a population of slaves, the benefit of whose labour would accrue to industry. The immediate effect was to reduce Soviet agriculture to a state of decline from which it has not yet recovered… The destruction of the Soviet peasantry, who formed three quarters of the population, was not only an economic but a moral disaster for the entire country. Tens of millions were driven into semi-servitude, and millions more were employed as executants…” (Kolakowski, Main Currents of Marxism). Why did Stalin destroy the peasants? Lenin’s wishful “alliance between the proletariat and the peasantry” in reality could lead only to the peasants being pauperised into proletarians. At least five million peasants died and (Stalin told Churchill at Yalta) another ten million in the resultant famine of 1932-1933. “Certainly it involved a struggle ~ but chiefly one between urban Communists and villagers… it enabled the regime to obtain much of the capital desired for industrialization from the defeated village… it was the decisive step in the building of Soviet totalitarianism, for it imposed on the majority of the people a subjection which only force could maintain” (Treadgold, 20th Century Russia). Mr Bhattacharjee’s CPI-M is fond of extolling Chinese communism, and the current New Delhi establishment have made Beijing and Shanghai holiday destinations of choice. Dr Singh’s Government has been eager to create hundreds of “Special Economic Zones” run by organised capital and unionised labour, and economically privileged by the State. In fact, the Singur and Nandigram experiences of police sealing off villages where protests occur are modelled on creation of “Special Economic Zones” in China in recent years. For example, Chinese police on 6 December 2005 cracked down on farmers and fishermen in the seaside village of Dongzhou, 125 miles North East of Hong Kong. Thousands of Dongzhou villagers clashed with troops and armed police protesting confiscation of their lands and corruption among officials. The police immediately sealed off the village and arrested protesters. China’s Public Security Ministry admitted the number of riots over land had risen sharply, reaching more than seventy thousand across China in 2004; police usually suppressed peasant riots without resort to firing but in Dongzhou, police firing killed 20 protesters. Such is the reality of the “emergence” of China, a totalitarian police-state since the Communist takeover in 1949, from its period of mad tyranny until Mao’s death in 1976, followed by its ideological confusion ever since. Modern India’s political economy today remains in the tight grip of metropolitan “Big Business” and “Big Labour”. Ordinary anonymous individual citizens ~ whether housewife, consumer, student, peasant, non-union worker or small businessman ~ have no real voice or representation in Indian politics. We have no normal conservative, liberal or social democratic party in this country, as found in West European democracies where the era of land-grabbing has long-ceased. If our polity had been normal, it would have known that economic development does not require business or government to pauperise the peasantry but instead to define and secure individual property rights and the Rule of Law, and establish proper conditions for the market economy. The Congress and BJP in Delhi and CPI-M in Kolkata would not have been able to distract attention from their macroeconomic misdeeds over the decades ~ indicated, for example, by increasing interest-expenditure paid annually on Government debt as a fraction of tax revenues… This macroeconomic rot originated with the Indira Gandhi-PN Haksar capriciousness and mismanagement, which coincided with the start of Dr Singh’s career as India’s best known economic bureaucrat….”
“Professor Amartya Sen, Harvard University, Dear Professor Sen, Everyone will be delighted that someone of your worldwide stature has joined the debate on Singur and Nandigram; The Telegraph deserves congratulations for having made it possible on July 23. I was sorry to find though that you may have missed the wood for the trees and also some of the trees themselves. Perhaps you have relied on Government statements for the facts. But the Government party in West Bengal represents official Indian communism and has been in power for 30 years at a stretch. It may be unwise to take at face-value what they say about their own deeds on this very grave issue! Power corrupts and absolute power corrupts absolutely, and there are many candid communists who privately recognise this dismal truth about themselves. To say this is not to be praising those whom you call the “Opposition” ~ after all, Bengal’s politics has seen emasculation of the Congress as an opposition because the Congress and communists are allies in Delhi. It is the Government party that must reform itself from within sua sponte for the good of everyone in the State. The comparisons and mentions of history you have made seem to me surprising. Bengal’s economy now or in the past has little or nothing similar to the economy of Northern England or the whole of England or Britain itself, and certainly Indian agriculture has little to do with agriculture in the new lands of Australia or North America. British economic history was marked by rapid technological innovations in manufacturing and rapid development of social and political institutions in context of being a major naval, maritime and mercantile power for centuries. Britain’s geography and history hardly ever permitted it to be an agricultural country of any importance whereas Bengal, to the contrary, has been among the most agriculturally fertile and hence densely populated regions of the world for millennia. Om Prakash’s brilliant pioneering book The Dutch East India Company and the Economy of Bengal 1630-1720 (Princeton 1985) records all this clearly. He reports the French traveller François Bernier saying in the 1660s “Bengal abounds with every necessary of life”, and a century before him the Italian traveller Verthema saying Bengal “abounds more in grain, flesh of every kind, in great quantity of sugar, also of ginger, and of great abundance of cotton, than any country in the world”. Om Prakash says “The premier industry in the region was the textile industry comprising manufacture from cotton, silk and mixed yarns”. Bengal’s major exports were foodstuffs, textiles, raw silk, opium, sugar and saltpetre; imports notably included metals (as Montesquieu had said would always be the case). Bengal did, as you say, have industries at the time the Europeans came but you have failed to mention these were mostly “agro-based” and, if anything, a clear indicator of our agricultural fecundity and comparative advantage. If “deindustrialization” occurred in 19th Century India, that had nothing to do with the “deindustrialization” in West Bengal from the 1960s onwards due to the influence of official communism. You remind us Fa Hiaen left from Tamralipta which is modern day Tamluk, though he went not to China but to Ceylon. You suggest that because he did so Tamluk effectively “was greater Calcutta”. I cannot see how this can be said of the 5th Century AD when no notion of Calcutta existed. Besides, modern Tamluk at 22º18’N, 87º56’E is more than 50 miles inland from the ancient port due to land-making that has occurred at the mouth of the Hooghly. I am afraid the relevance of the mention of Fa Hiaen to today’s Singur and Nandigram has thus escaped me. You say “In countries like Australia, the US or Canada where agriculture has prospered, only a very tiny population is involved in agriculture. Most people move out to industry. Industry has to be convenient, has to be absorbing”. Last January, a national daily published a similar view: “For India to become a developed country, the area under agriculture has to shrink, urban and industrial land development has to take place, and about 100 million workers have to move out from agriculture into industry and services. This is the only way forward for bringing prosperity to the rural population”. Rice is indeed grown in Arkansas or Texas as it is in Bengal but there is a world of difference between the technological and geographical situation here and that in the vast, sparsely populated New World areas with mechanized farming! Like shoe-making or a hundred other crafts, agriculture can be capital-intensive or labour-intensive ~ ours is relatively labour-intensive, theirs is relatively capital-intensive. Our economy is relatively labour-abundant and capital-scarce; their economies are relatively labour-scarce and capital-abundant (and also land-abundant). Indeed, if anything, the apt comparison is with China, and you doubtless know of the horror stories and civil war conditions erupting across China in recent years as the Communist Party and their businessman friends forcibly take over the land of peasants and agricultural workers, e.g. in Dongzhou. All plans of long-distance social engineering to “move out” 40 per cent of India’s population (at 4 persons per “worker”) from the rural hinterlands must also face FA Hayek’s fundamental question in The Road to Serfdom: “Who plans whom, who directs whom, who assigns to other people their station in life, and who is to have his due allotted by others?” Your late Harvard colleague, Robert Nozick, opened his brilliant 1974 book Anarchy, State and Utopia saying: “Individuals have rights, and there are things no person or group may do to them (without violating their rights)”. You have rightly deplored the violence seen at Singur and Nandigram. But you will agree it is a gross error to equate violence perpetrated by the Government which is supposed to be protecting all people regardless of political affiliation, and the self-defence of poor unorganised peasants seeking to protect their meagre lands and livelihoods from state-sponsored pogroms. Kitchen utensils, pitchforks or rural implements and flintlock guns can hardly match the organised firepower controlled by a modern Government. Fortunately, India is not China and the press, media and civil institutions are not totally in the hands of the ruling party alone. In China, no amount of hue and cry among the peasants could save them from the power of organised big business and the Communist Party. In India, a handful of brave women have managed to single-handedly organise mass movements of protest which the press and media have then broadcast that has shocked the whole nation to its senses. You rightly say the land pricing process has been faulty. Irrelevant historical prices have been averaged when the sum of discounted expected future values in an inflationary economy should have been used. Matters are even worse. “The fear of famine can itself cause famine. The people of Bengal are afraid of a famine. It was repeatedly charged that the famine (of 1943) was man-made.” That is what T. W. Schultz said in 1946 in the India Famine Emergency Committee led by Pearl Buck, concerned that the 1943 Bengal famine should not be repeated following dislocations after World War II. Of course since that time our agriculture has undergone a Green Revolution, at least in wheat if not in rice, and a White Revolution in milk and many other agricultural products. But catastrophic collapses in agricultural incentives may still occur as functioning farmland comes to be taken by government and industry from India’s peasantry using force, fraud or even means nominally sanctioned by law. If new famines come to be provoked because farmers’ incentives collapse, let future historians know where responsibility lay. West Bengal’s real economic problems have to do with its dismal macroeconomic and fiscal position which is what Government economists should be addressing candidly. As for land, the Government’s first task remains improving grossly inadequate systems of land-description and definition, as well as the implementation and recording of property rights. With my most respectful personal regards, I remain, Yours ever, Suby”
How does India, as a state, treat its weakest and most vulnerable citizens? Not very well at all. It is often only because families and society have not collapsed completely, as they have elsewhere, that the weakest survive. Can we solve in the 21st Century, in a practical manner appropriate to our times, the problem Buddha raised before he became the Buddha some twenty six centuries ago? Says Eliot,
“The legend represents him as carefully secluded from all disquieting sights and as learning the existence of old age, sickness and death only by chance encounters which left a profound impression”
It is to this list we add “the poor” too, especially if we want to include a slightly later and equally great reformer some miles west of the Terai in the Levant. I said some years ago “As we as infants and children need to be helped to find courage to face the start of life, we when very elderly can need to be helped to find courage to face life’s end”. Old age carries with it the fear of death, fear of the end of life and what that means, which raises the meaning of life itself, or at least of the individual life, because we can hardly grasp what the end of life is if we haven’t what it is supposed to be the end of in the first place. What the very elderly need, as do the dying and terminally ill, is to find courage within themselves to comprehend all this with as much equanimity as possible. Companionship and camaraderie — or perhaps let us call it love — go towards that courage coming to be found; something similar goes for the sick, whether a sick child missing school or the elderly infirm, courage that they are not alone and that they can and will recover and not have to face death quite yet, that life will indeed resume.
As for the poor, I said in 2009 about the bizarre Indian scheme of “interrogating, measuring, photographing and fingerprinting them against their will” that “the poor have their privacy and their dignity. They are going to refuse to waste their valuable time at the margins of survival volunteering for such gimmickry.”
“What New Delhi’s governing class fails to see is that the masses of India’s poor are not themselves a mass waiting for New Delhi’s handouts: they are individuals, free, rational, thinking individuals who know their own lives and resources and capacities and opportunities, and how to go about living their lives best. What they need is security, absence of state or other tyranny, roads, fresh water, electricity, functioning schools for their children, market opportunities for work, etc, not handouts from a monarch or aristocrats or businessmen….” Or, to put it differently in Kant’s terms, the poor need to be treated as ends in themselves, and not as the means towards the ends of others…
Part II India’s Right Road Forward Now: Some Thoughtful Analysis for Grown Ups
5. Transcending a Left-Right/Congress-BJP Divide in Indian Politics
6. Budgeting Military & Foreign Policy
7. Solving the Kashmir Problem & Relations with Pakistan
8. Dealing with Communist China
9. Towards Coherence in Public Accounting, Public Finance & Public Decision-Making
10. India’s Money: Towards Currency Integrity at Home & Abroad
Cambridge Economics & the Disputation in India’s Economic Policy (2013)
May 19, 2013 — drsubrotoroySee also
2021: https://independentindian.com/2021/07/26/critique-of-amartya-or-rather-critique-of-team-amartya-sens-production-of-home-in-the-world-etc/
1986-1992
2006: https://independentindian.com/2006/05/21/the-politics-of-dr-singh/
2008: https://independentindian.com/2008/04/25/assessing-manmohan-the-doctor-of-deficit-finance-should-realise-the-currency-is-at-stake/
23 August 2013 :
https://independentindian.com/2013/08/23/did-jagdish-bhagwati-originate-pioneer-intellectually-father-indias-1991-economic-reform-did-manmohan-singh-or-did-i-through-my-encounter-with-rajiv-gandhi-just-as-siddhartha-shan/
19 May 2013
“Manmohan and Sonia have violated Rajiv Gandhi’s intended reforms; the Communists have been appeased or bought; the BJP is incompetent”
is what I said in Sep 2007 in an op-ed in The Statesman. I have to say it again, adding Amartya Sen too for his backing of the so-called “Food Security Bill”…
[Sonia was livid in a speech after I said in 2007 “Manmohan and Sonia have violated Rajiv Gandhi’s intended reforms” … Her stooges wanted me arrested! One said “lined up and shot”… Then she said she only meant to refer to Haryana politics! … https://twitter.com/subyroy/status/1064737873746976768?s=20 ]
But taking Sonia and Rajiv out of it all, we are left with a battle from within Cambridge economics, viz,
Sen and Singh (disciples of Joan Robinson, Kaldor, Dobb et al in the 1950s)
vs
myself … in my PhD thesis of 1981 under Frank Hahn...
15 July 2013
I am afraid I cannot remember a cogent coherent book authored by Amartya Sen since his 1972 *On Economic Inequality*, which had nice surveys of the Gini coefficient and related concepts…
My 2006 conversation with him about his book *Identity and Violence* is here. (see too “Is “Cambridge Philosophy” dead, in Cambridge? Can it be resurrected, there? Case Study: Renford Bambrough (& Subroto Roy) preceded by decades Cheryl Misak’s thesis on Wittgenstein being linked with Peirce via Ramsey…”)
I now see he and a co-author seem to have produced yet one more piece of extended undergraduate waffle…E.g. “If development is about the expansion of freedom, it has to embrace the removal of poverty as well as paying attention to ecology as integral parts of a unified concern, aimed ultimately at the security and advancement of human freedom. Indeed, important components of human freedoms — and crucial ingredients of our quality of life — are thoroughly dependent on the integrity of the environment, involving the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the epidemiological surroundings in which we live….”
15 July 2013
Where is Amartya’s reply to this?
And where is Manmohan’s reply to this?
And where is Manmohan’s reply to this?
And Manmohan was given a copy of this
by me at a luncheon at the Indian Embassy Residence in Washington in September 1993 when the Ambassador, the late Barrister SS Ray, told him in the presence of all his senior aides including Montek Ahluwalia and C. Rangarajan, that I had authored the 1991 reform for the then-dead Rajiv Gandhi… on my laptop…
So, to cut to the chase, I have not and do not accept that either Amartya Sen or Manmohan Singh have been leaders of economic thought about India at least (US and British economists can judge for themselves the impact of the former on their own economics). The Sonia Congress has misled itself on the basis of their advocacy and the pity is the BJP, Communists et al in India seem to be even worse…
See also
Memo to the PM
May 30, 2011 — drsubrotoroyFrom Facebook May 29 2011:
Subroto Roy hears Dr Manmohan Singh said yesterday (to journalists “on board Air India One” returning with him from Africa) “I think industrialisation is essential for the country to solve the problems of unemployment and poverty”. Nonsense Prime Minister! That is obsolescent or, at the very least, rather quaint Stalinist chatter. Try to provide public goods properly, which means getting the judiciary etc to work well. Try to get the public finances & public decision-making processes right, which means getting govt accounting & audit right and legislatures to work across the country. Try to drastically raise the productivity of public investments and expenditures. And try not to debauch India’s money any further than you have done. All that may make a good start. (And only when you have done all that do you really need to travel abroad again on “Air India One”; that thing the telephone really is a great invention…)
Subroto Roy is scolded by Ms Siddiqui: “Out of all the corrupt money grabbing racist ministers and governors and politicians you could find only Manmohan Singh to attack? Truly discerning arent you?”,
to which I have to say Hello Ms Siddiqi, Thank you for your comment. It is I am afraid ill-informed. There is nothing personal in my critical assessment of Dr Singh’s economics and politics. To the contrary, he has been in decades past a friend or at least a colleague of my father’s, and in the autumn of 1973 visited our then-home in Paris at the request of my father to advise me, then aged 18, before I embarked on my undergraduate studies at the London School of Economics. My assessments in recent years like “The Politics of Dr Singh” https://www.facebook.com/note.php?note_id=177565501125“Assessing Manmohan”https://www.facebook.com/note.php?note_id=177600651125, “The Dream Team: A Critique” https://www.facebook.com/note.php?note_id=184178641125 “Mistaken Macroeconomics” https://www.facebook.com/note.php?note_id=179676656125 etc need to be seen along with my “Assessing Vajpayee: Hindutva True and False”, “The Hypocrisy of the CPI-M”, “Against Quackery”, “Our Dismal Politics”, “Political Paralysis” etc.
Nothing personal is intended in any of these; the purpose at hand has been to contribute to a full and vigorous discussion of the public interest in India.
Twenty Years Ago in New Delhi March 18-23 1991: Excerpt from “Rajiv Gandhi & the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform” (2011)
March 21, 2011 — drsubrotoroyTwenty Years Ago in New Delhi March 18-23 1991: Excerpt from https://independentindian.com/thoughts-words-deeds-my-work-1973-2010/rajiv-gandhi-and-the-origins-of-indias-1991-economic-reform/
“I returned to Delhi on Monday, March 18, 1991 as new elections had been announced. Rasgotra said I should be in touch with Krishna Rao, and the next day March 19 Krishna Rao met me for several hours. I told him what I thought were the roots and results of the Gulf war. He in turn generously told me what had happened while I had been away. He said the group had met Rajiv in December with the proposal that Rajiv better organize his time by having an “office manager” of larger political stature than George. The name of a UP Congressman of integrity had been put forward, but nothing had come of it. Rajiv had been advised to keep Chandrashekhar in power through the autumn of 1991, as Chandrashekhar was doing Rajiv’s work for him of sidelining V. P. Singh. The idea was to cooperate with Chandrashekhar until he could be pushed up to the Presidency when that fell vacant. Rajiv had been advised not to work in a Chandrashekhar cabinet, though in my opinion, had we been like the Scandinavians, it was not impossible for a former prime minister to enter another cabinet on the right terms in the national interest of providing stable government, which was imperative at the time. Things seem to have slipped out of control when Chandrashekhar resigned. At that point, Rajiv called the group together and instructed them to write a draft of the manifesto for the impending elections. I had advised readiness back in September but the lack of organization had prevented much tangible progress at the time. Our group was to now report to a political manifesto-committee of three senior party leaders who would report to Rajiv. They were Narasimha Rao, Pranab Mukherjee and Madhavsingh Solanki. Krishna Rao liased with Narasimha Rao, Krishnamurty with Mukherjee, Pitroda with Solanki. While Rajiv would obviously lead a new Congress Government, Mukherjee was the presumptive Finance Minister, while Narasimha Rao and Solanki would have major portfolios though Narasimha Rao was expected to retire before too long.
Krishna Rao said I should be in touch with Krishnamurty who was preparing the economic chapters of the draft of the manifesto. Krishnamurty told me he had brought in A. M. Khusro to the group, and there would be a 5 p.m. meeting at Khusro’s office at the Aga Khan Foundation. I arrived early and was delighted to meet Khusro, and he seemed pleased to meet me. Khusro seemed excited by my view that India and Pakistan were spending excessively on defence against each other, which resonated with his own ideas, and he remarked the fiscal disarray in India and Pakistan could start to be set right by mutually agreed cuts in military spending. (Khusro was eventually to accompany Prime Minister Vajpayee to Lahore in 1999).
Krishnamurty had prepared a draft dated March 18 of several pages of the economic aspects of the manifesto. After our discussions, Krishnamurty was hospitable enough to open the draft to improvement. That evening, the 19th, I worked through the night and the next morning to get by noon copies of a revised version with all the members of the group. At 4 p.m. on the 20th there was a meeting at Andhra Bhavan of the whole group except Pitroda, which went on until the night. The next day the 21st , Krishnamurty, Khusro and I met again at Andhra Bhavan for a few hours on the economic aspects of the draft. Then in mid-afternoon I went to Rasgotra’s home to work with him and Krishna Rao. They wanted me to produce the economic draft which they could then integrate as they wished into the material they were dictating to a typist. I offered instead to absorb their material directly on to my laptop computer where the economic draft was. Rasgotra was reluctant to let go control, and eventually I gave in and said I would get them a hard copy of the economic draft, which they then planned to re-draft via a stenographer on a typewriter. At this, Rasgotra gave in and agreed to my solution. So the work began and the three of us continued until late.
That night Krishna Rao dropped me at Tughlak Road where I used to stay with friends. In the car I told him, as he was a military man with heavy security cover for himself as a former Governor of J&K, that it seemed to me Rajiv’s security was being unprofessionally handled, that he was vulnerable to a professional assassin. Krishna Rao asked me if I had seen anything specific by way of vulnerability. With John Kennedy and De Gaulle in mind, I said I feared Rajiv was open to a long-distance sniper, especially when he was on his campaign trips around the country.
This was one of several attempts I made since October 1990 to convey my clear impression to whomever I thought might have an effect that Rajiv seemed to me extremely vulnerable. Rajiv had been on sadhbhavana journeys, back and forth into and out of Delhi. I had heard he was fed up with his security apparatus, and I was not surprised given it seemed at the time rather bureaucratized. It would not have been appropriate for me to tell him directly that he seemed to me to be vulnerable, since I was a newcomer and a complete amateur about security issues, and besides if he agreed he might seem to himself to be cowardly or have to get even closer to his security apparatus. Instead I pressed the subject relentlessly with whomever I could. I suggested specifically two things: (a) that the system in place at Rajiv’s residence and on his itineraries be tested, preferably by some internationally recognized specialists in counter-terrorism; (b) that Rajiv be encouraged to announce a shadow-cabinet. The first would increase the cost of terrorism, the second would reduce the potential political benefit expected by terrorists out to kill him. On the former, it was pleaded that security was a matter being run by the V. P. Singh and then Chandrashekhar Governments at the time. On the latter, it was said that appointing a shadow cabinet might give the appointees the wrong idea, and lead to a challenge to Rajiv’s leadership. This seemed to me wrong, as there was nothing to fear from healthy internal contests for power so long as they were conducted in a structured democratic framework. I pressed to know how public Rajiv’s itinerary was when he travelled. I was told it was known to everyone and that was the only way it could be since Rajiv wanted to be close to the people waiting to see him and had been criticized for being too aloof. This seemed to me totally wrong and I suggested that if Rajiv wanted to be seen as meeting the crowds waiting for him then that should be done by planning to make random stops on the road that his entourage would take. This would at least add some confusion to the planning of potential terrorists out to kill him. When I pressed relentlessly, it was said I should probably speak to “Madame”, i.e. to Mrs. Rajiv Gandhi. That seemed to me highly inappropriate, as I could not be said to be known to her and I should not want to unduly concern her in the event it was I who was completely wrong in my assessment of the danger. The response that it was not in Congress’s hands, that it was the responsibility of the V. P. Singh and later the Chandrashekhar Governments, seemed to me completely irrelevant since Congress in its own interests had a grave responsibility to protect Rajiv Gandhi irrespective of what the Government’s security people were doing or not doing. Rajiv was at the apex of the power structure of the party, and a key symbol of secularism and progress for the entire country. Losing him would be quite irreparable to the party and the country. It shocked me that the assumption was not being made that there were almost certainly professional killers actively out to kill Rajiv Gandhi — this loving family man and hapless pilot of India’s ship of state who did not seem to have wished to make enemies among India’s terrorists but whom the fates had conspired to make a target. The most bizarre and frustrating response I got from several respondents was that I should not mention the matter at all as otherwise the threat would become enlarged and the prospect made more likely! This I later realized was a primitive superstitious response of the same sort as wearing amulets and believing in Ptolemaic astrological charts that assume the Sun goes around the Earth — centuries after Kepler and Copernicus. Perhaps the entry of scientific causality and rationality is where we must begin in the reform of India’s governance and economy. What was especially repugnant after Rajiv’s assassination was to hear it said by his enemies that it marked an end to “dynastic” politics in India. This struck me as being devoid of all sense because the unanswerable reason for protecting Rajiv Gandhi was that we in India, if we are to have any pretensions at all to being a civilized and open democratic society, cannot tolerate terrorism and assassination as means of political change. Either we are constitutional democrats willing to fight for the privileges of a liberal social order, or ours is truly a primitive and savage anarchy concealed beneath a veneer of fake Westernization.
The next day, Friday March 22, I worked from dawn to get the penultimate draft to Krishna Rao before noon as planned the night before. Rasgotra arrived shortly, and the three of us worked until evening to finish the job. I left for an hour to print out copies for a meeting of the entire group, where the draft we were going to submit would come to be decided. When I got back I found Rasgotra had launched an extended and quite unexpected attack on what had been written on economic policy. Would someone like Manmohan Singh, Rasgotra wanted to know, agree with all this talk we were putting in about liberalization and industrial efficiency? I replied I did not know what Manmohan Singh’s response would be but I knew he had been in Africa heading something called the South-South Commission for Julius Nyrere of Tanzania. I said what was needed was a clear forceful statement designed to restore India’s credit-worthiness, and the confidence of international markets. I said that the sort of thing we should aim for was to make clear, e.g. to the IMF’s man in Delhi when that person read the manifesto, that the Congress Party at least knew its economics and was planning to make bold new steps in the direction of progress. I had argued the night before with Rasgotra that on foreign policy we should “go bilateral” with good strong ties with individual countries, and drop all the multilateral hogwash. But I did not wish to enter into a fight on foreign policy which he was writing, so long as the economic policy was left the way we said. Krishnamurty, Khusro and Pitroda came to my defence saying the draft we had done greatly improved on the March 18 draft. For a bare half hour or so with all of us present, the draft was agreed upon. Later that night at Andhra Bhavan, I gave Krishna Rao the final copy of the draft manifesto which he was going to give Narasimha Rao the next day, and sent a copy to Krishnamurty who was liaising with Pranab Mukherjee. Pitroda got a copy on a floppy disc the next day for Solanki.
In its constructive aspects, the March 22 1991 draft of the Congress manifesto went as follows with regard to economic policy: “CHAPTER V AGENDA FOR ECONOMIC ACTION 1. Control of Inflation …. The Congress believes the inflation and price-rise of essential commodities… is a grave macroeconomic problem facing the country today. It has hit worst the poorest and weakest sections of our people and those with fixed incomes like pensioners. The Congress will give highest priority to maintaining the prices of essential commodities, increasing their production and supply using all appropriate economic instruments. 2. Macroeconomic Policy Framework To control inflation of the general price-level, the Congress will provide a predictable long-term policy framework. The average Indian household and business will not have their lives and plans disrupted by sudden changes in economic policy. Coherent monetary policy measures will be defined as called for by the Report of Experts of the Reserve Bank of India in 1985. The Long-Term Fiscal Policy introduced by the Congress Government of 1984-1989 will be revived. Medium and long-term export-import policies will be defined. The basis for a strong India must be a strong economy. The Congress believes a high rate of real growth is essential for securing a strong national defence, social justice and equity, and a civilized standard of living for all. As the party of self-reliance, Congress believes resources for growth must be generated from within our own economy. This means all wasteful and unproductive Government spending has to be cut, and resources transferred from areas of low priority to areas of high national priority. Subsidies have to be rationalized and reduced, and productivity of investments already made has to be improved. The widening gap between revenue receipts and revenue expenditure must be corrected through fiscal discipline, and the growing national debt brought under control as a matter of high priority. These policies in a consistent framework will create the environment for the freeing of the rupee in due course, making it a hard currency of the world of which our nation can be proud. Public resources are not unlimited. These have to be allocated to high priority areas like essential public services, poverty-reduction, strategic sectors, and protection of the interests of the weaker sections of society. Government has to leave to the initiative and enterprise of the people what can be best done by themselves. Government can now progressively vacate some areas of activity to the private, cooperative and non-government sectors. Black money in the parallel economy has become the plague of our economic and political system. This endangers the social and moral fabric of our nation. Artificial price controls, excessive licensing, capacity restrictions, outmoded laws on rent control and urban ceiling, and many other outdated rules and regulations have contributed to pushing many honest citizens into dishonest practices. The Congress will tackle the problem of black money at its roots by attacking all outmoded and retrograde controls, and simplifying procedures in all economic spheres. At the same time, the tax-base of the economy must be increased via simplification and rationalization of tax-rates and coverage, user-fees for public goods, and reduction of taxes wherever possible to improve incentives and stimulate growth. 3. Panchayati Raj India’s farmers and khet mazdoors are the backbone of our economy. Economic development is meaningless until their villages provide them a wholesome rural life. The Congress will revitalize Panchayat Raj institutions to decentralize decision-making, so development can truly benefit local people most effectively. 4. Rural Development Basic economic infrastructure like roads, communications, fresh drinking water, and primary health and education for our children must reach all our villages. The Congress believes such a policy will also relieve pressures from migration on our towns and cities…… Through the Green Revolution which the Congress pioneered over 25 years, our farmers have prospered. Now our larger farmers must volunteer to contribute more to the national endeavour, and hence to greater equity and overall economic development. Equity demands land revenue should be mildly graduated so that small farmers holding less than one acre pay less land revenue per acre…. 9. Education and Health The long-run prosperity of our nation depends on the general state of education, health and well-being of our people. Small families give themselves more choice and control over their own lives. Improving female literacy, promoting the welfare of nursing mothers and reducing infant mortality will have a direct bearing on reducing the birth-rate and improving the health and quality of all our people. Primary and secondary education has high social returns and is the best way in the long-run for achievement of real equality. Efforts will be made to reduce the cost of education for the needy through concessional supply of books and other study materials, scholarships and assistance for transportation and residential facilities. The Congress Party pledges to dedicate itself to promoting education, especially in rural areas and especially for girls and the weaker sections of society. The next Congress Government will prepare and launch a 10-year programme for introduction of free and compulsory primary education for all children of school age. It will continue to emphasize vocational bias in education, integrating it closely with employment opportunities…. 11. Industrial Efficiency Our industrial base in the private and public sectors are the core of our economy. What we have achieved until today has been creditable, and we are self-reliant in many areas. Now the time has come for industry to provide more efficiency and better service and product-quality for the Indian consumer. The public sector has helped the Indian economy since Independence and many national goals have been achieved. Now it has become imperative that the management of public sector units is made effective, and their productivity increased. Major steps must be taken for greater accountability and market-orientation. Failure to do this will make our country lose more and more in the international economy. Budgetary support will be given only for public sector units in the core and infrastructure sectors. Emphasis will be on improving performance and productivity of existing investments, not on creating added organizations or over manning. Units not in the core sector will be privatised gradually. Even in core sectors like Telecommunications, Power, Steel and Coal, incremental needs can be taken care of by the private sector. The Government-Enterprise interface must be properly defined in a White Paper. The Congress believes privatisation must distribute the profits equitably among the people of India. In order to make our public enterprises truly public, it is essential that the shares of many such enterprises are widely held by the members of the general public and workers. Congress pledges to allot a proportion of such shares to the rural Panchayats and Nagarpalikas. This will enhance their asset-base and yield income for their development activities, as well as improve income-distribution. 12. Investment and Trade Indian industry, Government and professional managers are now experienced enough to deal with foreign companies on an equal footing, and channel direct foreign investment in desired directions. Foreign companies often bring access to advanced technological know-how, without which the nation cannot advance. The Congress Government will formulate a pragmatic policy channelling foreign investment into areas important to the national interest. Every effort must be made also to encourage Indians who are outside India to invest in the industry, trade and real estate of their homeland. Because of the protected and inflationary domestic market, Indian industry has become complacent and the incentive for industrial exports has been weakened. When all production is comfortably absorbed at home, Indian industry makes the effort to venture into exports only as a last resort. This must change. A Congress Government will liberalize and deregulate industry to make it competitive and export-oriented, keeping in mind always the interests of the Indian consumer in commercial policy. Export-oriented and predictable commercial policies will be encouraged. Existing procedural constraints and bottlenecks will be removed. Quotas and tariffs will be rationalized. Thrust areas for export-development will be identified and monitored. Efforts will be made to develop a South Asian Community. Trade and economic cooperation among South Asian countries must be increased and simplified.”
This March 22 1991 draft of the Congress’s intended economic policies got circulated and discussed, and from it rumours and opinions appeared that Congress was planning to launch a major economic reform in India. Economic Times said the manifesto “is especially notable for its economic agenda” and Business Standard said “if party manifestos decide election battles” Congress must be “considered home and dry”. A senior IMF official told me three years later the manifesto had indeed seemed a radical and bold move in the direction of progress, which had been exactly our intended effect.
When I met Manmohan Singh at the residence of S. S. Ray in September 1993 in Washington, Ray told him and his senior aides the Congress manifesto had been written on my computer. Manmohan Singh smiled and said that when Arjun Singh and other senior members of the Congress had challenged him in the cabinet, he had pointed to the manifesto. Yet, oddly enough, while the March 22 draft got discussed and circulated, and the Indian economic reform since July 1991 corresponded in fundamental ways to its contents as reproduced above, the actual published Congress manifesto in April 1991 was as tepid and rhetorical as usual, as if some party hack had before publication put in the usual nonsense about e.g. bringing down inflation via price-controls. Certainly the published manifesto was wholly undistinguished in its economic aspects, and had nothing in it to correspond to the bold change of attitude towards economic policy that actually came to be signalled by the 1991 Government.
On March 23, our group was to meet Rajiv at noon. There was to be an event in the inner lawns of Rajiv’s residence in the morning, where he would launch Krishna Rao’s book on India’s security. Krishna Rao had expressly asked me to come but I had to wait outside the building patiently, not knowing if it was a mistake or if it was deliberate. This was politics after all, and I had ruffled feathers during my short time there. While I waited, Rajiv was speaking to a farmers’ rally being held at grounds adjoining his residence, and there appeared to be thousands of country folk who had gathered to hear him. When it was over, Rajiv, smiling nervously and looking extremely uncomfortable, was hoisted atop people’s shoulders and carried back to the residence by his audience. As I watched, my spine ran cold at the thought that any killer could have assassinated him with ease in that boisterous crowd, right there in the middle of Delhi outside his own residence. It was as if plans for his security had been drawn up without any strategic thinking underlying them.
Krishna Rao arrived and graciously took me inside for his book launch. The event was attended by the Congress’s top brass, including Narasimha Rao whom I met for the first time, as well as foreign military attaches and officers of the Indian armed forces. The attaché of one great power went about shaking hands and handing out his business card to everyone. I stood aside and watched. Delhi felt to me that day like a sieve, as if little could be done without knowledge of the embassies. One side wanted to sell arms, aircraft or ships, while the other wanted trips abroad or jobs or green cards or whatever for their children. And I thought Islamabad would be worse — could India and Pakistan make peace in this fetid ether?
Proceedings began when Rajiv arrived. This elite audience mobbed him just as the farmers had mobbed him earlier. He saw me and beamed a smile in recognition, and I smiled back but made no attempt to draw near him in the crush. He gave a short very apt speech on the role the United Nations might have in the new post-Gulf War world. Then he launched the book, and left for an investiture at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
We waited for our meeting with him, which finally happened in the afternoon. Rajiv was plainly at the point of exhaustion and still hard-pressed for time. He seemed pleased to see me and apologized for not talking in the morning. Regarding the March 22 draft, he said he had not read it but that he would be doing so. He said he expected the central focus of the manifesto to be on economic reform, and an economic point of view in foreign policy, and in addition an emphasis on justice and the law courts. I remembered our September 18 conversation and had tried to put in justice and the courts into our draft but had been over-ruled by others. I now said the social returns of investment in the judiciary were high but was drowned out again. Rajiv was clearly agitated that day by the BJP and blurted out he did not really feel he understood what on earth they were on about. He said about his own family, “We’re not religious or anything like that, we don’t pray every day.” I felt again what I had felt before, that here was a tragic hero of India who had not really wished to be more than a happy family man until he reluctantly was made into a national leader against his will. We were with him for an hour or so. As we were leaving, he said quickly at the end of the meeting he wished to see me on my own and would be arranging a meeting. One of our group was staying back to ask him a favour. Just before we left, I managed to say to him what I felt was imperative: “The Iraq situation isn’t as it seems, it’s a lot deeper than it’s been made out to be.” He looked at me with a serious look and said “Yes I know, I know.” It was decided Pitroda would be in touch with each of us in the next 24 hours. During this time Narasimha Rao’s manifesto committee would read the draft and any questions they had would be sent to us. We were supposed to be on call for 24 hours. The call never came. Given the near total lack of system and organization I had seen over the months, I was not surprised. Krishna Rao and I waited another 48 hours, and then each of us left Delhi. Before going I dropped by to see Krishnamurty, and we talked at length. He talked especially about the lack of the idea of teamwork in India. Krishnamurty said he had read everything I had written for the group and learned a lot. I said that managing the economic reform would be a critical job and the difference between success and failure was thin.
I got the afternoon train to Calcutta and before long left for America to bring my son home for his summer holidays with me. In Singapore, the news suddenly said Rajiv Gandhi had been killed. All India wept. What killed him was not merely a singular act of criminal terrorism, but the system of humbug, incompetence and sycophancy that surrounds politics in India and elsewhere. I was numbed by rage and sorrow, and did not return to Delhi. Eleven years later, on 25 May 2002, press reports said “P. V. Narasimha Rao and Manmohan Singh lost their place in Congress history as architects of economic reforms as the Congress High command sponsored an amendment to a resolution that had laid credit at the duo’s door. The motion was moved by…. Digvijay Singh asserting that the reforms were a brainchild of the late Rajiv Gandhi and that the Rao-Singh combine had simply nudged the process forward.” Rajiv’s years in Government, like those of Indira Gandhi, were in fact marked by profligacy and the resource cost of poor macroeconomic policy since bank-nationalisation may be as high as Rs. 125 trillion measured in 1994 rupees. Certainly though it was Rajiv Gandhi as Leader of the Opposition in his last months who was the principal architect of the economic reform that came to begin after his passing.”
 Rajiv Gandhi 20 August 1944- 21 May 1991
Rajiv Gandhi 20 August 1944- 21 May 1991
Rajiv-Gandhi-and-the-origins-of-indias-1991-economic-reform/
. See also https://independentindian.com/2013/08/23/did-jagdish-bhagwati-originate-pioneer-intellectually-father-indias-1991-economic-reform-did-manmohan-singh-or-did-i-through-my-encounter-with-rajiv-gandhi-just-as-siddhartha-shan/also
https://independentindian.com/2011/05/21/twenty-years-ago-today-march-23-1991-an-excerpt/
“I’m on my way out”: Siddhartha Shankar Ray (1920-2010)…
November 7, 2010 — drsubrotoroy





November 7, 2010
I am grieved to hear of the death of Siddhartha Shankar Ray last night.
I was introduced to him by an uncle who had been his college-buddy, and he took up a grave personal matter of mine in the Supreme Court of India in 1990 with great kindness, charging me not a penny, being impressed by a little explicit “civil disobedience” I had had to show at the time towards Judge Evelyn Lance.
He also told me he and his wife had been in London on May 29 1984 and had seen *The Times*’s leader that day about my critique of Indian economic policy. He invited me to his Delhi home where I told him about the perestroika-for-India project I had led at the University of Hawaii since 1986, at which he, of his own accord, declared
“You must meet Rajiv Gandhi. I will arrange a meeting”.
That led to my meeting with Rajiv Gandhi, then Congress President & Leader of the Opposition, on September 18 1990, which contributed to the origins of India’s 1991 economic reform as has been told elsewhere. https://independentindian.com/thoughts-words-deeds-my-work-1973-2010/rajiv-gandhi-and-the-origins-of-indias-1991-economic-reform/
Rajiv’s assistant George told me Rajiv had said he had not heard more fulsome praise.
In Bengal, he took me as a guest to visit the Legislative Assembly in session when he was Leader of the Opposition; it was the legislature of which my great grandfather, Surendranath Roy, had been a founder, being the first Deputy President and acting President too; Surendranath had been friends with his maternal grandfather, CR Das, leader of the Congress Party before MK Gandhi, and he said to me in the car heading to the legislature about that relationship in Bengal’s politics some seven decades earlier “They were friends”.
He introduced me to all the main leaders of the Bengal Congress at the time (except Mamata Banerjee who could not come) and I was tasked by him to write the manifesto for the State elections that year, which I did (in English, translated into Bangla by Professor Manjula Bose); the Communists won handily again but one of their leaders (Sailen Dasgupta) declared there had never been a State Congress manifesto of the sort before, being as it was an Orwell-like critique of Bengal’s Stalinism.
In a later conversation, I said to him I wished he be appointed envoy to Britain, he instead came to be appointed envoy to the USA.
In Washington in September 1993, he said “You must meet Manmohan Singh”, and invited me to a luncheon at the Ambassador’s Residence where, to Manmohan Singh and all his aides, he declared pointing at me
“The Congress manifesto (of 1991) was written on his (laptop) computer”.
In later years I kept him informed of developments and gave him my publications. We last met in July last year where I gave him a copy, much to his delight, of *Margaret Thatcher’s Revolution: How it Happened and What it Meant*.
I said to him Bengal’s public finances were in abysmal condition, calling for emergency measures financially, and that Mamata Banerjee seemed to me to be someone who knew how to and would dislodge the Communists from their entrenched misgovernance of decades but not quite aware that dislodging a bad government politically was not the same thing as knowing how to govern properly oneself.
He, again of his own accord, said immediately,
“I will call her and her main people to a meeting here so you can meet them and tell them that directly”.
It never transpired.
He and I were supposed to meet a few months ago but could not due to his poor health; on the phone in our last conversation I mentioned to him my plans of creating a Public Policy Institute — an idea he immediately and fully endorsed as being essential though adding
“I can’t be part of it, I’m on my way out”.
“I’m on my way out”. 🙂
That was Siddhartha Shankar Ray — always intelligent, always good-humoured, always public-spirited, always a great Indian.
I shall miss a good friend, indeed my only friend among politicians other than the late Rajiv Gandhi himself.
Well done! The Sonia-Manmohan Congress takes a *third* Rajivist step!
October 15, 2010 — drsubrotoroyFrom Facebook October 15 2010
Subroto Roy thinks the Sonia-Manmohan Govt throwing auditors with their rule-books ex post facto at the Games’ organisers is a good if miniscule first step (though it is, in my estimation, the third Rajivist step in total, see infra…). May we please have the same done asap to military contracts (especially for Russian fighter jets, used aircraft carriers etc), Boeing & Airbus contracts, railway contracts, power sector contracts including nuclear business contracts, IIT and IIM building contracts, in fact *all* government sector building contracts, in fact *all* government sector contracts……
From Facebook March 28 2010
Subroto Roy is pleased that according to this morning’s news reports of a “national convention” on “Law, Justice & the Common Man”, the Sonia-Manmohan Congress took a small second step yesterday on the same road that Rajiv Gandhi and I had chalked out in 1990-1991. Better late than never!
On Applying Disraeli’s “Two Nations” of Victorian England to Modern India: Roy & James, Rajiv, Rahul & Manmohan
September 7, 2010 — drsubrotoroyFrom Subroto Roy & WE James’s Introduction 1989-1990 to Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s edited by them, published by Sage 1992, received by Rajiv Gandhi on September 1990 in manuscript form.
“Finally, no discussion of the subcontinent’s political economy can ignore the fact of the monumental poverty of external goods on the part of a vast population, in contrast with a fairly large class of people with adequate livelihoods, in turn contrasting with small islands of indolence and conspicuous consumption. Benjamin Disraeli said of Victorian England that it consisted of two nations. The Indian subcontinent today consists in many respects of two nations living side by side, the real division being much less longitudinal on religious or communal lines (as intended by Muslim separatists at the time of Partition and Hindu imperialists today) as it is latitudinal on class lines between “bhadralok” and “janata”, middle class and working classes, bourgeoisie and masses, “nomenclatura” and proletariat. The sheer numbers can justify speaking of whole nations, the janata in India alone consisting of something like seven hundred million people, the bhadralok of one hundred and fifty million. The Indian bhadralok on their own constitute one of the largest nations on earth.
The bhadralok are not to be distinguished from the janata by any self-styled civility, nor is there any inevitable conflict which will lead to the victory of one and decimation of the other, nor is it that one derives its income from productive effort or enterprise and the other does not. A more effective criterion by which to distinguish the two nations of India may have to do not with work but with leisure, as well as with the kind of capital that comes to be inherited over time. The janata are the unleisured nation of India, people who mostly due to the meagreness of their initial resources come to possess little or no leisure in the course of their lifetimes. They are scattered and illiterate, without connections in high places, often too involved with the hardships of daily life to care for much else. They eat and sleep to maintain the minimum energy needed to survive, reproduce and send their children to school or work, travelling through life day by day and week by week. They may have some short time devoted to religion or entertainment, but life is too often too hard, not so much without happiness or culture as without much time for either. Expectations of what life has to offer may be unambitious and yet successful.
Inequality from an economic point of view may consist of the fact that the poor do not inherit any leisure from the past. They do not inherit the savings of their parents and ancestors because most did not have parents and ancestors who had any savings to leave behind. Capital and the income it generates, and the consumption which such income makes possible, are among the most subtle notions of political economy. As a rough approximation, if we distinguish between human capital, physical and financial capital, and social and political capital, it may be said that the inheritance of economic inequality in India may consist of the inheritance of economic inequality in India may consist of the inheritance by the janata of no form of capital except their own stock of human capital. There is little or no inheritance from parents of savings or any other form of capital. Hence the janata are also the “garib lok”, the masses are also the poor folk.
By contrast the bhadralok are also the leisured nation of the subcontinent, with the time and inclination to praise or decry the state of the culture or the economy or the prime minister, to visit or return from the outside world (“baahar”) to the subcontinent or vice versa, to take a walk in the morning or a nap in the afternoon, to express compassion for or embarrassment about the existence of the janata (especially in relation to the foreigner since the bhadralok have to explain both their privileged position relative to the janata and their often underprivileged position relative to the foreigner with whom they desire to consort), to study the janata or lead them in revolution or take measurements of them, and to read, write, edit or publish books such as this one. The bhadralok are the “respectable people” of the subcontinent, with names, family histories and reputations, literate and often highly educated, bilingual at least, with an inheritance of or illusions about acknowledged places in society. They inherit from their parents and save for their children physical and financial capital, invest in their human capital, and bestow to them as much social and political capital as they can. The mercantile and industrial bhadralok own and transfer to their children relatively more physical and financial capital, while the managerial, administrative and professional bhadralok may transfer relatively more social and political capital. At the apex of both groups is an elite amounting to a few million people, united perhaps by their membership or attempted membership of the post-British social clubs and centres of intellectualism, or foreign universities and the lower middle classes of Britain and North America.
What may be expected in the long run is mobility between the two nations and in both directions. Through indolence or bad luck, families can fall by a half or a third of a social class each generation, or move in the opposite direction through chance or cunning or enterprise and effort. It is an essential feature of mass economic development that there will be net mobility upwards in the long run, and an attendant breakdown of social barriers and the gradual assimilation of classes and castes into one another. Contrary to an assumption of the working classes being united in their despair and contempt for the middle class, and motivated in their desire to bloodily dispose of them, it may be more accurate to say that what unleisured people want most (after employment, food, shelter and clothing) is what they value most at the margin, namely, leisure. What the working classes desire most may be something like the kind of life as the bourgeoisie. Let aside there being a potential or open conflict arising from the janata against the bhadralok, the truth of the matter could be there is a desire of the janata to have at least some leisure like the bhadralok.
If this is an accurate assumption, the main source of conflict between the two nations of India or the subcontinent could be different from what is often supposed by many people. Instead of being revolutionary in nature and deriving from below, the source may be reactionary in nature and amount to resistance from the top. Like all cartels, the bhadralok may want to preserve their numbers and not look with favour at the prospect of large-scale mass economic development, entailing as this will greater competition on all fronts, the erosion of privilege, the breakdown of social barriers and the assimilation of classes into one another.
The Jacobin/Bolshevik/Maoist method of reducing inequalities was to expropriate physical and financial capital, and decimate social and political capital and all that stands in the way of such destruction. The upheaval and chaos of such blood-letting leaves a new order which is, or seems, for a moment, more egalitarian than the regime it replaces. But it also leaves a society without knowledge of its past, alternately enervated by its present and terrified of its future. Recovery from such a state of near social death has been long and hard and painful, where it has happened at all. Despite the wishes of a few, India does not seem likely to experience such social death on a national scale, although the temporary effects of terrorism and civil chaos in pockets of the country would seem to be similar.
A more far-sighted method would be by the creation of capital for the janata to increase their sources of income and consumption and thereby reduce the inequality of wealth and political power. It would mean investment in the only form of capital that the janata have: their own human capital. It would mean fundamentally a change of focus away from the theoretical and grandiose in the drawing-rooms and corridors of New Delhi (and Washington), and towards the simple and commonsensical: stopping the wastage of the tax-resources; making the currency sound at home and abroad; redirecting public investment towards public goods such as civil justice, roads, fresh water and sanitation; and fostering a civilized rural life, built around village schools with blackboards and chalk, with playgrounds and libraries and hot meals, with all-weather buildings and all-weather roads to their doors.
India today resembles a kind of gigantic closed city with high walls and few gates. Within the walls are concurrently represented many different ages in the history of man, from pre-historic and early Aryan, to medieval and Moghul, to Dickensian and American, the members of each age having some common and some individual sets of life-expectations, yet all being due to enter the next century together. Outside is the rest of human civilization, as well as the free circulation of gold and foreign exchange. Nearabouts the gates of the city, and with ability to travel in and out, are the few million of the elite. If the walls of the city are to be knocked down or at least if the gates opened and kept wide open, it will have to be the elite who do this or consent to have it done.
If it is done properly, after adequate preparation of the economic and political expectations of citizens, there may be many positive results, not only for the economy but also for the culture and civilization of the subcontinent as a whole. The free flow of ideas and opportunities across national borders; the freedom to travel in the world; the free movement of goods and capital; the freedom to save one’s tangible wealth, small as this may be, in whatever form or currency one considers best — these are fundamentally important freedoms which have been denied to most of the people of the subcontinent thus far and yet are taken for granted elsewhere in the world. There seems little reason to doubt that if such freedoms come to be gradually exercised by the janata there would be a permanent trend of increase in mass income and consumption.
Yet there are genuine questions of sovereignty which have to be anticipated as well. The consequences of a true opening are not fully or easily foreseeable. The prompt arrival of new East India Companies may be expected. Will there be enough competition between them? Or will the elite come to be further subverted, taking the first Indian Republic with it? After the long experience of foreign rule and nationalism and independent democracy, is the Indian polity mature enough to survive and gain from such an opening, or will it collapse once again as it did in the eighteenth century? The spectres of Plassey and Avadh must haunt every Indian nationalist, even as the hopes of a free economy and a progressive culture and an open civilization, beckon from the future. Is it a silent and implicit fear of this sort which constitutes the only possible rational barrier to greater freedom? Has the continued poverty been, in effect, the cost of nationalism? These are hard questions to which answers may not be found easily. It is hoped by the editors that the present volume may engage the citizens and friends of India to reflect upon them….”
From Facebook 7 Sep 2010:
Rajiv Gandhi received this book in manuscript form in hand from me on Sep 18 1990, and it contributed to the origins of India’s 1991 economic reform as has been described elsewhere. I am delighted to hear his son Rahul has in the last few days also been referring to India as “Two Nations”, rich and poor. Dr Manmohan Singh received the book itself in hand from me at the Indian Ambassador’s Residence in Washington in Sepember 1993; I am glad to see he too has yesterday mentioned the same “Two Nations” theory that I had applied from Disraeli’s book about Victorian England.
Did the GoI’s MoF’s CEA certify India’s fiscal health yesterday? If so, it is a mistaken certificate
June 15, 2010 — drsubrotoroyFrom Facebook:
Subroto Roy reads that Dr Kaushik Basu, Chief Economic Adviser to the Finance Ministry of the Manmohan Singh Government, has “expressed great confidence in the fiscal health of the economy” and says to Kaushik:
Notes on Macroeconomics and India
February 28, 2010 — drsubrotoroyDr Kaushik Basu, Chief Economic Adviser, Ministry of Finance
Hello Kaushik,
Long time no see. Happy Holi 2010.
I was glad to see the phrase “the relatively neglected subject of the micro-foundations of macroeconomic policy” mentioned in Chapter 2 of your document for the GoI a few days ago.
But I am unable to see what you could mean by it because your chapter seems devoid of any reference or allusion to the vast discussion over decades of the subject known as the “microeconomic foundations of macroeconomics”. Namely, the attempt to integrate the theory of value (microeconomics) with the theory of money (macroeconomics); or alternatively, the attempt to comprehend aggregate variables like Consumption, Savings, Investment, the Demand for & Supply of Money etc in conceptual terms rooted in theories of constrained optimization by masses of individual people.
It is not an easy task. Keynes made no explicit attempt at it (recall Joan Robinson’s famous quip) and probably did not have time or patience to try. Hicks and Patinkin failed, though after valiant efforts. The modern period on this work began with Clower and Leijonhufvud, followed by the French (like Grandmont), and especially Frank Hahn. Hahn’s 1976 IMSSS paper “Keynesian Economics and General Equilibrium Theory” is the survey to read, viz., Equilibrium and Macroeconomics and Money, Stability and Growth as well as of course Arrow & Hahn’s General Competitive Analysis. You may agree that the general theory of value culminated in an important sense in the Arrow-Debreu model of the 1950s — yet that is something in which no money, and hence no macroeconomics, needs to or can really appear. The hard part is to develop macroeconomic models for policy-discussion which allow for money and public finance while still making some pretence of being rooted in a theory of constrained optimization by individuals, i.e., in microeconomic behaviour. (E Roy Weintraub wrote a textbook with “Microfoundations” in its title.)
In the Indian case, I tried to do a little in my Cambridge PhD thesis thirty years ago: “a full frontal assault from the point of view of microeconomic theory on the ‘development planning’ to which everyone routinely declared their fidelity, from New Delhi’s bureaucrats and Oxford’s ‘development’ school to McNamara’s World Bank with its Indian staffers”. Frank Hahn was very kind to say he thought my “critique of Development Economics was powerful not only on methodological but also on economic theory grounds”. Some of the results appeared in my December 1982 talk to the AEA’s NYC meetings “Economic Theory & Development Economics” (World Development 1983), and in my 1984 monograph with London’s IEA. Dr Manmohan Singh received a copy of the latter work in 1986, as well as, in 1993, a published copy of a work presented to Rajiv Gandhi in 1990, Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s.
I am glad to see from your Chapter 2 that the GoI now seems to agree with what I had said in 1984 of the need for systems that “locally include direct subsidies to those (whether in rural or urban areas) who are unable to provide any income for themselves…” Your material on the “enabling State” would also find much support in what I said there about the functions of civil government and the need for better, not necessarily more, government. On the other hand, your reliance on the very expensive (Rs.19 billion this year!) Nandan Nilekani Numbering idea is odd as there seem to me to be insurmountable “incentive-compatibility” problems with that project no matter how much gets spent on it.
Returning to possible “microfoundations of macroeconomics” relevant to the Indian case, you may find of interest
“India’s Macroeconomics” (2007)
“Fiscal Instability” (2007)
“Fallacious Finance” (2007)
“Monetary Integrity and the Rupee” (2008)
“Growth and Government Delusion” (2008)
“India in World Trade & Payments” (2007)
“Our Policy Process” (2007)
“Indian Money and Credit” (2006)
“Indian Money and Banking” (2006)
“Indian Inflation” (2008)
“Growth of Real Income, Money & Prices in India 1869-2004” (2005)
“How to Budget” (2008)
“The Dream Team: A Critique” (2006)
“Against Quackery” (2007)
“Mistaken Macroeconomics” (2009)
These together outline an idea that the link between macroeconomic policy in India and individual microeconomic budgets of our one billion citizens arises via the “Government Budget Constraint”. More specifically, the continual deficit-finance indulged in by the GoI for decades has been paid for by invisible taxation of nominal assets, causing the general money-price of real goods and services to rise. I.e., the GoI’s wild deficit spending over the decades has been paid for by debauching money through inflation.
(The unrecorded untaxed “black economy” needs a separate chapter altogether, and it seems to me possible it provides enough real income and transactions to be absorbing some of the wilder money supply growth into its hoards.)
India cannot be a major economy of the world until and unless the Rupee some day becomes a hard currency — for the first time in many decades, indeed perhaps for the first time since the start of fiat money. It is going to take much more than the GoI inventing a trading symbol for the Rupee! The appalling state of our government accounting, public finance and monetary policy, caused by the GoI over decades, disallows this from happening any time soon as domestic bank assets (mostly GoI debt, and mostly held by government banks) would inevitably be re-evaluated at world prices foreshadowing a monetary crisis. Perhaps you will help slow the rot — I trust you will not add to it.
Cordially yours
Suby Roy
Postscript March 1 2010: I recalled it as Joan Robinson’s quip, had forgotten it was in fact her quoting Gerald Shove’s quip: “Keynes was not interested in the theory of relative prices. Gerald Shove used to say that Maynard had never spent the twenty minutes necessary to understand the theory of value.” (1963)
see also
My Recent Works, Interviews etc on India’s Money, Public Finance, Banking, Trade, BoP, etc (an incomplete list)
Will the Telangana flare-up awaken New Delhi from its dream-world and into India’s political reality?
December 13, 2009 — drsubrotoroySubroto Roy thinks the flare-up of the Telangana issue has one and only one positive consequence: it brings home to New Delhi’s ruling elite that there are real political questions in India, and not everything can be left to spin-doctors and lobbyists to handle.
Question for the Sonia-Manmohan Govt: is a little polo in Washington expected to benefit India’s “aam admi”?
December 2, 2009 — drsubrotoroyFrom Facebook:
Subroto Roy must ask Dr Manmohan Singh’s Government how it sees India’s “aam admi” coming to benefit by the United States Polo Team welcoming India in 2010 in the world championship polo matches on the DC National Mall, as has been very kindly reported by Mr and Mrs Tareq Salahi following the “Sensational Night honoring India”.
Is Dr Manmohan Singh the “aam admi” that the Congress Party means?
November 14, 2009 — drsubrotoroyDr Manmohan Singh has in a televised meeting with children said about himself:
“I am an aam admi“.
I am afraid this caused me to say at Facebook today:
Subroto Roy finds disconcerting Prime Minister Manmohan Singh’s claim of being himself “a common man”.
In “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform”, I wrote about my encounter with Rajiv:
“I said the public sector’s wastefulness had drained scarce resources that should have gone instead to provide public goods. Since the public sector was owned by the public, it could be privatised by giving away its shares to the public, preferably to panchayats of the poorest villages. The shares would become tradable, drawing out black money, and inducing a historic redistribution of wealth while at the same time achieving greater efficiency by transferring the public sector to private hands. Rajiv seemed to like that idea too, and said he tried to follow a maxim of Indira Gandhi’s that every policy should be seen in terms of how it affected the common man. I wryly said the common man often spent away his money on alcohol, to which he said at once it might be better to think of the common woman instead. (This remark of Rajiv’s may have influenced the “aam admi” slogan of the 2004 election, as all Congress Lok Sabha MPs of the previous Parliament came to receive a previous version of the present narrative.)”
I am afraid I do not think Dr Singh was whom Rajiv or Indira had in mind in speaking of the common man.
Subroto Roy
Kolkata
My Ten Articles on China, Tibet, Xinjiang, Taiwan in relation to India (2007-2009)
September 19, 2009 — drsubrotoroy
I have had a close interest in China ever since the “Peking Spring” more than thirty years ago (if not from when I gave all my saved pocket money to Nehru in 1962 to fight the Chinese aggression) but I had not published anything relating to China until 2007-2008 when I published the ten articles listed below:
“Understanding China”, The Statesman Oct 22 2007
“India-US interests: Elements of a serious Indian foreign policy”, The Statesman Oct 30 2007
“China’s India Aggression”, The Statesman, Nov 5 2007,
“Surrender or Fight? War is not a cricket match or Bollywood movie. Can India fight China if it must? “ The Statesman, Dec 4 2007
“China’s Commonwealth: Freedom is the Road to Resolving Taiwan, Tibet, Sinkiang” The Statesman, December 17, 2007
“Nixon & Mao vs India: How American foreign policy did a U-turn about Communist China’s India aggression”. The Statesman, January 7 2008.
“Lessons from the 1962 War: there are distinct Tibetan, Chinese and Indian points of view that need to be mutually comprehended,” The Statesman, January 15, 2008
“China’s India Example: Tibet, Xinjiang May Not Be Assimilated Like Inner Mongolia, Manchuria”, The Statesman, March 25, 2008
“China’s force and diplomacy: The need for realism in India”, The Statesman, May 31, 2008
“Transparency and history” (with Claude Arpi), Business Standard, Dec 31 2008
With new tensions on the Tibet-India border apparently being caused by the Chinese military, these may be helpful for India to determine a Plan B, or even a Plan A, in its dealings with Communist China.
See also https://independentindian.com/1990/09/18/my-meeting-jawaharlal-nehru-2/
https://independentindian.com/2009/11/25/on-the-zenith-and-nadir-of-us-india-relations/
Disquietude about France’s behaviour towards India on July 14 2009
July 14, 2009 — drsubrotoroyThe Indian press and media, especially the Government-owned part, exulted about Dr Manmohan Singh’s presence at France’s Bastille Day parade this year. And of course it was generally a splendid occasion and there were things that the organisers of Indian military parades could have and should have learnt from it. But there were two sources of disquietude.
Did anyone but myself notice that Dr Manmohan Singh had been placed on the left hand side of the French President? Is that the place of a Guest of Honour?
Who was on the right hand side? Germany’s President Horset Köhler. Why? Some French reports said Dr Singh was the Guest of Honour; others said both were. Either way diplomatic protocol should have placed Dr Singh to the right of President Sarkozy. If President Köhler too was an equivalent Guest of Honour through some last minute diplomatic mishap, he should have been to the right of Dr Singh.
France slighted India by placing Dr Singh to the left of President Sarkozy and still calling him the Guest of Honour. (And why Dr Singh was invited was clearly not because of any new great power status for India but firstly to reciprocate the recent invitation to President Sarkozy last 26 January, and secondly, to gain advantage in business deals with India.)
Secondly, what business did a French paratrooper have to parachute out of an aircraft holding India’s tricolour and then, upon landing, drag it momentarily on the ground? What business did two French paratroopers have to be holding the Indian tricolour in a salute to the French President?
Again, France has slighted India.
I love Paris and I am generally Francophilic — except for such instances of Napoleonic self-aggrandisement.
Subroto Roy
Postscript July 15: Where her husband did not, Mme Sarkozy did get the protocol right, placing Mme Singh to her immediate right and Mme Köhler to Mme Singh’s right.

Schoolboys exchanging fisticuffs in a school playground or elderly men battling over power and policy? Why did Manmohan Singh and LK Advani apologize to one another? Is Indian politics essentially collusive, not competitive, aiming only to preserve and promote the post-1947 Dilli Raj at the expense of the whole of India? We seem to have no Churchillian repartee (except perhaps from Bihar occasionally)
June 18, 2009 — drsubrotoroyYesterday the PM is reported to have been asked by someone travelling on his aeroplane from Moscow “whether he had forgiven Advani for calling him a ‘weak Prime Minister’”.
The question was absurd, almost ridiculous, typical of our docile ingratiating rather juvenile English-language press and media, as if any issue of forgiveness arises at all about what one politician says during an election campaign about another politician’s performance in office.
Dr Manmohan Singh’s answer was surprising too: “I was compelled to reply to what Advani said…On May 16 when (Advani) telephoned me, he told me that he was hurt by some of my statements. He said he was hurt and regretted his statements… I apologised to him if I have hurt him. I am looking forward to a close relationship with the Leader of the Opposition.”
So LK Advani appears to have apologised to Manmohan Singh and Manmohan Singh to LK Advani for what they said about each other during the recent general election campaign! What is going on? Were they schoolboys exchanging fisticuffs in a school playground or elderly men battling over power and policy in modern Indian politics?
What would we have done if there was a Churchill in Indian politics today – hurling sarcastic insults at domestic opponents and foreign leaders while guiding a nation on its right course during turbulent times?
Churchill once famously said his parents had not shown him “The Boneless Wonder” in PT Barnum’s circus because it was too horrible a sight but now he had finally seen such a “Boneless Wonder” in his opponent on the Treasury Benches, namely, Ramsay MacDonald. Of the same opponent he said later “He has the gift of compressing the largest number of words into the smallest amount of thought”.
When accused of being drunk by a woman MP he replied “And you are very ugly, but tomorrow I’ll be sober”. Today’s politically correct world would scream at far less. Field Marshall Montgomery told Churchill, “I neither drink nor smoke and am 100% fit,” to which Churchill replied, “I drink and smoke and I am 200% fit”. That too would be politically incorrect today.
Churchill described Prime Minister Clement Attlee as “a modest man with much to be modest about”; also about Attlee: “If any grub is fed on Royal Jelly it turns into a Queen Bee”. Yet Attlee had enough dignity and self-knowledge and self-confidence to brush it all off and instead respect and praise him. In the 1954 volume Winston Spencer Churchill Servant of Crown and Commonwealth Attlee added his own tribute to his great opponent: “I recall…the period when he was at odds with his own party and took a seat on the Bench below the Gangway on the Government side. Here he was well placed to fire on both parties. I remember describing him as a heavily armed tank cruising in No Man’s Land. Very impressive were the speeches he delivered as the international horizon grew darker. He became very unpopular with the predominant group in his own party, but he never minded fighting a lone battle.”
Stanley Baldwin, who as PM first appointed Churchill as Chancellor of the Exchequer, once said “There comes Winston with his hundred horsepower mind”. Yet Churchill was to later say harshly “I wish Stanley Baldwin no ill, but it would have been much better had he never lived.”
Of Lenin, Churchill said, he was “transported in a sealed truck like a plague bacillus from Switzerland into Russia”. Of Molotov: “I have never seen a human being who more perfectly represented the modern concept of a robot.” Of Hitler, “If [he] invaded hell I would at least make a favourable reference to the devil in the House of Commons”. Of De Gaulle, “He was a man without a country yet he acted as if he was head of state”.” Of John Foster Dulles, “[He] is the only bull who carries his china shop with him”. Of Stafford Cripps, British Ambassador to the USSR, “…a lunatic in a country of lunatics”; and also “There but for the Grace of God, goes God”.
Decades later, that great neo-Churchillian Margaret Thatcher was on the receiving end of a vast amount of sarcasm. “President Mitterrand once famously remarked that Thatcher had ‘the eyes of Caligula and the lips of Marilyn Monroe’. Rather less flatteringly, Dennis Healey described her as Attila the Hen. She probably took both descriptions as compliments.” (Malcolm Rifkind in Margaret Thatcher’s Revolution: How it Happened and What it Meant edited by Subroto Roy and John Clarke, 2005).
Politics is, and should be, grown up stuff because it deals with human lives and national destinies, and really, if you can’t take the heat please do not enter the kitchen. The slight Churchillian sarcasm that does arise within modern Indian politics comes very occasionally from Bihar but nowhere else, e.g. about the inevitability of aloo in samosas and of bhaloos in the jungle but no longer of Laloo being in the seat of power. In general, everyone seems frightfully sombre and self-important though may be in fact short of self-knowledge and hence self-confidence.
What had Manmohan Singh said about LK Advani that he felt he had to apologise for? That Advani had no substantial political achievement to his credit and did not deserve to be India’s PM. Manmohan was not alone in making the charge – Sonia Gandhi, Rahul Gandhi and numerous other spokesmen and representatives of their party said the same. Has Manmohan’s apology to Advani been one on behalf of the whole Congress Party itself?
Was Advani’s apology to Manmohan one on behalf of the whole BJP too?
What had the BJP charged Manmohan with that Advani felt he had to apologise for? Being a “weak PM”.
Hmmm. Frankly, thinking about it, it is hard to count who has not been weak as a PM in India’s modern history.
Certainly Vallabhai Patel as a kind of co-PM was decisive and far from weak back in 1947-48.
Lal Bahadur Shastri was not weak when he told Pakistan that a Pakistani attack on Kashmir would result in an Indian attack on Pakistan.
Indira Gandhi was not weak when she resisted the Yahya Khan-Tikka Khan tyranny against Bangladesh.
Had he not been assassinated, Rajiv Gandhi in a second term would have been decisive and not weak in facing up to and tackling the powerful lobbies and special interest groups that have crippled our domestic economic policy for decades.
But the number of such examples may be counted by hand. Perhaps VP Singh might count, riding in an open jeep to Amritsar, as might AB Vajpayee’s Pokhran II and travelling on a bus to Lahore. In general, the BJP’s charge that Manmohan was “weak” may have constructively led to serious discussion in the country about the whole nature of the Prime Ministership in modern India, which means raising a whole gamut of issues about Indian governance – about India being the softest of “soft states”, with the softest of “soft government budget constraints” (i.e., endless deficit finance and paper money creation) etc.
Instead, what we have had thus far is apologies being exchanged for no real political reason between the leaderships of the Government and the Opposition. If two or three sellers come to implicitly carve up a market between themselves they are said by economic theory to be colluding rather than being in competition. Indian politics may be revealing such implicit collusive behaviour. The goal of this political oligopoly would seem to be to preserve and promote the status quo of the post-1947 Dilli Raj with its special hereditary nomenclatura, at the expense of anonymous diffused teeming India.
Subroto Roy
Postscript July 15 2009: Churchill’s mature opinion of Baldwin was one of the fullest praise at the 20 May 1950 unveiling of a memorial to him. See his In the Balance, edited by Randolph S Churchill, 1951, p. 281
Mistaken Macroeconomics: An Open Letter to Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh 12 June 2009
June 12, 2009 — drsubrotoroy12 June 2009
The Hon’ble Dr Manmohan Singh, MP, Rajya Sabha
Prime Minister of India
Respected Pradhan Mantriji:
In September 1993 at the residence of the Indian Ambassador to Washington, I had the privilege of being introduced to you by our Ambassador the Hon’ble Siddhartha Shankar Ray, Bar-at-Law. Ambassador Ray was kind enough to introduce me saying the 1991 “Congress manifesto had been written on (my laptop) computer” – a reference to my work as adviser on economic and other policy to the late Rajiv Gandhi in his last months. I presented you a book Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s created and edited by myself and WE James at the University of Hawaii since 1986 — the unpublished manuscript of that book had reached Rajivji by my hand when he and I first met on September 18 1990. Tragically, my pleadings in subsequent months to those around him that he seemed to my layman’s eyes vulnerable to the assassin went unheeded.
When you and I met in 1993, we had both forgotten another meeting twenty years earlier in Paris. My father had been a long-time friend of the late Brahma Kaul, ICS, and the late MG Kaul, ICS, who knew you in your early days in the Government of India. In the late summer of 1973, you had acceded to my father’s request to advise me about economics before I embarked for the London School of Economics as a freshman undergraduate. You visited our then-home in Paris for about 40 minutes despite your busy schedule as part of an Indian delegation to the Aid-India Consortium. We ended up having a tense debate about the merits (as you saw them) and demerits (as I saw them) of the Soviet influence on Indian economic “planning”. You had not expected such controversy from a lad of 18 but you were kindly disposed and offered when departing to write a letter of introduction to Amartya Sen, then teaching at the LSE, which you later sent me and which I was delighted to carry to Professor Sen.
I may add my father, back in 1973 in Paris, had predicted to me that you would become Prime Minister of India one day, and he, now in his 90s, is joined by myself in sending our warm congratulations at the start of your second term in that high office.
The controversy though that you and I had entered that Paris day in 1973 about scientific economics as applied to India, must be renewed afresh!
This is because of your categorical statement on June 9 2009 to the new 15th Lok Sabha:
“I am convinced, since our savings rate is as high as 35%, given the collective will, if all of us work together, we can achieve a growth-rate of 8%-9%, even if the world economy does not do well.” (Statement of Dr Manmohan Singh to the Lok Sabha, June 9 2009)
I am afraid there may be multiple reasons why such a statement is gravely and incorrigibly in error within scientific economics. From your high office as Prime Minister in a second term, faced perhaps with no significant opposition from either within or without your party, it is possible the effects of such an error may spell macroeconomic catastrophe for India.
As it happens, the British Labour Party politician Dr Meghnad Desai made an analogous statement to yours about India when he claimed in 2006 that China
“now has 10.4% growth on a 44 % savings rate… ”
Indeed the idea that China and India have had extremely high economic growth-rates based on purportedly astronomical savings rates has become a commonplace in recent years, repeated endlessly in international and domestic policy circles though perhaps without adequate basis.
1. Germany & Japan
What, at the outset, is supposed to be measured when we speak of “growth”? Indian businessmen and their media friends seem to think “growth” refers to something like nominal earnings before tax for the organised corporate sector, or any unspecified number that can be sold to visiting foreigners to induce them to park their funds in India: “You will get a 10% return if you invest in India” to which the visitor says “Oh that must mean India has 10% growth going on”. Of such nonsense are expensive international conferences in Davos and Delhi often made.
You will doubtless agree the economist at least must define economic growth properly and with care — what is referred to must be annual growth of per capita inflation-adjusted Gross Domestic Product. (Per capita National Income or Net National Product would be even better if available).
West Germany and Japan had the highest annual per capita real GDP growth-rates in the world economy starting from devastated post-World War II initial conditions. What were their measured rates?
West Germany: 6.6% in 1950-1960, falling to 3.5% by 1960-1970 falling to 2.4% by 1970-1978.
Japan: 6.8 % in 1952-1960 rising to 9.4% in 1960-1970 falling to 3.8 % in 1970-1978.
Thus in recent decadesonly Japan measured a spike in the 1960s of more than 9% annual growth of real per capita GDP. Now India and China are said to be achieving 8%-10 % and more year after year routinely!
Perhaps we are observing an incredible phenomenon of world economic history. Or perhaps it is just something incredible, something false and misleading, like a mirage in the desert.
You may agree that processes of measurement of real income in India both at federal and provincial levels, still remain well short of the world standards described by the UN’s System of National Accounts 1993. The actuality of our real GDP growth may be better than what is being measured or it may be worse than what is being measured – from the point of view of public decision-making we at present simply do not know which it is, and to overly rely on such numbers in national decisions may be unwise. In any event, India’s population is growing at near 2% so even if your Government’s measured number of 8% or 9% is taken at face-value, we have to subtract 2% population growth to get per capita figures.
2. Growth of the aam admi’s consumption-basket
The late Professor Milton Friedman had been an invited adviser in 1955 to the Government of India during the Second Five Year Plan’s formulation. The Government of India suppressed what he had to say and I had to publish it 34 years later in May 1989 during the 1986-1992 perestroika-for-India project that I led at the University of Hawaii in the United States. His November 1955 Memorandum to the Government of India is a chapter in the book Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s that I and WE James created.
At the 1989 project-conference itself, Professor Friedman made the following astute observation about all GNP, GDP etc growth-numbers that speaks for itself:
“I don’t believe the term GNP ought to be used unless it is supplemented by a different statistic: the rate of growth of the average consumption basket consumed by the ordinary individual in the country. I think GNP rates of growth can give very misleading information. For example, you have rapid rates of growth of GNP in the Soviet Union with a declining standard of life for the people. Because GNP includes monuments and includes also other things. I’m not saying that that is the case with India; I’m just saying I would like to see the two figures together.”
You may perhaps agree upon reflection that not only may our national income growth measurements be less robust than we want, it may be better to be measuring something else instead, or as well, as a measure of the economic welfare of India’s people, namely, “the rate of growth of the average consumption basket consumed by the ordinary individual in the country”, i.e., the rate of growth of the average consumption basket consumed by the aam admi.
It would be excellent indeed if you were to instruct your Government’s economists and other spokesmen to do so this as it may be something more reliable as an indicator of our economic realities than all the waffle generated by crude aggregate growth-rates.
3. Logic of your model
Thirdly, the logic needs to be spelled out of the economic model that underlies such statements as yours or Meghnad Desai’s that seek to operationally relate savings rates to aggregate growth rates in India or China. This seems not to have been done publicly in living memory by the Planning Commission or other Government economists. I have had to refer, therefore, to pages 251-253 of my own Cambridge doctoral thesis under Professor Frank Hahn thirty years ago, titled “On liberty and economic growth: preface to a philosophy for India”, where the logic of such models as yours was spelled out briefly as follows:
Let
Kt be capital stock
Yt be national output
It be the level of real investment
St be the level of real savings
By definition
It = K t+1 – Kt
By assumption
Kt = k Yt 0 < k < 1
St = sYt 0 < s <1
In equilibrium ex ante investment equals ex ante savings
It = St
Hence in equilibrium
sYt = K t+1 – Kt
Or
s/k = g
where g is defined to be the rate of growth (Y t+1-Yt)/Yt .
The left hand side then defines the “warranted rate of growth” which must maintain the famous “knife-edge” with the right hand side “natural rate of growth”.
Your June 9 2009 Lok Sabha statement that a 35% rate of savings in India may lead to an 8%-9% rate of economic growth in India, or Meghnad Desai’s statement that a 44% rate of savings in China led to a 10.4% growth there, can only be made meaningful in the context of a logical economic model like the one I have given above.
[In the open-economy version of the model, let Mt be imports, Et be exports, Ft net capital inflows.
Assume
Mt = aIt + bYt 0 < a, b < 1
Et = E for all t
Balance of payments is
Bt = Mt – Et – Ft
In equilibrium It = St + Bt
Or
Ft = (s+b) Yt – (1-a) It – E is a kind of “warranted” level of net capital inflow.]
You may perhaps agree upon reflection that building the entire macroeconomic policy of the Government of India merely upon a piece of economic logic as simplistic as the
s/k = g
equation above, may spell an unacceptable risk to the future economic well-being of our vast population. An alternative procedural direction for macroeconomic policy, with more obviously positive and profound consequences, may have been that which I sought to persuade Rajiv Gandhi about with some success in 1990-1991. Namely, to systematically seek to improve towards normalcy the budgets, financial positions and decision-making capacities of the Union and all state and local governments as well as all public institutions, organisations, entities, and projects in general, with the aim of making our domestic money a genuine hard currency of the world again after seven decades, so that any ordinary resident of India may hold and trade precious metals and foreign exchange at his/her local bank just like all those glamorous privileged NRIs have been permitted to do. Such an alternative path has been described in “The Indian Revolution”, “Against Quackery”, “The Dream Team: A Critique”, “India’s Macroeconomics”, “Indian Inflation”, etc.
4. Gross exaggeration of real savings rate by misreading deposit multiplication
Specifically, I am afraid you may have been misled into thinking India’s real savings rate, s, is as high as 35% just as Meghnad Desai may have misled himself into thinking China’s real savings rate is as high as 44%.
Neither of you may have wanted to make such a claim if you had referred to the fact that over the last 25 years, the average savings rate across all OECD countries has been less than 10%. Economic theory always finds claims of discontinuous behaviour to be questionable. If the average OECD citizen has been trying to save 10% of disposable income at best, it appears prima facie odd that India’s PM claims a savings rate as high as 35% for India or a British politician has claimed a savings rate as high as 44% for China. Something may be wrong in the measurement of the allegedly astronomical savings rates of India and China. The late Professor Nicholas Kaldor himself, after all, suggested it was rich people who saved and poor people who did not for the simple reason the former had something left over to save which the latter did not!
And indeed something is wrong in the measurements. What has happened, I believe, is that there has been a misreading of the vast nominal expansion of bank deposits via deposit-multiplication in the Indian banking system, an expansion that has been caused by explosive deficit finance over the last four or five decades. That vast nominal expansion of bank-deposits has been misread as indicating growth of real savings behaviour instead. I have written and spoken about and shown this quite extensively in the last half dozen years since I first discovered it in the case of India. E.g., in a lecture titled “Can India become an economic superpower or will there be a monetary meltdown?” at Cardiff University’s Institute of Applied Macroeconomics and at London’s Institute of Economic Affairs in April 2005, as well as in May 2005 at a monetary economics seminar invited at the RBI by Dr Narendra Jadav. The same may be true of China though I have looked at it much less.
How I described this phenomenon in a 2007 article in The Statesman is this:
“Savings is indeed normally measured by adding financial and non-financial savings. Financial savings include bank-deposits. But India is not a normal country in this. Nor is China. Both have seen massive exponential growth of bank-deposits in the last few decades. Does this mean Indians and Chinese are saving phenomenally high fractions of their incomes by assiduously putting money away into their shaky nationalized banks? Sadly, it does not. What has happened is government deficit-financing has grown explosively in both countries over decades. In a “fractional reserve” banking system (i.e. a system where your bank does not keep the money you deposited there but lends out almost all of it immediately), government expenditure causes bank-lending, and bank-lending causes bank-deposits to expand. Yes there has been massive expansion of bank-deposits in India but it is a nominal paper phenomenon and does not signify superhuman savings behaviour. Indians keep their assets mostly in metals, land, property, cattle, etc., and as cash, not as bank deposits.”
An article of mine in 2008 in Business Standard put it like this:
“India has followed in peacetime over six decades what the US and Britain followed during war. Our vast growth of bank deposits in recent decades has been mostly a paper (or nominal) phenomenon caused by unlimited deficit finance in a fractional reserve banking system. Policy makers have widely misinterpreted it as indicating a real phenomenon of incredibly high savings behaviour. In an inflationary environment, people save their wealth less as paper deposits than as real assets like land, cattle, buildings, machinery, food stocks, jewellery etc.”
If you asked me “What then is India’s real savings rate?” I have little answer to give except to say I know what it is not – it is not what the Government of India says it is. It is certainly unlikely to be anywhere near the 35% you stated it to be in your June 9 2009 Lok Sabha statement. If the OECD’s real savings rate has been something like 10% out of disposable income, I might accept India’s is, say, 15% at a maximum when properly measured – far from the 35% being claimed. What I believe may have been mismeasured by you and Meghnad Desai and many others as indicating high real savings is actually the nominal or paper expansion of bank-deposits in a fractional reserve banking system induced by runaway government deficit-spending in both India and China over the last several decades.
5. Technological progress and the mainsprings of real economic growth
So much for the g and s variables in the s/k = g equation in your economic model. But the assumed constant k is a big problem too!
During the 1989 perestroika-for-India project-conference, Professor Friedman referred to his 1955 experience in India and said this about the assumption of a constant k:
“I think there was an enormously important point… That was the almost universal acceptance at that time of the view that there was a sort of technologically fixed capital output ratio. That if you wanted to develop, you just had to figure out how much capital you needed, used as a statistical technological capital output ratio, and by God the next day you could immediately tell what output you were going to achieve. That was a large part of the motivation behind some of the measures that were taken then.”
The crucial problem of the sort of growth-model from which your formulation relating savings to growth arises is that, with a constant k, you have necessarily neglected the real source of economic growth, which is technological progress!
I said in the 2007 article referred to above:
“Economic growth in India as elsewhere arises not because of what politicians and bureaucrats do in capital cities, but because of spontaneous technological progress, improved productivity and learning-by-doing on part of the general population. Technological progress is a very general notion, and applies to any and every production activity or commercial transaction that now can be accomplished more easily or using fewer inputs than before.”
In “Growth and Government Delusion” published in The Statesman last year, I described the growth process more fully like this:
“The mainsprings of real growth in the wealth of the individual, and so of the nation, are greater practical learning, increases in capital resources and improvements in technology. Deeper skills and improved dexterity cause output produced with fewer inputs than before, i.e. greater productivity. Adam Smith said there is “invention of a great number of machines which facilitate and abridge labour, and enable one man to do the work of many”. Consider a real life example. A fresh engineering graduate knows dynamometers are needed in testing and performance-certification of diesel engines. He strips open a meter, finds out how it works, asks engine manufacturers what design improvements they want to see, whether they will buy from him if he can make the improvement. He finds out prices and properties of machine tools needed and wages paid currently to skilled labour, calculates expected revenues and costs, and finally tries to persuade a bank of his production plans, promising to repay loans from his returns. Overcoming restrictions of religion or caste, the secular agent is spurred by expectation of future gains to approach various others with offers of contract, and so organize their efforts into one. If all his offers ~ to creditors, labour, suppliers ~ are accepted he is, for the moment, in business. He may not be for long ~ but if he succeeds his actions will have caused an improvement in design of dynamometers and a reduction in the cost of diesel engines, as well as an increase in the economy’s produced means of production (its capital stock) and in the value of contracts made. His creditors are more confident of his ability to repay, his buyers of his product quality, he himself knows more of his workers’ skills, etc. If these people enter a second and then a third and fourth set of contracts, the increase in mutual trust in coming to agreement will quickly decline in relation to the increased output of capital goods. The first source of increasing returns to scale in production, and hence the mainspring of real economic growth, arises from the successful completion of exchange. Transforming inputs into outputs necessarily takes time, and it is for that time the innovator or entrepreneur or “capitalist” or “adventurer” must persuade his creditors to trust him, whether bankers who have lent him capital or workers who have lent him labour. The essence of the enterprise (or “firm”) he tries to get underway consists of no more than the set of contracts he has entered into with the various others, his position being unique because he is the only one to know who all the others happen to be at the same time. In terms introduced by Professor Frank Hahn, the entrepreneur transforms himself from being “anonymous” to being “named” in the eyes of others, while also finding out qualities attaching to the names of those encountered in commerce. Profits earned are partly a measure of the entrepreneur’s success in this simultaneous process of discovery and advertisement. Another potential entrepreneur, fresh from engineering college, may soon pursue the pioneer’s success and start displacing his product in the market ~ eventually chasers become pioneers and then get chased themselves, and a process of dynamic competition would be underway. As it unfolds, anonymous and obscure graduates from engineering colleges become by dint of their efforts and a little luck, named and reputable firms and perhaps founders of industrial families. Multiply this simple story many times, with a few million different entrepreneurs and hundreds of thousands of different goods and services, and we shall be witnessing India’s actual Industrial Revolution, not the fake promise of it from self-seeking politicians and bureaucrats.”
Technological progress in a myriad of ways and discovery of new resources are important factors contributing to India’s growth today. But while India’s “real” economy does well, the “nominal” paper-money economy controlled by Government does not. Continuous deficit financing for half a century has led to exponential growth of public debt and broad money, and, as noted, the vast growth of nominal bank-deposits has been misinterpreted as indicating unusually high real savings behaviour when it in fact may just signal vast amounts of government debt being held by our nationalised banks. These bank assets may be liquid domestically but are illiquid internationally since our government debt is not held by domestic households as voluntary savings nor has it been a liquid asset held worldwide in foreign portfolios.
What politicians of all parties, especially your own and the BJP and CPI-M since they are the three largest, have been presiding over is exponential growth of our paper money supply, which has even reached 22% per annum. Parliament and the Government should be taking honest responsibility for this because it may certainly portend double-digit inflation (i.e., decline in the value of paper-money) perhaps as high as 14%-15% per annum, something that is certain to affect the aam admi’s economic welfare adversely.
6. Selling Government assets to Big Business is a bad idea in a potentially hyperinflationary economy
Respected PradhanMantriji, the record would show that I, and really I alone, 25 years ago, may have been the first among Indian economists to advocate the privatisation of the public sector. (Viz, “Silver Jubilee of Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India”.) In spite of this, I have to say clearly now that in present circumstances of a potentially hyperinflationary economy created by your Government and its predecessors, I believe your Government’s present plans to sell Government assets may be an exceptionally unwise and imprudent idea. The reasoning is very simple from within monetary economics.
Government every year has produced paper rupees and bank deposits in practically unlimited amounts to pay for its practically unlimited deficit financing, and it has behaved thus over decades. Such has been the nature of the macroeconomic process that all Indian political parties have been part of, whether they are aware of it or not.
Indian Big Business has an acute sense of this long-term nominal/paper expansion of India’s economy, and acts towards converting wherever possible its own hoards of paper rupees and rupee-denominated assets into more valuable portfolios for itself of real or durable assets, most conspicuously including hard-currency denominated assets, farm-land and urban real-estate, and, now, the physical assets of the Indian public sector. Such a path of trying to transform local domestic paper assets – produced unlimitedly by Government monetary and fiscal policy and naturally destined to depreciate — into real durable assets, is a privately rational course of action to follow in an inflationary economy. It is not rocket-science to realise the long-term path of rupee-denominated assets is downwards in comparison to the hard-currencies of the world – just compare our money supply growth and inflation rates with those of the rest of the world.
The Statesman of November 16 2006 had a lead editorial titled Government’s land-fraud: Cheating peasants in a hyperinflation-prone economy which said:
“There is something fundamentally dishonourable about the way the Centre, the state of West Bengal and other state governments are treating the issue of expropriating peasants, farm-workers, petty shop-keepers etc of their small plots of land in the interests of promoters, industrialists and other businessmen. Singur may be but one example of a phenomenon being seen all over the country: Hyderabad, Karnataka, Kerala, Haryana, everywhere. So-called “Special Economic Zones” will merely exacerbate the problem many times over. India and its governments do not belong only to business and industrial lobbies, and what is good for private industrialists may or may not be good for India’s people as a whole. Economic development does not necessarily come to be defined by a few factories or high-rise housing complexes being built here or there on land that has been taken over by the Government, paying paper-money compensation to existing stakeholders, and then resold to promoters or industrialists backed by powerful political interest-groups on a promise that a few thousand new jobs will be created. One fundamental problem has to do with inadequate systems of land-description and definition, implementation and recording of property rights. An equally fundamental problem has to do with fair valuation of land owned by peasants etc. in terms of an inconvertible paper-money. Every serious economist knows that “land” is defined as that specific factor of production and real asset whose supply is fixed and does not increase in response to its price. Every serious economist also knows that paper-money is that nominal asset whose price can be made to catastrophically decline by a massive increase in its supply, i.e. by Government printing more of the paper it holds a monopoly to print. For Government to compensate people with paper-money it prints itself by valuing their land on the basis of an average of the price of the last few years, is for Government to cheat them of the fair present-value of the land. That present-value of land must be calculated in the way the present-value of any asset comes to be calculated, namely, by summing the likely discounted cash-flows of future values. And those future values should account for the likelihood of a massive future inflation causing decline in the value of paper-money in view of the fact we in India have a domestic public debt of some Rs. 30 trillion (Rs. 30 lakh crore) and counting, and money supply growth rates averaging 16-17% per annum. In fact, a responsible Government would, given the inconvertible nature of the rupee, have used foreign exchange or gold as the unit of account in calculating future-values of the land. India’s peasants are probably being cheated by their Government of real assets whose value is expected to rise, receiving nominal paper assets in compensation whose value is expected to fall.”
Shortly afterwards the Hon’ble MP for Kolkata Dakshin, Km Mamata Banerjee, started her protest fast, riveting the nation’s attention in the winter of 2006-2007. What goes for government buying land on behalf of its businessman friends also goes, mutatis mutandis, for the public sector’s real assets being bought up by the private sector using domestic paper money in a potentially hyperinflationary economy. If your new Government wishes to see real assets of the public sector being sold for paper money, let it seek to value these assets not in inconvertible rupees that Government itself has been producing in unlimited quantities but perhaps in forex or gold-units instead!
In the 2004-2005 volume Margaret Thatcher’s Revolution: How it Happened and What it Meant, edited by myself and Professor John Clarke, there is a chapter by Professor Patrick Minford on Margaret Thatcher’s fiscal and monetary policy (macroeconomics) that was placed ahead of the chapter by Professor Martin Ricketts on Margaret Thatcher’s privatisation (microeconomics). India’s fiscal and monetary or macroeconomic problems are far worse today than Britain’s were when Margaret Thatcher came to power. We need to get our macroeconomic problems sorted before we attempt the microeconomic privatisation of public assets.
It is wonderful that your young party colleague, the Hon’ble MP from Amethi, Shri Rahul Gandhi, has declined to join the present Government and instead wishes to reflect further on the “common man” and “common woman” about whom I had described his late father talking to me on September 18 1990. Certainly the aam admi is not someone to be found among India’s lobbyists of organised Big Business or organised Big Labour who have tended to control government agendas from the big cities.
With my warmest personal regards and respect, I remain,
Cordially yours
Subroto Roy, PhD (Cantab.), BScEcon (London)
see also https://independentindian.com/thoughts-words-deeds-my-work-1973-2010/rajiv-gandhi-and-the-origins-of-indias-1991-economic-reform/did-jagdish-bhagwati-originate-pioneer-intellectually-father-indias-1991-economic-reform-did-manmohan-singh-or-did-i-through-my-e/
Parliament is supposed to control the Government, not be bullied or intimidated by it: Will Rahul Gandhi be able to lead the Backbenches in the 15th Lok Sabha?
June 1, 2009 — drsubrotoroyAny Lok Sabha MP who neither sits with the Opposition nor is a sworn-in member of the Government is a Backbench MP of the Government party or its coalition.
Shrimati Sonia Gandhi is the most prominent of such Backbench MPs in the 15th Lok Sabha, just as she was of the 14th Lok Sabha, and has chosen to be in a most peculiar position from the point of view of parliamentary law. As the leader of the largest parliamentary party, she could have been not merely a member of the Government but its Prime Minister. She has in fact had a decisive role in determining the composition of the Manmohan Government as well as its policies. She in fact sits on the Frontbenches in the Lok Sabha along with the Manmohan Government. But she is not a member of the Government and is, formally speaking, a Backbench MP who is choosing to sit in the Frontbenches.
(Dr Manmohan Singh himself, not being a member of the Lok Sabha, may, formally speaking, sit or speak from among the Frontbenches of his own Government only by invitation of the Lok Sabha Speaker as a courtesy – such would have been the cardinal reason why Alec Douglas-Home resigned from being Lord Home and instead stood for a House of Commons seat when he was appointed British Prime Minister.)
Sonia Gandhi’s son, Mr Rahul Gandhi, is also a Backbench MP. From all accounts, including that of Dr Singh himself, he could have been a member of Dr Singh’s Government but has specifically chosen not to be. He has appeared to have had some much lesser role than Sonia Gandhi in determining the composition of the Government and its policies but he is not a member of it. He is, formally speaking, a Backbench MP, indeed the most prominent to actually sit in the Backbenches, as he had done in the 14th Lok Sabha, which, it is to be hoped, he does in the 15th Lok Sabha too.
Now Rahul Gandhi, Sonia Gandhi and their 541 other fellow 15th Lok Sabha MPs were declared winners by May 16 2009 having won the Indian people’s vote.
(Incidentally, I predicted the outcome here two hours before polls closed on May 13 – how I did so is simply by having done the necessary work of determining that some 103 million people had voted for Congress in 2004 against some 86 million for the BJP; in my assessment Congress had done more than enough by way of political rhetoric and political reality to maintain if not extend that difference in 2009, i.e., the BJP had not done nearly enough to even begin to get enough of a net drift in its favour. I expect when the data are out it shall be seen that the margin of the raw vote between them has been much enlarged from 2004.)
As I have pointed out here over the last fortnight, there was no legal or logical reason why the whole 15th Lok Sabha could not have been sworn in latest by May 18 2009.
Instead, Dr Manmohan Singh on May 18 held a purported “Cabinet” meeting of the defunct 14th Lok Sabha – an institution that had been automatically dissolved when Elections had been first announced! The Government then went about forming itself over two weeks despite the 15th Lok Sabha, on whose confidence it depended for its political legitimacy, not having been allowed to meet. Everyone – the Congress Party’s Supreme Court advocates, the Lok Sabha Secretariat, the Election Commission, Rashtrapati Bhavan too – seems to have gotten it awfully wrong by placing the cart before the horse.
In our system it is Parliament that is sovereign, not the Executive Government. In fact the Executive is accountable to Parliament, specifically the Lok Sabha, and is supposed to be guided by it as well as hold its confidence at all times.
What has happened instead this time is that Government ministers have been busy taking oaths and entering their offices and making policy-decisons days before they have taken their oaths and their seats as Lok Sabha MPs! The Government has thus started off by diminishing Parliament’s sovereignty and this should not be allowed to happen again.
(Of course why it took place is because of the peculiarity of the victory relative to our experience in recent decades – nobody could remember parliamentary traditions from Nehru’s time in the 1950s. Even so, someone, e.g. the former Speaker, should have known and insisted upon explaining the relevant aspect of parliamentary law and hence avoided this breach.)
A central question now is whether a Government which has such a large majority, and which is led by someone in and has numerous ministers from the Rajya Sabha, is going to be adequately controlled and feel itself accountable to the Lok Sabha.
Neither of the Lok Sabha’s most prominent Backbenchers, Sonia Gandhi and Rahul Gandhi, have thus far distinguished themselves as Parliamentarians on the floor of the Lok Sabha. In the 14th Lok Sabha, Sonia Gandhi, sitting in the Frontbenches, exercised the enormous control that she did over the Government not on the floor of the House itself but from outside it.
It would be best of all if she chose in the 15th Lok Sabha to actually physically sit in the Congress’s Backbenches because that would ensure best that the Government Party’s ministers in the Frontbenches will keep having to seek to be accountable to the Backbenches!
But this seems unlikely to happen in view of the fact she herself seems to have personally influenced the choice of a Speaker for the 15th Lok Sabha and it may be instead expected that she continues to sit on the Frontbenches with the Government without being a member of it.
That leaves Rahul Gandhi. If he too comes to be persuaded by the sycophants to sit on the Frontbenches with the Government, that will not be a healthy sign.
On the other hand, if he continues to sit on the Backbenches, he may be able to have a salubrious influence on the 15th Lok Sabha fulfilling its responsibility of seeking to seriously control and hold accountable the Executive Government, and not be bullied or intimidated by it. His paternal grandfather, Feroze Gandhi, after all, may have been India’s most eminent and effective Backbench MP yet.
Subroto Roy, Kolkata
How to Design a Better Cabinet for the Government of India
May 29, 2009 — drsubrotoroyCabinet Government has become far too unwieldy and impractical in India, and the new Cabinet chosen by Sonia Gandhi and Manmohan Singh over almost a fortnight — of some 79 Ministers, almost certainly the largest number in the world — may be destined to be so as well. If there is going to be “fiscal prudence” as the PM and Finance Minister have declared, it really needs to start at the top with the Union Government itself. Remember we also have more than two dozen State Governments plus Union Territories and myriad local governments too.
Here then is an example of a better-designed Cabinet for the Government of India with Cabinet Ministers in bold-face, others not so:
Prime Minister
– Parliamentary Affairs
– Intra-Government Liaison
Defence War/Forces (Raksha, Yudh/Fauj)
– Army
– Navy & Coast Guard
– Air Force & Strategic Forces
– Ordnance
Finance
– Money & Banking
– Accountant General
– Planning
Home Affairs
– Law & Justice
– Internal Security
– Disaster Management & Civil Defence
– Archaeology, Art & Culture
Foreign
– Commerce & Tourism
– Overseas Indians
– International Organisations
Transport
– Railways
– Roads & Highways
– Shipping & Waterways
– Civil Aviation
– Urban Development
Agriculture & Food
– Rural Development
– Water, Flood Control & Irrigation
– Environment
– Forestry & Tribal Affairs
Industry
– Competition and Monopoly-Control
– Steel
– Textiles
– Power
– Petroleum and Energy
– Chemicals & Fertilizers
– Coal and Mines
– Communications and IT
Education
– Schools
– Higher Education
– Vocational Education
– Sports
– Science and Technology
Labour & Employment
Health and Human Services
– Housing
– Women and Child Development
– Social Security
There are just eleven Cabinet Ministers (in bold-face above) including the PM, so, along with the Cabinet Secretary, they could sit with ease around a normal table which should help the process of deliberation.
This document has arisen out of one during my work as an adviser to Rajiv Gandhi in his last months in 1990-1991 though the latter never reached him; I had intended to talk to him about its contents but it was not to be.
It may be profitably read alongside my “Distribution of Government Expenditure in India”, which is part of my ongoing research and was released in the public interest last year.
Subroto Roy, Kolkata
Why does India not have a Parliament ten days after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected? Nehru and Rajiv would both have been appalled (2009)
May 27, 2009 — drsubrotoroysee too
Why has the Sonia Congress done something that the Congress under Nehru-Indira-Rajiv would not have done, namely, exaggerate the power of the Rajya Sabha and diminish the power of the Lok Sabha?
There are at least three Supreme Court lawyers, all highly voluble, among the higher echelons of Congress Party politicians; it is surprising that not one of them has been able to get the top Party leadership of Sonia Gandhi and Manmohan Singh to see the apparent breach of normal constitutional law in Parliament not having met more than 10 days after it was elected.
A Government has been formed, Ministers have entered their offices and have been holding press-conferences and taking executive decisions, wannabe-Ministers continue to be wrangling night-and-day for the plums of office — BUT THERE IS NO PARLIAMENT!
Today is the death-anniversary of Jawaharlal Nehru and last week was the death anniversary of Rajiv Gandhi.
Nehru, whatever his faults and infirmities, was an outstanding parliamentarian and a believer in the Westminster model in particular. He was intimately familiar with its unpoken customs and unwritten laws. He would have been completely appalled by the situation today where luminaries of the party that goes by the same name as the one he had led are paying obeisance to his memory 45 years after his death but have failed to see the absurdity in having a Government in office with no new Parliament ten days after a month-long General Election was over! (Incidentally, had he not left explicit instructions against any hero-worship taking place of himself too?)
Rajiv knew his grandfather and had acquired a sense of noblesse oblige from him. He too would have been appalled that the procedural business of government had been simply procrastinated over like this.
It surprises me that Dr Manmohan Singh, having been a post-graduate of Cambridge, having earned a doctorate from Oxford, and more recently having been awarded honorary doctorates from both Ancient Universities, should seem so unaware of the elements of the Westminster model of constitutional jurisprudence which guides our polity too.
It is too late now and the mistakes have been made. I hope his new Government will come to realise at some point and then keep in mind that our Executive receives political legitimacy from Parliament, not vice versa. An Executive can hardly be legitimately in office until the Parliament that is supposed to elect it has been sworn in.
As for our putative Opposition in the Parliament-yet-to-meet, it seems to have drawn a blank too, and eo ipso revealed its own constitutional backwardness and lethargy.
Subroto Roy
Parliament’s sovereignty has been diminished by the Executive: A record for future generations to know (2009)
May 25, 2009 — drsubrotoroySad to say, Parliament’s sovereignty has been diminished, indeed usurped, by the new Executive Government.
Here is a brief record for future generations to know.
India’s people completed their voting in the 15th General Elections on Wednesday May 13 2009.
The results of how they had spoken, what was their will, were known and declared by Saturday May 16 2009.
There was no legal or logical reason why the 543 members of the 15th Lok Sabha could not have been sworn in as new MPs by the close-of-business on Monday May 18 at the latest.
On Tuesday May 19 the 15th Lok Sabha could have and should have met to elect itself a pro tem or even a permanent Speaker.
The Speaker would have divided the new House into its Government Party and its Opposition.
There would have been a vote of confidence on the floor of the House, which in the circumstances would have been in favour of the Government Party.
Observing this to have taken place, the Hon’ble President of India as the Head of State would have sent for the leader of the Government Party and invited her to form the new Government.
In this particular case, the leader of the largest political party, namely Sonia Gandhi, would have been accompanied perhaps by the Leader of the Lok Sabha, Pranab Mukherjee, as well as her personal nominee for the position of PM, namely, Manmohan Singh.
Sonia Gandhi would have respectfully declined the invitation of the President to be the new Prime Minister, and she would have also explained that she wanted Manmohan Singh to have the position instead.
The President would have said “Very well, Dr Singh, can you please form the Government?”
He would have said, “Yes Madame President it shall be a privilege and an honour to do so”.
The President would have added, “Thank you, and I notice you are not a member of the Lok Sabha at the moment but I am sure you are taking steps towards becoming one.”
End of visit.
Manmohan Singh would have been sworn in as PM and would have gone about adding Ministers at a measured pace. Later, he would have resigned his Rajya Sabha seat and sought election to the Lok Sabha on the parliamentary precedent set by Alec Douglas-Home.
What has happened instead?
On May 18 2009, instead of 543 members of the 15th Lok Sabha taking their oaths as required by parliamentary law and custom, Dr Singh held a purported “Cabinet” meeting of the 14th Lok Sabha — a long-since dead institution!
Some of the persons attending this meeting as purported “Cabinet ministers” had even lost their seats in the elections decided a few days earlier and so had absolutely zero democratically legitimate status left. All these persons then submitted their purported resignations which Dr Singh carried to the President, stating his Government had resigned. The President then appointed him a caretaker PM and he, along with Sonia Gandhi, then went about “staking claim” to form the next Government — turning up at the President’s again with “letters of support” signed by some 322 persons who were MP-elects but were yet to become MPs formally by not having been sworn in.
The President appeared satisfied the party Sonia Gandhi and Manmohan Singh belonged to would command a majority in prospect in the Lok Sabha and invited him to be PM. Some major public wrangling then took place with at least one of his allies about cabinet berths — and that is the situation as of the present moment except that Dr Singh and several others have been sworn in as the Council of Ministers even though the new 15th Lok Sabha of 543 members has still not convened! It has been all rather sloppy and hardly uplifting.
Parliament is supposed to be sovereign in India.
Not the Executive Government or the largest political party or its leader.
The sovereignty of Parliament required Sonia Gandhi and Dr Singh to have realised
first, that the 14th Lok Sabha stood automatically dissolved when elections were announced;
secondly, that the 15th Lok Sabha could have and should have been sworn in by Monday May 18;
thirdly, that there should have been a vote of confidence in the Lok Sabha immediately which would have gone in favour of the Government Party;
fourthly, that only then should the Executive Government have been sought to be formed;
and of course fifthly, that if that Executive Government was to be led by someone who happened to be a member of the Rajya Sabha and not the Lok Sabha, parliamenary law and custom required him to follow the Douglas-Home precedent of resigning from the former and seeking election to the latter at the earliest opportunity.
Let future generations know that as of today, May 25, the 543 persons whom the people of India voted to constitute the 15th Lok Sabha still remain in limbo without having been sworn in though we already have an Executive Government appointed!
The sovereignty of Parliament, specifically that of the Lok Sabha, has come to be diminished, indeed usurped, by the Executive. It is the Executive that receives its political legitimacy from Parliament, not vice versa. Nehru and his generation knew all this intimately well and would have been appalled at where we in the present have been taking it.
Subroto Roy
May we have reviews & reforms of protocols & practices to be followed at Rashtrapati Bhavan and elsewhere? (2009)
May 23, 2009 — drsubrotoroyThe Hon’ble President of India has invited you to join the Council of Ministers and has invited you to Rashtrapati Bhavan to be sworn in by an oath she shall administer. You are awaiting your name to be called. Your name is called and what do you do? You stand up and do a namaste to the PM and then walk a bit to do another namaste to Sonia Gandhi sitting in the audience opposite the President, and then you move towards the microphone ignoring or turning your back on the President herself and then you suddenly remember where you are and realize it is the President who has invited you and shall be administering your oath so you turn around and do a small namaste to her smiling apologetically for having made her an afterthought, and then you go about taking your oath, and then you perhaps do another namaste or two to the President more deeply because you want to make up for having forgotten her last time and finally you feel so happy and pleased with yourself you do another big namaste to Sonia Gandhi in the audience and finally get back to your seat! Phew!
Such was how several of Dr Singh’s new and senior-most cabinet members behaved yesterday at their swearing-in. Dr Singh himself walked straight to the President and did a very gracious bow to her before taking his oath, though on the way back he may have started the ball rolling by doing an exceptionally glad namaste to Sonia Gandhi sitting in the audience. AK Antony was the first and the most senior on the list who most blatantly ignored the President herself initially and turned his back on her momentarily before correcting himself, though he did not fail to do an initial namaste to Shrimati Gandhi. By contrast, Sharad Pawar may have got the whole thing right by walking straight to the President and doing a proper namaste, followed by his oath fluently spoken in Hindi followed by a small acknowledgment of the audience as a whole before returning to his seat.
But in half a dozen cases it all seemed a little sloppy, and even though the President seemed game and sportsmanlike about it, a discourtesy was noticeable to her high office as Head of State which needs to be apologized for and corrected. After all, these were the senior-most ministers, what might lesser ministers do next week?
In fact, a strong case might exist for a rational review nationwide of all such practices and protocols in Delhi and the State capitals, some of which have become so ossified from ancient times that they look bizarre today. Why do we have to have such an elaborate ceremony at all for a mere swearing in, which gets repeated too in each of the states with the Governors and State Governments? Yes perhaps the Head of State did administer the oath to the PM back in 1947 but it is not really necessary for the Head of State to do so now – it could be, for example, the Chief Justice of India who does so, at least to the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister could then himself/herself administer the oath to everyone else in his/her Cabinet, while someone, even the Cabinet Secretary perhaps, could administer the oath to everyone else. The oath itself is what is important, not so much the status of the person administering it. There need not be any such elaborate ceremony at all in Rashtrapati Bhavan that risks the dignity of the President like this and spends everyone’s time.
(And did anyone else notice the private sector lobbyists and public sector fixers seated in the audience? Precisely what were they doing there? Is this just another New Delhi social occasion for people to put on a show of showing their presence?)
For that matter, why was the National Anthem apparently played twice not by any live or noticeable orchestra or band but as a rather grainy recording? It is all a bit depressing when it should have been uplifting. Imagine instead some splendid soprano or tenor leading the singing of the Anthem in that splendid Hall accompanied by a first-class band.
I have long thought we need a National Commission to review all such matters and much more.
It would need to start with the 15th August Red Fort speech by the PM. 15th August was a date chosen by Mountbatten and its auspiciousness was diminished by all the bloodshed that flowed with it. It has become quite unseemly in recent decades to hear our PMs read out party-slogans or government propaganda statements from behind a bullet-proof barrier there. If I was a perceptive school-child being compelled to wait for hours in front of the Red Fort on a hot and muggy August morning to hear such dreary stuff, I might be justifiably upset, and of course many schoolchildren faint every year from exhaustion at being forced to do such things across the country. My own recommendation would be that August 15 be renamed Martyrs’ Day and be a solemn holiday marked only by a long five-minute nationwide silence, say at noon, in memory of all those who have died for India to be what it is today.
Then there is 26 January, going all the way to the “Beating of the Retreat”. Why on earth do we feel a need in this modern age to have such a display in the capital city once a year? Marching bands and parades and floats and fireworks can be great fun for all citizens but they can be and should be spread year-round all across the country’s many cities and towns, and the occasion need not be made a pompous one only in Delhi once a year (with some pale imitations in the State capitals). Republic Day can be a happy holiday for everyone in January when the weather is splendid around the country, with fireworks and fun for everyone, not merely New Delhi’s already delusional Ruling Class.
Then there is the oh-so-common ceremony all over the country from Parliament downwards of standing before the portrait or statue of someone long dead and throwing flowers at it along with a namaste (or in the case of communists, a clenched-fist Black Panther salute). Have we so lost our secular ethos that we do not realize that, for example, a Muslim or Jewish believer might find throwing flowers and doing namaste to a portrait something awkward to do? Both Ariel Sharon and Pervez Musharraf seemed to feel awkward when we took them to the Mahatma Gandhi memorial and said right, now, this is what we expect you to do, throw flowers and walk around it in this manner… it is not enough for you as a visiting dignitary to merely place a bouquet… ! We need to chill out a bit about all this ritualism.
And so it goes. To their considerable credit, neither Nehru nor Indira or Rajiv stood on ceremony much, and the same seems to apply to Sonia Gandhi and her children. The time may be opportune for all such matters to be reviewed calmly and soberly by a National Commission– in the meantime, the PM needs to send a small apology to the President for any unintended discourtesy from his Council of Ministers that may have occurred yesterday or at least a promise that it will not get repeated.
Subroto Roy, Kolkata
Postscript: Then there is the matter of Presidents, Prime Ministers, Governors, Chief Ministers et al taking salutes from the uniformed armed forces or the paramilitary — if you are not yourself a commissioned officer or have never been one, do not respond to a salute from uniformed men and women by saluting or trying to salute them back yourself. What is required is instead to perhaps stand to attention when they salute you, and perhaps bow your head slightly to acknowledge their salute. Salutes are exchanged only within the uniformed services. We instead have civilian leaders seeming to greatly enjoying trying to return salutes themselves….
Why has the Sonia Congress done something that the Congress under Nehru-Indira-Rajiv would not have done, namely, exaggerate the power of the Rajya Sabha and diminish the power of the Lok Sabha?
May 21, 2009 — drsubrotoroyWe in India did not invent the idea of Parliament, the British did. Even the British did not invent the idea of a “Premier Ministre”, the French did that, though the British came to develop its meaning most. Because these are not our own inventions, when something unusual happens in contemporary India to political entities and offices known as “Parliament”, “Prime Minister” etc, contrast and comparison is inevitable with standards and practices that have prevailed around the world in other parliamentary democracies.
Indeed we in India did not even fully invent the idea of our own Parliament though the national struggle led by the original Indian National Congress caused it to come to be invented. The Lok Sabha is the outcome of a long and distinguished constitutional and political history from the Morley-Minto reforms a century ago to the Montagu-Chelmsford reforms and Government of India Act of 1919 to the Government of India Act of 1935 and the first general elections of British India in 1937 (when Jawaharlal Nehru briefly became PM for the first time) and in due course the 1946 Constituent Assembly. Out of all this emerged the 1950 Constitution of India, drafted by that brilliant jurist BR Ambedkar as well as other sober intelligent well-educated and dedicated men and women of his time, and thence arose our first Lok Sabha following the 1951 General Elections.
About the Lok Sabha’s duties, I said in my March 30 2006 article “Logic of Democracy” in The Statesman
“What are Lok Sabha Members and State MLAs legitimately required to be doing in caring for their constituents? First of all, as a body as a whole, they need to elect the Government, i.e. the Executive Branch, and to hold it accountable in Parliament or Assembly. For example, the Comptroller and Auditor General submits his reports directly to the House, and it is the duty of individual legislators to put these to good use in controlling the Government’s waste, fraud or abuse of public resources. Secondly, MPs and MLAs are obviously supposed to literally represent their individual constituencies in the House, i.e. to bring the Government and the House’s attention to specific problems or contingencies affecting their constituents as a whole, and call for the help, funds and sympathy of the whole community on their behalf. Thirdly, MPs and MLAs are supposed to respond to pleas and petitions of individual constituents, who may need the influence associated with the dignity of their office to get things rightly done. For example, an impoverished orphan lad once needed surgery to remove a brain tumour; a family helping him was promised the free services of a top brain surgeon if a hospital bed and operating theatre could be arranged. It was only by turning to the local MLA that the family were able to get such arrangements made, and the lad had his tumour taken out at a public hospital. MPs and MLAs are supposed to vote for and create public goods and services, and to use their moral suasion to see that existing public services actually do get to reach the public.”
What about the Rajya Sabha? I said in the same article:
“Rajya Sabha Members are a different species altogether. Most if not all State Legislative Councils have been abolished, and sadly the present nature of the Rajya Sabha causes similar doubts to arise about its utility. The very idea of a Rajya Sabha was first mooted in embryo form in an 1888 book A History of the Native States of India, Vol I. Gwalior, whose author also advocated popular constitutions for the “Indian India” of the “Native States” since “where there are no popular constitutions, the personal character of the ruler becomes a most important factor in the government… evils are inherent in every government where autocracy is not tempered by a free constitution.” When Victoria was declared India’s “Empress” in 1877, a “Council of the Empire” was mooted but had remained a non-starter even until the 1887 Jubilee. An “Imperial Council” was now designed of the so-called “Native Princes”, which came to evolve into the “Chamber of Princes” which became the “Council of the States” and the Rajya Sabha. It was patterned mostly on the British and not the American upper house except in being not liable to dissolution, and compelling periodic retirement of a third of members. The American upper house is an equal if not the senior partner of the lower house. Our Rajya Sabha follows the British upper house in being a chamber which is duty-bound to oversee any exuberance in the Lok Sabha but which must ultimately yield to it if there is any dispute. Parliament in India’s democracy effectively means the Lok Sabha — where every member has contested and won a direct vote in his/her constituency. The British upper house used to have an aristocratic hereditary component which Tony Blair’s New Labour Government has now removed, so it has now been becoming more like what the Rajya Sabha was supposed to have been like.”
The Canadian upper house is similar to ours in intent: a place for “sober second thought” intended to curb the “democratic excesses” of the lower house. In the Canadian, British, Australian, Irish and our own cases, the Prime Minister, as the chief executive of the lower house has immense indirect power over the upper house, whether in appointing members or even, in the Australian case, dissolving the entire upper house if he/she wishes.
Now yesterday apparently Shrimati Sonia Gandhi, as the duly elected leader of the largest political party in the 15th Lok Sabha, accompanied by Dr Manmohan Singh, as her party’s choice for the position of Prime Minister, went to see the President of India where the Hon’ble President apparently appointed Dr Singh to be the Prime Minister of India – meaning the Prime Minister of the 15th Lok Sabha, except that Dr Singh is not a member of the Lok Sabha and apparently has had no intent of becoming one.
In 2004 Shrimati Gandhi had declined to accept an invitation to become PM and instead effectively recommended Dr Singh to be PM despite his not being a member of the Lok Sabha nor intending to be so. This exploited a constitutional loophole to the extent that the drafters of our 1950 Constitution happened not to have explicitly stated that the PM must be from the Lok Sabha. But the reason the founders of our democratic polity such as BR Ambedkar and Jawaharlal Nehru did not specify that the PM must be from the Lok Sabha was quite simply that it was a matter of complete obviousness to them and to their entire generation that this must be so — it would have been appalling to them and something beyond their wildest imagination that a later generation, namely our own, would exploit such a loophole and allow a PM to be appointed who is not a member of the Lok Sabha and intends not to be so.
Ambedkar, Nehru and all others of their time knew fully well that the history and intended purpose of the Lok Sabha was completely different from the history and intended purpose of the Rajya Sabha. They knew too fully well that Lord Curzon had been explicitly denied the leadership of Britain’s Tory Party in 1922 because that would have made him a potential PM when he was not prepared to be a member of the House of Commons. That specific precedent culminated a centuries’-old democratic trend of political power flowing from monarchs to lords to commoners, and has governed all parliamentary democracies worldwide ever since — until Dr Singh’s appointment in 2004.
When such an anomalous situation once arose in Britain, Lord Home resigned his membership of the House of Lords to contest a House of Commons seat as Sir Alec Douglas Home so that he could be PM in a manner consistent with parliamentary law.
Dr Singh instead for five years remained PM of India while not being a member of the Lok Sabha. Even if reasons and exigencies of State could have been cited for such an anomalous situation during his first term, there was really no such reason for him not to contest the 2009 General Election if he wished to be the Congress Party’s prime ministerial candidate a second time. Numerous Rajya Sabha members alongside him have contested Lok Sabha seats this time, and several have won.
As of today, Dr Singh is due to be sworn in tomorrow as Prime Minister for a second term while still having no declared intention of resigning from the Rajya Sabha and contesting a Lok Sabha seat instead. What the present-day Congress has done is elect him the leader of the “Congress Parliamentary Party” and claim that it is in such a capacity that he received the invitation to be Prime Minister of India. But surely if the question had been asked to the Congress Party under Nehru or Indira or Rajiv: “Can you foresee a circumstance ever in which the PM of India is not a member of the Lok Sabha?” their answer in each case would have been a categorical and resounding “no”.
So the question does arise why the Congress under Sonia Gandhi has with deliberation allowed such an anomalous situation to develop. Its effect is to completely distort the trends of relative political power between the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. On the one hand, the Lok Sabha’s power is deliberately made to diminish as the chief executive of the Government of India shall not be from the Lok Sabha but from “the other place” despite the Lok Sabha having greater political legitimacy by having been directly elected by India’s people. This sets a precedent that might get repeated in India in the future but which contradicts the worldwide trend in parliamentary democracies over decades and centuries in precisely the opposite direction – of power flowing in the direction of the people not away from them. On the other hand, the fact this anomalous idea has been pioneered by the elected leader of the largest political party in the Lok Sabha while her PM is in the Rajya Sabha causes a member of the lower house to have unexpected control over the upper house when the latter is supposed to be something of an independent check on the former!
It all really seems an unnecessary muddle and a jumbling up of normal constitutional law and parliamentary procedure. The Sonia-Manmohan Government at the outset of its second term should hardly want to be seen by history as having set a poor precedent using brute force. The situation can be corrected with the utmost ease by following the Alec Douglas Home example, with Dr Singh being given a relatively safe seat to contest as soon as possible, if necessary by some newly elected Congress MP resigning and allowing a bye-election to be called.
Subroto Roy
What’s all this business about political parties “staking a claim” to Government? Can there not be more dignified behaviour towards the President of India?
May 20, 2009 — drsubrotoroyPress reports today say “With a comfortable majority in the Lok Sabha, UPA Chairperson Sonia Gandhi and Prime Minister Manmohan Singh will meet President Pratibha Patil to stake claim (sic) to form the new government. This was decided unanimously at a meeting of the leaders of the United Progressive Alliance in which Gandhi was re-elected its Chairperson.” (emphasis added)
“Stake claim”?
“To stake a claim” is to show that you believe something is yours or to declare that something belongs to you.
Is that what Jawaharlal Nehru did with Dr Rajendra Prasad or Dr Radhakrishnan? He went and said something like “Now look here Mr President, I would like to stake my claim to be Prime Minister of India now that this here General Election is over and I won”?
Is anyone else at present submitting any competing “claims” to the President? Of course not. Is the President unaware of the fact the General Elections are now over, or that she has a solemn duty to perform of inviting the leader of the largest political party in the new Lok Sabha to Rashtrapati Bhavan for an important chat? Why does it have to be said that someone has to “stake a claim” to be asked to form the Government when the field is open and there is no sign of any other “claimant”? Besides there has been the rush of political parties shooting off letters to the President declaring their support of Shrimati Gandhi and Dr Singh when they “stake claim” to the Government. What does the President of India do with such letter-carriers when they turn up at her doorstep uninvited? Offer each of them a cup of tea and a smile?
It is all hardly sober or uplifting — in fact, it is all rather undignified.
Perhaps a President of India might someday murmur something to the politicians like “Really, why do we need such talk about “staking claims”; I was going to invite you anyway.”
Starting with Procedural Error: Why has the “Cabinet” of the 14th Lok Sabha been meeting today AFTER the results of the Elections to the 15th Lok Sabha have been declared?!
May 18, 2009 — drsubrotoroyThe 14th Lok Sabha stood automatically dissolved when General Elections to the 15th Lok Sabha were first announced. A fortiori so did its Council of Ministers and its “Cabinet”.
Yet this morning Dr Manmohan Singh has held a purported “Cabinet Meeting” of the 14th Lok Sabha where its “members” (some of whom lost their seats!) purportedly submitted their “resignations” which he will then convey to the President with a request that the 14th Lok Sabha be dissolved!
Nyet!
The 14th Lok Sabha was dissolved and came to end eo ipso with the calling of the General Elections and any Council of Ministers and Cabinet that continued in existence was necessarily of a caretaker nature.
The 15th Lok Sabha has been elected as soon as the Election Commission has certified its final results. There can be no legitimate “Cabinet” of the 14th Lok Sabha subsisting alongside the 15th Lok Sabha even for one logical moment.
It is surprising we must begin perhaps with such a simple procedural error. It suggests there may be more to come. We must be sorry to see the steady corrosion of parliamentary law and custom.
Subroto Roy
Postscript: In the interregnum between the dissolution of the 14th Lok Sabha when General Elections are announced and the actual declaration of the results of the 15th, which has in fact taken a month or more, there is no functioning legislative branch of Government — though I would not disagree that if a national emergency like a war occurred during that period, the President in her wisdom would have a right to recall the 14th Lok Sabha if necessary as a kind of “caretaker” body for the duration of the emergency.
Inviting a new Prime Minister of India to form a Government: Procedure Right and Wrong (updated 2019 since 2009)
May 18, 2009 — drsubrotoroy2019
Better Procedure:
So @LokSabhaSectt @rashtrapatibhvn please follow my timetable for #17thLokSabha: Th 23/5 Results declared Fri 24/5 EC certifies results Sat Sun 25 26/5 Members sworn in Mon 27/5 Speaker pro tem divides House; Prez invites new @PMOIndia to form a Gov’t Tue 28/5 Cabinet appointed
Better Procedure for #17thLokSabha.. Respected @rashtrapatibhvn @VPSecretariat @LokSabhaSectt @PMOIndia 16LS no longer exists as soon as results are certified by @ECISVEEP… Let 543 members of new #17thLokSabha be sworn in immediately one by one; let them elect a Speaker pro tem.
Let the Speaker pro tem divide the House between a putative Government & Opposition… Let @rashtrapatibhvn then invite the leader of the former side to visit him for a chat… @VPSecretariat @LokSabhaSectt @PMOIndia #17thLokSabha better then before please
Gen Chohan: Utopia not possible Prof. We can only dream IMO.
It’s the correct parliamentary logic tho.. Not hard to do… @ECISVEEP @SpokespersonECI informs @LokSabhaSectt of winning candidates; LS informs 543 new members of #17thLokSabha to turn up pronto and be sworn in; elect a Speaker pro tem, divide the House; @rashtrapatibhvn invites
Worse Procedure:
Halla gulla … lists… parades of signatories… you know… Dilliwalla histrionics…
2009:
Better Procedure
The Hon’ble President of India invites the leader of the single largest political party in the 15th Lok Sabha to visit Rashtrapati Bhavan.
The leader does so, bringing with her, her own nominee for the Prime Ministership of India as she herself wishes to decline the invitation to be PM.
The President meets the leader alone and extends the invitation.
The invitation is respectfully declined with the recommendation that the Hon’ble President may perhaps consider instead the name of the person nominated by the leader.
The President agrees and extends the invitation to the latter in the presence of the leader. The latter accepts with thanks.
The President observes that since the PM-elect in this case happens not to be a member of the Lok Sabha, she hopes that he shall soon become one.
The meeting ends.
Worse Procedure
The leader of the single largest political party in the 15th Lok Sabha publicly announces her nominee for the position of Prime Minister.
The Hon’ble President of India comes to learn of this from the newspapers or television and extends an invitation to the latter.
The latter visits Rashtrapati Bhavan, receives and accepts the President’s invitation to form a Government.
Of related interest:
Parliament’s sovereignty has been diminished by the Executive
Memo to the Hon’ble President of India: It is Sonia Gandhi, not Manmohan Singh, who should be invited to our equivalent of the “Kissing Hands” Ceremony
Starting with Procedural Error: Why has the “Cabinet” of the 14th Lok Sabha been meeting today AFTER the results of the Elections to the 15th Lok Sabha have been declared?!
Memo to the Hon’ble President of India (May 16, 2009)
May 16, 2009 — drsubrotoroyH.E. The Hon’ble Shrimati Pratibha Patil
President of India
Your Excellency,
As India is fortunately a Republic and not a Monarchy, we do not have a “Kissing Hands Ceremony” where “the monarch invites the incoming prime minister to form a government and swear allegiance to the throne”.
While we do not have such a ceremony literally, we do have its republican equivalent in the well-established constitutional custom of the President of India after a General Election inviting one person to be Prime Minister and to form the new Government.
It soon shall be your solemn duty to invite such a new Prime Minister of India to form the Government.
Given the results of the 15th General Elections to the Lok Sabha, that invitation may be extended only to the Leader of the winning coalition in the Lok Sabha, who is Shrimati Sonia Gandhi.
The outgoing Prime Minister, Dr Manmohan Singh, not having contested the Lok Sabha election, may not by you be invited to be Prime Minister at this stage.
What happened in 2004 was that Shrimati Sonia Gandhi declined to accept such an invitation and instead effectively appointed Dr Singh to be PM despite his not being a member of the Lok Sabha nor intending to be so.
This exploited a constitutional loophole to the extent that our Constitution did not explicitly state that the PM must be from the Lok Sabha.
What may have been passable as the hurried exploitation of a loophole in 2004 is surely not acceptable in 2009.
Why the founders of our democratic polity such as BR Ambedkar and Jawaharlal Nehru did not specify that the PM must be from the Lok Sabha was quite simply that it was a matter of complete obviousness to them and to their entire generation that this must be so — it would have been appalling to them and something beyond their wildest imagination that a later generation, namely our own, would exploit this loophole and allow a PM to be appointed who is not a member of the Lok Sabha and intends not to be so.
Ambedkar, Nehru and all others of their time knew fully well that Lord Curzon had been explicitly denied the leadership of Britain’s Tory Party in 1922 because that would have made him a potential PM when he was not prepared to be a member of the House of Commons.
That specific precedent (culminating a centuries-old democratic trend of political power flowing from monarchs to lords to commoners) has governed all parliamentary democracies worldwide ever since — until Dr Singh’s appointment in 2004.
In fact, when such an anomalous situation once arose in Britain, Lord Home resigned his membership of the House of Lords to contest a House of Commons seat as Sir Alec Douglas Home so that he could be PM in a manner consistent with parliamentary law.
I believe you are fully within constitutional law and precedent to invite Shrimati Sonia Gandhi to form the new Government of India after the 15th General Elections to the Lok Sabha. If she declines and instead requests again the use of the loophole to appoint Dr Singh as PM, I believe that parliamentary law and precedent requires him to resign from the Rajya Sabha and instead contest a seat in the Lok Sabha.
Respectfully submitted
Subroto Roy, PhD (Cantab.), BScEcon (London)
Citizen and Voter
Postscript: Please see also here “Inviting a new Prime Minister of India to form a Government: Procedure Right and Wrong”.
India’s 2009 General Elections: How drastically will the vote-share of political parties change from 2004?
May 2, 2009 — drsubrotoroyClose to 389 million valid votes were cast in India’s previous General Election in 2004 to the 14th Lok Sabha, according to the Election Commission’s volume STATISTICAL REPORT ON GENERAL ELECTIONS, 2004 TO THE 14th LOK SABHA VOLUME III (DETAILS FOR ASSEMBLY SEGMENTS OF PARLIAMENTARY CONSTITUENCIES).
Unfortunately, the Election Commission, like the Government of India in general, remains extremely uncomfortable with using Excel or any spreadsheets at all, and hence much of the information they provide remains unproductive — reflecting, I am afraid, rather obsolescent technology and organisation and management. From an Excel spreadsheet I have had to create for myself using EC data, my calculations give the following breakdown of the votes received in 2004 by most of the larger political parties:
2004 Lok Sabha Elections
ADMK AllIndiaAnnaDravidaMunnetraKazhagam 8,547,014
AGP AsomGanaParishad 2,069,600
AIFB AllIndiaForwardBloc 1,365,055
AITC AllIndiaTrinamoolCongress 7,863,220
BJD BijuJanataDal 5,082,849
BJP BharatiyaJanataParty 86,181,116
BSP BahujanSamajParty 21,037,968
CPI CommunistPartyofIndia 5,484,111
CPI(ML)(L) CommunistPartyofIndia(Marxist-Leninist)(Liberation) 1,280,240
CPM CommunistPartyofIndia(Marxist) 22,065,283
DMK DravidaMunnetraKazhagam 7,064,393
INC IndianNationalCongress 103,118,475
IND Independents 16,523,857
INLD IndianNationalLokDal 1,918,943
JD(S) JanataDal(Secular) 5,732,296
JD(U) JanataDal(United) 9,129,366
JMM JharkhandMuktiMorcha 1,846,843
MDMK MarumalarchiDravidaMunnetraKazhagam 1,679,870
PMK PattaliMakkalKatchi 2,169,020
NCP NationalistCongressParty 7,019,236
RJD RashtriyaJanataDal 9,384,147
RLD RashtriyaLokDal 2,463,603
RSP RevolutionarySocialistParty 1,689,794
SAD ShiromaniAkaliDal 3,506,681
SHS ShivSena 7,050,432
SP SamajwadiParty 16,822,902
TDP TeluguDesam 11,844,811
TRS TelanganaRashtraSamithi 2,441,405
That accounts for 372,382,530. The precise total of valid votes that I get by tabulating EC data using my spreadsheet is 388,920,557. The EC itself reports in the very same document a total of 388,672,504. The percentage difference is close enough to zero but it should be zero itself; I shall be delighted if my spreadsheet’s total is the incorrect one somehow, even though it uses the EC’s own data; but it does lead me to ask: “Who, if anyone, audits the Election Commission’s numerical calculations and vote tallies? Why is India’s ordinary public not informed about all this and other processes of the Election Commission perfectly transparently as a matter of routine? Is reform necessary of the processes and procedures of the Election Commission itself?”.
(Incidentally, the slight discrepancy in the totals could have arisen perhaps because my spreadsheet does, correctly, include the relatively small number of postal ballots, whereas the EC’s total possibly has not done.)
Raw votes like those described above do not of course translate directly into seats in Parliament but even so they indicate the state of popular political opinion in 2004. By how much will that popular opinion be found to have changed in 2009? How will demographic changes, and the delimitation exercise that has redrawn constituencies, affect the new outcomes? These are the kind of grown-up adult questions to ask yourself if you get bored with the endless pretentious waffle that emerges from our talking-heads on TV etc regarding the ongoing election.
Notice too the 16.5 million people of India who voted in 2004 for Independents! What on earth has made Dr Manmohan Singh recently initiate an absurd debate against them?
Here below as well is the full list of all parties that were in contention in 2004; if you want to know the vote-share any of them received according to my spreadsheet, send in a comment to this post and I shall try to respond. Better still, look up the EC volume mentioned and create your own spreadsheet from its data, and tell me how accurate mine is. (But beware, the spreadsheet will have some 60,000 rows to start with!)
Subroto Roy
List of parties in 2004
AB AkhandBharti
ABCD(A) AkhilBharatiyaCongressDal(Ambedkar)
ABDBM AkhilBharatiyaDeshBhaktMorcha
ABHM AkhilBharatHinduMahasabha
ABHS AkhilBharatiyaSena
ABJS AkhilBharatiyaJanSangh
ABLTASJM AkhilBharatiyaLokTantrikAlp-SankhyakJanMorcha
ABLTP AkhilBharatiyaLoktantraParty
ABRAHP AkhilBharatiyaRashtriyaAzadHindParty
ABRS AkhilBharatiyaRajaryaSabha
AC ArunachalCongress
AD ApnaDal
ADMK AllIndiaAnnaDravidaMunnetraKazhagam
AGP AsomGanaParishad
AIFB AllIndiaForwardBloc
AIMF AllIndiaMinoritiesFront
AIMIM AllIndiaMajlis-E-IttehadulMuslimeen
AITC AllIndiaTrinamoolCongress
AJSU AllJharkhandStudentsUnion
AKMDMP AllKeralaM.G.R.DravidaMunnetraParty
AMB AmraBangalee
ANC AmbedkarNationalCongress
AP AwamiParty
ARP AmbedkaristRepublicanParty
ASDC AutonomousStateDemandCommittee
ASP AmbedkarSamajParty
BBM BharipaBahujanMahasangha
BBP BharatiyaBackwardParty
BED BharatiyaEktaDal
BEP BharatiyaEklavyaParty
BGTD BharatiyaGaonTajDal
BJD BijuJanataDal
BJP BharatiyaJanataParty
BJVP BharatiyaJanvadiParty
BKD BahujanKisanDal
BKLJP BharatKiLokJimmedarParty
BKRP BharatKrantiRakshakParty
BLKD BharatiyaLokKalyanDal
BLP BharatiyaLabourParty
BMP(AI) BharatiyaMuhabbatParty(AllIndia)
BMSM BharatiyaMinoritiesSurakshaMahasangh
BMVP BharatiyaManavataVikasParty
BNP BharatiyaNavshaktiparty
BNRP BharatiyaNagrikParty
BPSGKD BharatiyaPrajatantrikShudhGandhiwadiKrishakDal
BPSP BiharPeople’sParty
BPTP BharatiyaPrajatantraParty
BRP BharatiyaRashtravadiPaksha
BRPP BharatiyaRepublicanPaksha
BSDP BhartiSarvadarshiParishad
BSJM BharatiyaSurajyaManch
BSK BharatiyaSarvkalayanKrantiDal
BSP BahujanSamajParty
BVP BahujanVikasParty
CPI CommunistPartyofIndia
CPI(ML)(L) CommunistPartyofIndia(Marxist-Leninist)(Liberation)
CPM CommunistPartyofIndia(Marxist)
CSP ChhattisgarhiSamajParty
DBP DeshBhaktParty
DBSP DemocraticBharatiyaSamajParty
DMK DravidaMunnetraKazhagam
EKD(UP) EktaKrantiDalU.P.
ES EktaShakti
EU EphraimUnion
FCI FederalCongressofIndia
FPM FederalPartyofManipur
GGP GondvanaGantantraParty
HEAP HinduEktaAndolanParty
HJP HindustanJantaParty
HM HindMorcha
HVP HaryanaVikasParty
IBSP IndianBahujanSamajwadiParty
IFDP IndianFederalDemocraticParty
IJP IndianJusticeParty
INC IndianNationalCongress
IND Independent
INL IndianNationalLeague
INLD IndianNationalLokDal
JCP JanChetnaParty
JD(S) JanataDal(Secular)
JD(U) JanataDal(United)
JDP JharkhandDisomParty
JHP JaiHindParty
JHSP JanhitSamajParty
JJ JebamaniJanata
JKAL JammuAndKashmirAwamiLeague
JKN Jammu&KashmirNationalConference
JKNPP Jammu&KashmirNationalPanthersParty
JKP JharkhandParty
JKP(N) JharkhandParty(Naren)
JKPDP Jammu&KashmirPeoplesDemocraticParty
JKPP JharkhandPeople’sParty
JMM JharkhandMuktiMorcha
JMP JanmangalPaksh
JP JanataParty
JSP JansattaParty
JUM JanaUnnayanMancha
JVP JanataVikasParty
KEC KeralaCongress
KEC(M) KeralaCongress(M)
KKJHS KrantiKariJaiHindSena
KMM KrantikariManuwadiMorcha
KNDP KannadaNaduParty
KSVP KrantikariSamyavadiParty
KVSP KosiVikasParty
LBP LokBhalaiParty
LCP LoktantrikChetnaParty
LJNSP LokJanShaktiParty
LP(S) LabourParty(Secular)
LPI(V) LabourPartyOfIndia(V.V.Prasad)
LPSP LokpriyaSamajParty
LRP LokRajyaParty
LSD LokSewaDal
LSWP LoktantrikSamajwadiParty
MAG MaharashtrawadiGomantak
MB(S)P MoolBharati(S)Party
MBT MajlisBachaoTahreek
MC MominConference
MCO MarxistCo-Ordination
MCPI(S) MarxistCommunistPartyofIndia(S.S.Srivastava)
MDMK MarumalarchiDravidaMunnetraKazhagam
MJM ManavJagritiManch
MNF MizoNationalFront
MNVP ManuvadiParty
MPP ManipurPeople’sParty
MRRC MaharashtraRajivCongress
MRS MudirajRashtriyaSamithi
MUL MuslimLeagueKeralaStateCommittee
NBNP NavbharatNirmanParty
NCP NationalistCongressParty
NLP NationalLoktantrikParty
NMNP NidayaMalik(N)Party
NPF NagalandPeoplesFront
NPF NagalandPeoplesFront
NSP NationalStudentsParty
NSSP NiswarthSewaParty
NSTP NaariShaktiParty
NTRTDP(LP) NTRTeluguDesamParty(LakshmiParvathi)
PBLP PhuleBhartiLokParty
PBRML PaschimBangaRajyaMuslimLeague
PDP PeoplesDemocraticParty
PDS PartyforDemocraticSocialism
PHSP PichhraSamajParty
PMK PattaliMakkalKatchi
PMP ParmarthParty
PMSP PragatisheelManavSamajParty
PP PrajaParty
PPOI PyramidPartyofIndia
PRBP PeoplesRepublicanParty
PRCP PrabuddhaRepublicanParty
PRP PanchayatRajParty
PSJP ParivartanSamajParty
PTSS ProutistSarvaSamajParty
PWPI PeasantsAndWorkersPartyofIndia
RCP RashtravadiCommunistParty
RCPI(R) RevolutionaryCommunistPartyofIndia(RasikBhatt)
RGD RashtriyaGaribDal
RHD RashtriyaHamaraDal
RJAP RashtriyaJanadhikarParty
RJD RashtriyaJanataDal
RJVP RajasthanVikasParty
RKSP RashtriyaKrantikariSamajwadiParty
RLD RashtriyaLokDal
RLD RashtriyaLokDal
RLSM RashtriyaLokSevaMorcha
RPD RashtriyaParivartanDal
RPI RepublicanPartyofIndia
RPI(A) RepublicanPartyofIndia(A)
RPI(D) RepublicanPartyOfIndia(Democratic)
RPI(KH) RepublicanPartyOfIndia(Khobragade)
RSBP RashtriyaSwabhimaanParty
RSD RashtriyaSawarnDal
RSGP RashtriyaGarimaParty
RSKP RashtriyaSakarParty
RSMD RashtriyaSamantaDal
RSNP RashtriyaSamajikNayakPaksha
RSP RevolutionarySocialistParty
RSP RevolutionarySocialistParty
RSPS RashtriyaSamajPaksha
RVNP RashtravadiJanataParty
RVP RashtriyaVikasParty
SAD ShiromaniAkaliDal
SAD(M) ShiromaniAkaliDal(SimranjitSinghMann)
SAP SamataParty
SBS ShikshitBerozgarSena
SBSP SuheldevBhartiyaSamajParty
SDF SikkimDemocraticFront
SDP SocialisticDemocraticParty
SHRP SikkimHimaliRajyaParishad
SHS Shivsena
SHS Shivsena
SHSP ShoshitSamajParty
SJP(R) SamajwadiJanataParty(Rashtriya)
SLAP SocialActionParty
SLP(L) SocialistParty(Lohia)
SMSP SamataSamajParty
SP SamajwadiParty
SP SamajwadiParty
SPI SecularPartyofIndia
SPVD SampurnaVikasDal
SSD ShoshitSamajDal
SSJP SanatanSamajParty
SSP SikkimSangramParishad
SVRP ShivrajyaParty
SVSP SavarnSamajParty
SWD SwarajDal
SWJP SamajwadiJanParishad
TDK TamilDesiyakKatchi
TDP TeluguDesam
TNGP TrinamoolGanaParishad
TRS TelanganaRashtraSamithi
UGDP UnitedGoansDemocraticParty
UKKD UttarakhandKrantiDal
UMFA UnitedMinoritiesFront,Assam
USYP UrsSamyukthaPaksha
VJC VidharbhaJanataCongress
VJP VijetaParty
VP VikasParty
VRP VidharbhaRajyaParty
YGP YuvaGantantraParty
YSP YouthandStudentsParty
Did a full cricket team of Indian bureaucrats follow our PM into 10 Downing Street? Count for yourself!
April 3, 2009 — drsubrotoroyBritish PM Gordon Brown welcomed our PM into his official home at 10 Downing Street — but did he know there would be something like a dozen Indian bureaucrats following Dr Singh in? What did all these people talk about in such a short time? Or did they just sit around creating a receptive audience for the two PMs’ discussion? Perhaps they were planning a cricket match between the Prime Minister’s Offices of the United Kingdom and the Republic of India, and so the teams were getting introduced to one another.
SR
Of a new New Delhi myth and the success of the University of Hawaii 1986-1992 Pakistan project (with 2015 Postscript)
November 15, 2008 — drsubrotoroyA leading Indian commentator says in this morning’s paper (November 15 2008) about Manmohan Singh:
“His formulation on Kashmir (“I have no mandate to change borders, but we can make borders irrelevant”), became the obvious solution once he articulated it.”
Such may be how modern New Delhi’s myths and self-delusions get born — since in fact there is no evidence that Manmohan Singh or any of his acolytes had anything to do with originating the Pakistan-India peace process in recent decades, just as there has not been that Manmohan Singh or any of his acolytes had anything to do with originating the Congress Party’s new economic thinking in 1990-1991.
(Lest I be misunderstood I should add at the outset that I have the highest personal regard for Dr Singh, he has been in decades past a friend of my father’s, he at my father’s request consented to discuss economics with me in Paris in 1973 when I was a callow lad of 18, he himself has not claimed the originality that has been frequently mis-attributed to him by others for whatever reason, etc.)
The origins of the idea about India-Pakistan and J&K expressed by Manmohan Singh’s words are to be found in the last paragraph of the Introduction by the Editors of a book which arose from the University of Hawaii’s 1986-1992 Pakistan project, which read:
“Kashmir… must be demilitarised and unified by both countries sooner or later, and it must be done without force. There has been enough needless bloodshed on the subcontinent… Modern Pakistanis and Indians are free peoples who can voluntarily agree in their own interests to alter the terms set hurriedly by Attlee or Mountbatten in the Indian Independence Act 1947. Nobody but we ourselves keeps us prisoners of superficial definitions of who we are or might be. The subcontinent could evolve its political identity over a period of time on the pattern of Western Europe, with open borders and (common) tariffs to the outside world, with the free movement of people, capital, ideas and culture. Large armed forces could be reduced and transformed in a manner that would enhance the security of each nation. The real and peaceful economic revolution of the masses of the subcontinent would then be able to begin.”
The University of Hawaii’s Pakistan project, involving Pakistani and other scholars, including one Indian, led to the volume Foundations of Pakistan’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s published in Karachi, New Delhi and elsewhere. The book reached Nawaz Sharif and the Islamabad elite, including the most hawkish of Islamabad’s hawks, and Pervez Musharraf’s 2006 proposal on J&K, endorsed warmly by the US State Department, may have grown from that paragraph. The Editors of the book, as economists themselves, decried the waste of resources involved in the Pakistan-India confrontation, saying it had
“greatly impoverished the general budgets of both Pakistan and India. If it has benefited important sections of the political and military elites of both countries, it has done so only at the expense of the general welfare of the masses.”
Such words were impossibly bold in the late 1980s-early 1990s. However, as stated in a special editorial article “What to tell Musharraf” in The Statesman of December 16 2006, they seemed in recent years incomplete and rather naïve even to their author, who was myself, the only Indian in that project and the one who had conceived it. Most significantly, the position in international law in the context of historical facts had been wholly neglected. So had been the manifest nature of the Pakistani state (as it had become prior to the splendid 2008 elections).
The Hawaii project had involved top Pakistani economists, political scientists and other commentators but had deliberately chosen to keep the military and the religious clergy out of its chapters. And it was the military and religious clergy who in fact came to dominate Pakistan’s agenda in the 1990s, at least until the 9/11 attacks in America indirectly altered the political direction of the country.
The peaceful and mundane economic agenda outlined for Pakistan in the Hawaii project has come into its own by way of relevance ever since. A few weeks ago, the first trucks filled with fruit, woolens and many other goods traversed across the “Line of Control” in J&K for the first time in sixty years. The Pakistan project that James and I led at the University of Hawaii in the late 1980s may be now declared a success. Among other things, our book explained to Indians that there does exist a Pakistani point of view and perhaps explained to Pakistanis that there does exist an Indian point of view. That is something that had not existed before our book.
Postscript 18 Nov 2015: I have made clear at Twitter that I find the K.M. Kasuri book promoted and publicized in India by MS Aiyar, S Kulkarni, B Dutt and others in Delhi and Mumbai is mendacious where it is not merely self-serving. Its clear intent is to get India to accept the (false) ISI/Hurriyat narratives about 1947, Kashmir, Bangladesh, terrorism etc. Its purported ideas of demilitarisation and a borderless Kashmir are essentially lifted from my earlier 1980s work in America cited above — which I myself have rejected as naive since the Pakistani aggression in Kargil in 1999. More anon.
How the Liabilities/Assets Ratio of Indian Banks Changed from 84% in 1970 to 108% in 1998: the PurnimaMihir Graph
October 20, 2008 — drsubrotoroyThis graph was created by me in 2002 from Reserve Bank of India data published until 1998.

Although I had been “full professor” at the time for six years at something known as an “Institution of National Importance” in India, I had received not a rupee by way of any research-assistance, and had to be assisted in the creation of this graph by two very elderly lay persons, one aged 87 and another aged 77, who read out over many hours (despite frail eyesight) long columns of RBI data which I then typed into an Excel file.
[My Research Assistants about six years after they’d helped me create the graph from RBI data…so the graph deserves to be dubbed the PurnimaMihir Graph].

The graph came to be published for the first time to accompany my two-part article “Indian Inflation” published in The Statesman April 15-16 2008, and available elsewhere here.
The Prime Minister of India has today spoken in India’s Parliament of how sound India’s banking seems to him compared to that in the rest of the world at present. I trust he has available to him vast amounts of fresh data since 1998 which the many members of his “Dream Team” of government and other establishment economists in Delhi and Mumbai have analysed adequately to justify his confidence. The data in my RBI graph end at 1998 but they do cover all the years of the PM’s own career as India’s top economic bureaucrat up through his tenure as Finance Minister in the Narasimha Rao Government.
As it happens, I do think India’s banks are relatively insulated from the world economy and its present financial crisis but the reason for that insulation has nothing to do with any purportedly better bank governance in India; rather it has to do with the fact the rupee is not a hard convertible currency and therefore there has been a vast and continuing distortion of relative prices (including interest rates and wages) from world prices.
Subroto Roy, 20 October 2008
“Rangarajan Effect”
August 24, 2008 — drsubrotoroyDeath of Solzhenitsyn
August 3, 2008 — drsubrotoroyIn Chapter 6 of my Philosophy of Economics, is to be found a quote from Solzhenitsyn: “(Also Solzhenitsyn: “Fastenko, on the other hand, was the most cheerful person in the cell, even though, in view of his age, he was the only one who could not count on surviving and returning to freedom. Flinging an arm around my shoulders, he would say: To stand up for truth is nothing! For truth you have to sit in jail!”)”.
Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn, along with Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov, were heroes of mine after I had left school in India in December 1971 and reached Paris where my father was with the Embassy. My father had purchased Solzhenitsyn’s books and these I devoured eagerly at our then-home at 14 Rue Eugene Manuel, during breaks from my pre-University education at Haileybury College, across the English Channel. We had been in Odessa before Paris, and in Stockholm before Odessa. In 1969, we had travelled by ship and train from Stockholm via Helsinki to Leningrad, Moscow and Odessa. In December 1967, my father had gotten me to fly to Stockholm through Moscow and stay for a day or two with a colleague of his during my winter holidays from India. Moscow in December 1967 was celebrating the 50th Anniversary of the Bolshevik Revolution — I recall what the city felt and seemed like to me as a 12 year old: foreboding, awesome, intimidating.
Now in 1972-73 in Paris, the works of Solzhenitsyn and the example of Sakharov explained to me that brief boyhood experience of the USSR and a great deal more.
As it happens, the present PM of India, as a friend of my father’s, visited us at 14 Rue Eugene Manuel in the summer of 1973 at my father’s request to advise me about studying economics (I was on my way to the London School of Economics as an undergraduate). He stayed about 40 minutes during his busy schedule as part of an Indian economic delegation. I was 18, he was about 41. We ended up having a tense debate about the merits (as he saw them) and demerits (as I saw them) of the Soviet influence on Indian economic “planning”. He had not expected such controversy from a lad but he was kindly disposed and offered when departing to write a letter of introduction to a well-known Indian professor at the LSE for me to carry, which I did.
The works and example of Solzhenitsyn and Sakharov built my youthful understanding of the USSR at age 17-18. This contributed to my libertarianism at Cambridge University and later in America (until my experience of the American federal judiciary at age 37 or so).
When I mentioned my admiration for Solzhenitsyn’s work to Milton Friedman at a memorable luncheon at his San Francisco home in 1989, he said that they had been neighbours in Vermont though they had not interacted because of Solzhenitsyn’s desire to be reclusive.
Solzhenitsyn and Sakharov symbolised shoots of new life in the swamp that had been Soviet totalitarianism.
Nuksaan-Faida Analysis = Cost-Benefit Analysis in Hindi/Urdu
June 30, 2008 — drsubrotoroyI have published about a half dozen or more articles, mainly in The Statesman‘s Editorial Page, on the India-US Nuclear Deal, e.g. “Imperialism Redux”14 March 2006, “Towards an Energy Policy” 2 April 2006, “India’s Energy Interests” 27-28 August 2006, “Need for Clarity”, 19 August 2007. One of my main complaints has been that the Prime Minister and his acolytes seem to have failed to do a proper cost-benefit analysis of the whole thing. The same currency-risk that made the Dabhol-Enron project instantly unviable is also faced a fortiori in the idea of importing nuclear fuel and reactors. The Finance Minister and Finance Secretary who failed to calculate that currency risk in the former project, and hence caused its failure, have now failed again as PM and Planning Commission chief while advocating the latter project. Is the Indian rupee destined to depreciate in the long run? Of course it is: just look at the long run trends and compare our money supply growth rates and inflation rates with those of the USA or EU. The cost of imported nuclear power in India must be recalculated under different scenarios for the exchange-rate of the Indian rupee including e.g. a 20% depreciation.
It is not as if the Government of India is ignorant of what Cost-Benefit Analysis is supposed to be! For example, look up
“*Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions* * *THE INDIAN ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICES (PROBATIONERS’ FINAL EXAMINATION) REGULATIONS, 1955* * *In pursuance of rule 7 of the Indian Administrative Service (Probation) Rules, 1954, the Central Government, in consultation with the State Governments and the Union Public Service Commission, hereby makes the following regulations, namely* *1. Short title:- These regulations may be called the Indian Administrative Service (Probationers’ Final Examination) Regulations, 1955.* *2. Definition:- 2(1) In these regulations, unless the context otherwise requires,-* *(a) `Academay’ (sic) means Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration;* *(b) [ ];* *(c) `Director’ means the Director of the Academy; and * *(d) `Schedule’ means a Schedule appended to these regulations.* *2(2) All other words and expressions used in these regulations and not defined shall have the meanings respectively assigned to them in the Indian Administrative Service (Probation) Rules, 1954.* *3. Final examination.- 3(1) Every probationer shall, at or about the end of the period of training in the Academy appear at a final examination.* *3(2) The examination shall be conducted by the 4Director in the manner laid down in these regulations….4. PUBLIC ADMINSTRATION AND MANAGEMENT* *Essentials of Administration-Organisational Structure of Governments, Role of Civil Servants, Administrative Ethics and Accountability, Delegation and Decentralisation-District and Local Administration-Personal Administration, Police Administration-Jail Administration Panchayati Raj Administration- CalamityAdministration-Administration of Development and Welfare Programmes- Budget and Role of Audit and general financial principles-Role of District Officer/SDO-Conduct of Elections.* *Management and Organisation* *Behavioural Science Motivation, Leadership, Decision-Making, MBO, Management of Conflicts, Management of Change ,Transactional Analysis, -MIS-O&M & Work study-Pert-CPM, Time Management Methodology of Presentation of a subject-Financial Management Capital Budgeting, Discountal Cash Flow, Ratio Analysis, Project Formulation, Cost benefit Analysis, Project Evaluation Interpretation of Balance Sheets….” (emphasis added)
How come there has been none with the India-US nuclear deal then? I think we need a new more comprehensible term for Cost-Benefit Analysis, and that should be, most simply, its Hindi/Urdu equivalent: “Nuksaan-Faida Analysis”.
What is the estimated Nuksaan?
What is the estimated Faida?
How do they compare? It all becomes so much easier!
Subroto Roy
Leadership vacuum
June 7, 2008 — drsubrotoroyFirst published in The Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, June 7 2008, http://www.thestatesman.net
Leadership vacuum
Time & Tide Wait For No One In Politics: India Trails Pakistan & Nepal!
Subroto Roy
The Karnataka legislative elections, as well as to lesser extent the Bengal panchayat polls, have revealed the vacuum that exists across the leadership of India’s national-level politics today.
To start with the BJP: had India been a normal democratic country on the Western pattern, Mr Arun Jaitley would have rocketed to the top of his party’s leadership by now. Besides being articulate in both Hindi and English and in his fifties (the age-group of most leaders in democratic countries), Mr Jaitley’s political acumen and organisational skills have been acknowledged even by his Congress adversaries after the Karnataka result. He himself has been frank and expansive about his formula for winning in Karnataka, which was simply to focus on real issues, especially state-specific ones, as well as to project a single credible leader. Had the BJP been a normal political party in a normal country, Mr Jaitley would have been given the task of leading it to victory in the next General Election and, assuming he won a Lok Sabha seat, to become its prime ministerial candidate.
Dadagiri
Instead, the BJP chooses to remain backward, backward, backward in the majority of its thought-processes and behaviour-patterns ~ from its kneejerk anti-Muslim psychology via its hyperinflationary macroeconomics and protectionist trade to its embrace of astrology and bovine exclusiveness. The idea of uniting behind someone relatively modern-minded in his politics like Mr Jaitley would be simply unacceptable not merely to people in the party within his own age-cohort (including the present party president) but even more so to those in age-cohorts decades older (including the party’s present prime ministerial candidate).
The opposition of the first group would arise from, in a word, jealousy. The opposition of the second group would arise from, in a word, dadagiri, i.e. the gerontocratic idea that merely because one is older, one is owed respect, authority and the plums of office in precedence over someone who is younger. Jealousy is a universal emotion not something specific to Indian politics, but dadagiri and the lack of meritocracy in our political culture is one reason India remains an abnormal polity in the modern democratic world.
LK Advani, driven by his unfulfilled personal ambition, will likely lead the BJP in the next election and do so with Mr Jaitley’s explicit support; Mr Advani may lead it into defeat or even to a victory in which he, given his age, is not as successful a PM as a Jaitley might have been. Yet our sclerotic political culture is such that neither Mr Advani nor Mr Rajnath Singh will simply stand aside now and hand over the reins to a newer, more competent and progressive leadership.
The same idea of dadagiri pervades what passes for the official “Left” in India as exemplified by the CPI-M. Mr Jyoti Basu has in a recent letter to Harkishen Singh Surjeet reminisced of their times together, and in doing so remarked that he remained the Chief Minister of West Bengal for as many years as he did because the Party had instructed him to do so, and when he handed over power to Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee, he did so with the Party’s agreement.
Those who believe in India’s parliamentary democracy might have thought that what our system requires is for a Chief Minister to hold the confidence of the legislative assembly from the bottom up but clearly that is not so because what a CM or PM seems to need are Party instructions from the top down. When Mr Bhattacharjee was anointed the new CM, the present author had remarked to the then Editor of The Statesman that the transition seemed to take place even without a formal vote of confidence in the Assembly. Does anyone in fact recall the last confidence vote debated and passed in the West Bengal Assembly? Democratic legislatures the world over routinely begin their new sessions with a debate and vote of no confidence being brought by the Opposition against the Government-of-the-day.
Does that happen with us, purportedly the world’s largest democracy? Let aside State legislatures, even our Parliament sees only the rare vote of confidence, and LK Advani specifically as Leader of the Opposition seems to have introduced none. Oppositions that do not wish to properly oppose are of course complicit in a government’s misdeeds.
It is the dadagiri culture shared by the official Communists that has caused the generational handover of power from Mr Basu and Mr Surjeet to the JNU coterie of the Karats and Mr Sitaram Yechuri. The “Left” like the “Right” and everyone else in Indian politics, can only handle cherubic “known” faces at the top ~ genuine grassroots activists like Binayak Sen or Medha Patkar must languish in jail or starve on hunger-strike in seeking to represent the politically and economically powerless in India while the entrenched dadas of Indian politics continue with their dissimulation.
Puppet-masters
In case of the Congress, it is an even deeper aspect of the Indian joint family system than dadagiri that has dominated its political culture, namely, the question who is the karta of the family and, if the karta is or seems too young or naïve or inexperienced, who will act as Regent on the karta’s behalf? Indira Gandhi was successfully guided in international politics for several years by a coterie led by PN Haksar. Rajiv Gandhi was attempted to be guided by several different competing coteries of senior party dadas ~ one of whom first brought up the name of Manmohan Singh in Indian politics on 22 March 1991 in a challenge addressed to the present author on liberalisation plans that Rajiv had authorised.
It is almost true to say that Sonia Gandhi and Rahul Gandhi have been in recent years played by puppet-masters of whose personal interests and intrigues they remain clueless. As has been said before by this author, the most salubrious thing Sonia Gandhi could have done for the Congress Party was to remain steadfast in her decision to stay out of Indian politics, and to have organised a fair, tough intra-party contest among its putative senior leaders based on differences of political and economic ideology.
Instead there is now paralysis in decision-making induced by Sonia Gandhi and Manmohan Singh each mistakenly relying upon the other’s purported economic wisdom and political acumen. This confusion came to be most clearly illustrated in the choice of Head of State last year though that was something politically costless ~ the failures of which Karnataka is the current example may lead the Congress to lose what it, like other Indian parties, loves most of all, namely political power in Lutyens’ Delhi.
Indians should make no mistake: our good neighbours in Pakistan and Nepal (Muslim in Pakistan, Hindu and Buddhist and communist in Nepal) have been through healthy cathartic political experiences in recent months and years of a kind we have not. There continues to remain a dangerous intellectual vacuum around the throne of Delhi.
Assessing Manmohan: The Doctor of Deficit Finance should realise the currency is at stake
April 25, 2008 — drsubrotoroyAssessing Manmohan:
The Doctor of Deficit Finance should realise the currency is at stake
by Subroto Roy
First published in The Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, April 25 2008,
The best thing that may be said of the Manmohan Singh premiership is that when it began in May 2004, it seemed, for a short while, refreshing in comparison to the dysfunctional arrogance and brutality displayed by its predecessor. By the last months of the Vajpayee-Advani Government, there were party appointees who had ended all pretence of purportedly Hindu values and were raking it in shamelessly. The Golden Rule of Democracy is “Throw the rascals out”, which is what Indian democracy upheld as it has done time and again. By 2009, India’s electorate will have the chance to decide whether the incumbent government deserves the same fate.
Lok Sabha
Manmohan Singh was seriously discussed as the Congress’s putative nominee for PM as early as 2001. The idea brewing at the time with the party’s next generation of wannabe leaders (in their 50s and 60s, where Manmohan was near 70) was that they needed to maintain good relations with the Great White Queen and wait out one term of an inevitable Singh premiership before having a shot at the top job themselves.
What is surprising is Dr Singh appeared never to feel it necessary to educate himself privately on how to retool himself for the necessary transformation from being the archetypal bureaucrat he had been in his working career to becoming the national statesman he wished to be after retirement. It is doubtful, for example, if he ever stood in front of a mirror and practised an extempore political speech in Hindi in preparation for the highest executive post in the country, let aside writing a clear-headed, original vision or mission statement of substance as to where he wished to lead it. As Narasimha Rao’s Finance Minister, he could meekly take orders from his PM; it seemed he wished to continue in the same mode even when PM himself.
Jawaharlal Nehru is supposed to have been a hero of Dr Singh’s ~ but Nehru was a thorough parliamentarian, among the finest anywhere, and someone who always respected the Lok Sabha immensely. Dr Singh, after he lost to VK Malhotra for the South Delhi seat in 1999, made not the slightest effort to enter the Lok Sabha again, even when the Akalis indicated they might not oppose him in a Punjab contest. When asked specifically at a large press conference about not entering the Lok Sabha, Dr Singh murmured words to the effect he had better uses of his time ~ a display, if anything, of the misplaced arrogance of many New Delhi academics and intellectuals. Dr Singh may be the first PM in any parliamentary democracy never to have won a seat in the lower house nor felt a need to do so.
Dr Singh’s bureaucratic expertise assisted him well in the first national crisis that came his way, which was the Tsunami of 26 December 2004. There appeared to be an air of efficiency about the Government’s response and he seemed in his element as commander of bureaucratic forces while working with Pranab Mukherjee in enlisting the military. George W. Bush (not a great geographer or historian) was apparently impressed to see on a map that India had naval forces deployed as far as the Andamans.
By 2005 though, Dr Singh’s bureaucratic mindset had its negative impact. Montek Ahluwalia had been his Finance Secretary when he was Finance Minister. Mr Ahluwalia’s spouse had been a main supporter of Dr Singh’s unsuccessful Lok Sabha attempt. During the Vajpayee Government, Mr Ahluwalia remained a Planning Commission Member for several years before moving to Washington. With Dr Singh as PM, Mr Ahluwalia returned from the USA in mid 2004 to become Deputy Chair at the Planning Commission. Simultaneously with his return, the idea that the American nuclear industry would like to sell “six to eight lightwater reactors” to India arose.
That is as much as is presently known in public. Dr Singh and Mr Ahluwalia may in the national interest want to frankly and precisely explain to the Indian people the full story of the sudden origins of this idea. Certainly, none of the lessons of the Dabhol fiasco a decade earlier seemed to have been learnt, and the Maharasthtra Government (and hence the Government of India) ended up paying some $300 million to General Electric and Bechtel Corporation for Dabhol before any nuclear talks with the USA could begin. Nor had any serious cost-benefit analysis been done or discussion taken place comparing nuclear energy with coal, hydro and other sources in the Indian case.
Indian foreign policy became frozen in its focus on nuclear negotiations with the USA, swirling around Dr Singh’s fife-and-drum welcome at the White House and President Bush’s return visit to India. At the same time arose the issue of Paul Volcker’s UN committee mentioning the name of India’s foreign minister. As The Statesman put it, regardless of the latter’s involvement, “the damage to India’s diplomatic reputation in the world” was done and it was inevitable a new foreign minister would be necessary. After dilly-dallying and much 10 Janpath to-and-fro, Dr Singh followed Nehru’s mistake of becoming his own foreign minister. The idea was that this would be temporary but it became almost a year.
Instead of transforming himself towards Indian political statesmanship, Dr Singh advanced other retired bureaucrats’ ambitions on similar career-paths. Foreign policy went out of the MEA’s control and seemingly into the control of the new “National Security Adviser”. Dr Singh, sometimes with MK Narayanan beside him, travelled a large number of countries from Brazil to Finland and Uzbekistan to South Africa and Japan. Dr Singh also found time and willingness to accept honorary degrees from British and Russian universities during these short months.
While Dr Singh seemed thus preoccupied, two of India’s main neighbours underwent massive democratic revolutions (leave aside magnificent Bhutan). Nepal’s people practically stormed their Bastille while Dr Singh and Mr Narayanan visited Germany to discuss BMWs. Pakistan’s democratic forces could hardly believe the cold indifference shown to them by a New Delhi merely following Bush’s support for Pervez Musharraf. While Pakistan and Nepal, and to lesser extent Bangladesh, saw movements towards better governance, Sri Lanka descended towards civil war ~ India’s PM remained obsessed with the magic wand that the nuclear deal was supposed to be.
Inflation
Then suddenly the magic vanished ~ Dr Singh seemed to finally come to a silent private recognition that the economics of the nuclear deal simply did not add up if it meant India importing “six to eight lightwater reactors” on a turnkey basis from the USA or anywhere else. Dr Singh seemed to come out of his self-imposed trance and return a little better to reality. By the time he visited China, although he was as deferential to Hu Jintao in his body language as he had been to Bush and Musharraf and even accepted an indoor guard of honour, he also seemed willing to stand up for India. The Arunachal visit was a reality-check.
Now there is inflation ~ and one year left in the UPA’s term. What the country needs is tough sensible macroeconomics and clean public finance. A pandering profligate budget in February was not a healthy sign. Instructing Mr Ahluwalia to close down the Planning Commission and make it a minor R&D wing of the Finance Ministry would be instead a good step. Instructing the RBI to clean up its bureaucratic wastefulness and prepare itself for institutional independence from the Finance Ministry would be even better. Getting proper financial control over every Union and State government entity spending public money and resources would be most important of all. Such major institutional changes in the policy-making process are what an economist might expect of an economist prime minister who wishes to lead India in the 21st Century. India’s currency is at stake.
(See also: “The Politics of Dr Singh”, May 2006; “Mistaken Macroeconomics”, June 2009, etc.)
Growth & Government Delusion (2008)
February 22, 2008 — drsubrotoroyGrowth & Government Delusion:
Progress Comes From Learning, Enterprise, Exchange, Not The Parasitic State
By Subroto Roy
First published in The Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article,
February 22, 2008
P Chidambaram, Montek Ahluwalia and Manmohan Singh, like their BJP predecessors, delude themselves and the country as a whole when they claim responsibility for phenomenal economic growth taking place. “My goal is to continue to maintain growth but at the same time the government reserves the right to make rapid adjustments depending upon the evolving international situation” is a typical piece of nonsensical waffle.
Honest Finance Ministers in any country cannot take personal responsibility for rates of economic growth nor is any government in the world nimble, well-informed and intelligent enough to respond to exogenous shocks in a timely manner. The UPA and NDA blaming one another for low growth or taking credit for high growth merely reveal the crude mis-education of their pretentious TV economists. There are far too many measurement and data problems as well as lead-and-lag problems for any credibility to attach to what is said.
Per capita real GDP
Indian businessmen and their politician/ bureaucratic friends seem to think “growth” refers to nominal earnings before tax for the corporate sector, or some such number that can be sold to visiting foreigners to induce them to park their money in India: “You will get a 10 per cent return if you invest in India” to which the visitor says “Oh that must mean India has 10 per cent growth going on”. Of such nonsense are expensive Davos and Delhi conferences made.
What is supposed to be measured when we speak of economic growth? It is annual growth of per capita inflation-adjusted Gross Domestic Product (National Income or Net National Product would be better if available). West Germany and Japan had the highest annual per capita real GDP growth-rates in the world starting from devastated post-War initial conditions. What were their rates? West Germany: 6.6 per cent in 1950-1960, falling to 3.5 per cent by 1960-1970, and 2.4 per cent by 1970-1978. Japan: 6.8 per cent in 1952-1960; 9.4 per cent in 1960-1970, 3.8 per cent in 1970-1978. Thus, only Japan in the 1960s measured more than 9 per cent annual growth of real per capita GDP.
Now India and China are said to be achieving 9 per cent plus routinely. Perhaps we are observing an incredible phenomenon of world economic history. Or perhaps we are just being fed something incredible, some humbug. India’s population is growing at 2 per cent so even if the Government’s number of 9 per cent is taken at face-value, we have to subtract 2 per cent population growth to get per capita figures. Typical official fallacies include thinking clever bureaucratic use of astronomically high savings rates causes growth. For example, Meghnad Desai of Britain’s Labour Party says: “China now has 10.4 per cent growth on a 44 per cent savings rate… ” Indian savings have been alleged near 32 per cent. What has been mismeasured as high savings is actually paper expansion of bank-deposits in a fractional reserve banking system induced by runaway government deficit-spending in both countries.
Real economic growth arises from spontaneous technological progress, improved productivity and learning-by-doing of the general population. World economic history suggests growth occurs in spite of, rather than due to, behaviour of an often parasitic State. Technological progress in a myriad of ways and discovery of new resources are important factors contributing to India’s growth today. But while the “real” economy does well, the “nominal” paper-money economy controlled by Government does not.
Continuous deficit financing for half a century has led to exponential growth of public debt and broad money. The vast growth of bank-deposits has been misinterpreted as indicating unusual savings behaviour when it in fact signals vast government debt being held by nationalised banks. What Messrs Chidambaram, Ahluwalia,Manmohan Singh, the BJP et al have been presiding over is annual paper-money supply growth of 22 per cent! That is what they should be taking honest responsibility for because it certainly implies double-digit inflation (i.e. decline in the value of paper-money) perhaps as high as 14 or 15 per cent. If you believe Government numbers that inflationis near 5 per cent you may believe anything.
The mainsprings of real growth in the wealth of the individual, and so of the nation, are greater practical learning, increases in capital resources and improvements in technology. Deeper skills and improved dexterity cause output produced with fewer inputs than before, i.e. greater productivity. Adam Smith said there is “invention of a great number of machines which facilitate and abridge labour, and enable one man to do the work of many”.
Consider a real life example. A fresh engineering graduate knows dynamometers are needed in testing and performance-certification of diesel engines. He strips open a meter, finds out how it works, asks engine manufacturers what design improvements they want to see, whether they will buy from him if he can make the improvement. He finds out prices and properties of machine tools needed and wages paid currently to skilled labour, calculates expected revenues and costs, and finally tries to persuade a bank of his production plans, promising to repay loans from his returns.
Overcoming restrictions of religion or caste, the secular agent is spurred by expectation of future gains to approach various others with offers of contract, and so organize their efforts into one. If all his offers ~ to creditors, labour, suppliers ~ are accepted he is, for the moment, in business. He may not be for long ~ but if he succeeds his actions will have caused an improvement in design of dynamometers and a reduction in the cost of diesel engines, as well as an increase in the economy’s produced means of production (its capital stock) and in the value of contracts made. His creditors are more confident of his ability to repay, his buyers of his product quality, he himself knows more of his workers’ skills, etc. If these people enter a second and then a third and fourth set of contracts, the increase in mutual trust in coming to agreement will quickly decline in relation to the increased output of capital goods. The first source of increasing returns to scale in production, and hence the mainspring of real economic growth, arises from the successful completion of exchange.
Risk and enterprise
Transforming inputs into outputs necessarily takes time, and it is for that time the innovator or entrepreneur or “capitalist” or “adventurer” must persuade his creditors to trust him, whether bankers who have lent him capital or workers who have lent him labour. The essence of the enterprise (or “firm”) he tries to get underway consists of no more than the set of contracts he has entered into with the various others, his position being unique because he is the only one to know who all the others happen to be at the same time. In terms introduced by Professor Frank Hahn, the entrepreneur transforms himself from being “anonymous” to being “named” in the eyes of others, while also finding out qualities attaching to the names of those encountered in commerce.
Profits earned are partly a measure of the entrepreneur’s success in this simultaneous process of discovery and advertisement. Another potential entrepreneur, fresh from engineering college, may soon pursue the pioneer’s success and start displacing his product in the market ~ eventually chasers become pioneers and then get chased themselves, and a process of dynamic competition would be underway. As it unfolds, anonymous and obscure graduates from engineering colleges become by dint of their efforts and a little luck, named and reputable firms and perhaps founders of industrial families. Multiply this simple story many times, with a few million different entrepreneurs and hundreds of thousands of different goods and services, and we shall be witnessing India’s actual Industrial Revolution, not the fake promise of it from self-seeking politicians and bureaucrats.
see also 12 June 2009
A Note on the Indian Policy Process
February 21, 2008 — drsubrotoroyA Note on the Indian Policy Process
Subroto Roy
During the University of Hawaii perestroika-for-India project two decades ago, I had wished to attract Sukhamoy Chakravarty from Delhi. He very kindly met me on July 14 1987 and presented me his last personal signed copy of the famous RBI report his committee had chaired. He said he could not come to Hawaii because of ill health but he strongly recommended I take C. Rangarajan instead because, he said, Dr Rangarajan was the main author of the report. I met Dr Rangarajan in Kolkata at Jadavpur University where he was giving a speech in his role as President of the Indian Economic Society that year. Later in correspondence, he wrote to say he was over-committed but that if I took Amaresh Bagchi instead, he would help co-author Bagchi’s contribution to our project. So I commissioned Amaresh Bagchi, then Director of New Delhi’s National Institute of Public Finance and Policy.
In my next project-related visit to Delhi in December 1988, I met Amaresh Bagchi personally for the first time; he was about to retire or had already done so. He told me he knew my name from the fact the High Commission of India in London had sent the Finance Ministry in Delhi the May 29 1984 lead editorial of The Times of London on my work which had been very critical of Indian economic policy; Bagchi had been at the time in the Finance Ministry, and, as an old sarkari statist, had naturally taken exception to what I had said by way of liberal criticism. He wished to co-write his contribution for our Hawaii project with a young colleague of his; I declined permission for him to do that and told him our understanding was that Dr Rangarajan would be writing with him.
In any case, in May 1989, Amaresh was the first person to reach Honolulu in the team we had put together for the project, arriving early by several days. He was all alone and seemed miserable, so I took him to the supermarket and later invited him to dine with my small family at our home at Punahou Towers, 1621 Dole Street. It pleased him to eat some home-cooked Indian food, and he warmed slightly. He told me he had joined the Government as a bureaucrat in the income tax department and later acquired a doctoral degree in economics, though I did not get a sense that he was familiar with traditional public finance of the sort in Richard Musgrave’s classic textbook. I gifted him a copy of James Buchanan’s lectures that I had put together when Professor Buchanan had visited the University of Hawaii at my invitation in 1988 and which the University had then published with a preface by myself. He remarked he found it terrible that American supermarkets had all this canned pet food when the world was so hungry. Later I invited him to a larger dinner party again at my home before the conference began.
At the conference itself, I placed him next to Milton Friedman, which some said was a master-stroke. There was a long and somewhat heated interchange between him and TN Srinivasan, though not with Milton, as Milton was, as always, invariably polite, patient and clear-headed in argument for the two days that he stayed.
The chapter Amaresh Bagchi wrote for us in the book Foundations of India’s Political Economy, edited by myself and WE James, was useful as practically the only statement until that time on the fiscal-induced monetary weakness of India (that still continues today, indeed may have gotten worse since). It contributed to placing him in the policy-limelight in his post-retirement years. Dr Rangarajan was not a co-author after all but apparently contributed the most important paragraphs on the subject. (We have been trying for almost a year now to get the University of Hawaii to allow free republication of the book on the Internet; the original publisher, now dead, reneged on a promise to produce a paperback edition after there was leftist academic pressure on him in Delhi.)
I gave a copy of our book to Manmohan Singh when I met him and his senior aides in September 1993 in Washington at the Indian Ambassador’s Residence; I was introduced to Dr Singh by the then Ambassador of India SS Ray as the person on whose laptop computer the 1991 economic reform had been designed for Rajiv Gandhi during Rajiv’s last months, a statement accurate enough as has been told elsewhere. (Dr Singh had 20 years earlier kindly visited our then-home in Paris at 14 Rue Eugene Manuel at the invitation of my father who knew him, to advise me about economics just before I headed to the London School of Economics as an 18 year old freshman; but in 1993 both he and I had forgotten that earlier 1973 meeting.)
Today’s newspapers report Amaresh Bagchi’s passing and say that “When (Manmohan) Singh was finance minister in the early 1990s, Bagchi was one of his key advisers on fiscal policy”. Dr Singh has described Bagchi as “one of our most distinguished fiscal policy experts” and said “It is no exaggeration to state that Amaresh has been associated with almost every major fiscal policy reform in the past 30 years”.
I am afraid I disagree with the Prime Minister of India in that I do not see any “major fiscal policy reform” having taken place at all in India, just a lot of unsystematic tinkering here and there. The root cause has been the failure to face or want to comprehend the extremely dismal state of government and public sector accounts throughout the country. Without proper government accounting, there can be neither accountability nor any serious fiscal policy, and hence no serious monetary or macroeconomic policy either.
Anarchy in Bengal
February 10, 2008 — drsubrotoroyAnarchy in Bengal
Intra-Left bandh marks the final unravelling of “Brand Buddha”
First published in The Sunday Statesman, 10 February 2008, Editorial Page Special Article http://www.thestatesman.net
by
SUBROTO ROY
Once upon a time, not very long ago, there was something called “Brand Buddha”. The basic idea was that the CPI-M had quietly reformed itself, passing the baton from old unreconstructed communists like Jyoti Basu and Harkishan Surjeet to a new generation of pragmatists and modernists represented by Prakash Karat’s JNU coterie at the national level and the smartly dressed bhadralok persona of Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee in Kolkata itself.
Big businessmen and their foreign collaborators were no longer the “comprador bourgeoisie” but rather were allies to whom government subsidies and concessions, especially land, would be and should be granted. The “investment climate” and “work culture” under a CPI-M government would be among the best in India. High employment levels would be the hoped-for result, especially employment for those associated positively with the CPI-M and its friends. The usual set of academics, journalists, film and TV actors, dancers, sportsmen, singers, NRIs etc who were directly or indirectly recipients of the largesse of the West Bengal Government helped to contribute to the idea that a viable political brand had been identified and it represented the unique way forward for the State. “You are either with us or against us” has always been the brief philosophy of communist and fascist parties around the world ~ joining up with Brand Buddha meant you were part of the bandwagon of progress, if you did not join up you would be left behind. (No one thought Brand Buddha could be or would come to be actively opposed.)
At the national level, the old Indira Gandhi-Communist alliance was restored by way of a new one led by Sonia Gandhi. Jyoti Basu had frankly described Sonia as “a housewife” but now that the housewife was running the country and needed the Communists’ help in doing so, the opportunity was not to be missed to extract whatever price was possible. The main broker between 10 Janpath and West Bengal’s Communists was Pranab Mukherjee who was most familiar with the old Indira-style of opportunistic Indian politics, and who was given the mandate of appeasing the Communists with whatever they needed while also being the pointman to make a phone call to his friend Buddhadeb to see to it, e.g., that the CPI-M like everyone else enjoyed the American and Indian air force show at Kalaikunda.
The “enemy” (for, after all, every unholy alliance must have an identifiable enemy) was the wicked old BJP. Everyone from Sonia Gandhi via Pranab Mukherjee to Jyoti Basu would voice the fear that if they did not join hands in socialist secularist unity, the BJP Boogeyman was destined to return to power. And of course the BJP did nothing and had little positive in its record to dissipate those fears. It was indeed filled with old men and it had indeed behaved wickedly while in power. From negligence in the Graham Staines murder in Orissa to the pogrom in Gujarat, there was little to suggest the BJP’s leadership had any clear ideas or principles about right and wrong governance. In office from 1998-2004, its macroeconomic record was woeful, mainly because it knew no better than maintain the same economic bureaucrats as its predecessors, and allow its finance and other economic ministers to be wholly manipulated by big business lobbies. Now when those bureaucrats and big business lobbies created, endorsed and marketed Brand Buddha itself, the BJP found it had been successfully finessed and could hardly speak a word in opposition. If the BJP thinks it can win in 2009 by its discredited leaders merely recycling anti-Muslim or anti-Christian formulae as before, it may be in for a surprise and a disappointment.
Brand Buddha reached its pinnacle when Sonia Gandhi’s Prime Minister endorsed it personally at a big business meeting in Kolkata on 12 January 2005. But the contradiction involved in Sonia Gandhi then giving merely a perfunctory speech on behalf of the West Bengal Congress in the 2006 election campaign could not be covered up and did not escape the notice of her local partymen.
Brand Buddha started to unravel when Mamata Banerjee realized that all the CPI-M really had was a brand being marketed, not something based on any new and fresh political and economic reality. Mamata has never accepted Sonia’s right to lead the Congress which is what had led to the Trinamul breaking away ~ at the same time, even when she was allied to the BJP, no one could accuse her of being anti-Muslim or anything but secular in her political identity. Her three-week long fast over Singur blocked Metro Channel and riveted the country’s political attention while TV broadcasts of the police-behaviour at Singur acted as a signal to the people of Nandigram to prepare for the same or worse.
The fact the Nandigram peasants who feared losing their land were mostly Muslim caused the central Sonia-Pranab-Buddhadeb myth to explode that only they stood to protect Muslims from the BJP. Once that myth had exploded, the fact the emperor was naked came to be seen by all. There never had been a viable political or economic product behind the brand that was being so heavily advertised and endorsed. If Buddhadeb and his party had been genuinely confident of possessing a constructive new economic policy for West Bengal, they should have transparently and honestly discussed it in detail and gone to the people to ask for a mandate on it before the 2006 elections.
Or when the issue boiled over and Mamata went on her fast at the end of 2006, Buddhadeb could have dissolved the Assembly and gone for fresh elections asking for a specific mandate from Bengal’s voters. Instead, the Chief Minister or his senior ministers not once found the need or courage to address all of West Bengal’s people on television even though the State came to be rocked by violence, mayhem and tragedy – hardly a climate for investment and new employment.
2007 saw the CPI-M and its New Delhi Congress friends being revealed to be bunglers, who could not cope with things as small as Rizwanur’s love-marriage or Taslima’s writings except with heavy-handed repression. The CPI-M’s own unions had crippled their own Government and the State before with bandhs, but not until the Cooch Behar firings has the anarchy become complete. The Forward Bloc protesters were, after all, merely asking for implementation of Sonia Gandhi’s favourite scheme of rural employment guarantees! Anarchy is the absence of government and when a government is so divided that its members cannot decide if they are the government or the opposition, it has to be said there is an absence of government.
Recovery requires candour which in turn requires honesty and introspection, all of which may be qualities too difficult to find. What Brand Buddha could have and should have been about is this: the CPI-M cutting waste, fraud and abuse of publicly owned resources from all the organs, departments and projects of the West Bengal Government that they have controlled for decades, and drastically improving the productivity of all those receiving State government wages or contracts. Real governance does not require any phony advertising because success advertises itself.
Nixon & Mao vs India: How American foreign policy did a U-turn about Communist China’s India aggression
January 7, 2008 — drsubrotoroyNixon & Mao vs India
How American foreign policy did a U-turn about Communist China’s India aggression. The Government of India should publish its official history of the 1962 war.
by
SUBROTO ROY
First published in The Sunday Statesman, Jan 6 2008, The Statesman Jan 7 2008
Editorial Page Special Article
THE 1972-74 conversations between Richard Nixon and Henry Kissinger on one hand and Mao Zedong, Zhou Enlai and Deng Xiaoping on the other, especially about India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, have been public for a few years now. They make disturbing reading for Indians and Bangladeshis, and for Pakistanis too who may be concerned about the political health of their country. Yahya Khan, Pakistan’s debauched military dictator, made the Nixon-Mao meeting possible and received much praise from Zhou and support from Nixon and Kissinger. Pakistan’s official assessment of Yahya following the 1971 military defeat and secession of Bangladesh was far more candid and truthful, giving the lie to the praise bestowed upon him by Nixon and Zhou in their conversation.
Nixon and Kissinger were decidedly second-rate intellects in political power who believed themselves first-rate ~ a dangerous circumstance. Their policy caused Chiang Kaishek’s Republic of China to be expelled from the UN, its veto-wielding seat taken by Mao’s People’s Republic. The Government of India, under influence of communist sympathisers like Krishna Menon, KM Pannikar, KPS Menon et al, had been pleading the same case at the UN since 1949/1950, rebuffed each time by American veto. Now Nixon and Kissinger yielded to the idea to the delight of Mao-Zhou, and ganged up with Pakistan’s military against democratic India and the new Bangladesh.
Nixon went to Beijing at a time the catastrophic American involvement in Vietnam had reached a peak ~ something that itself was an outcome of the Dulles-Nixon doctrine of a “domino effect” in South East Asia. The Americans failed to comprehend Vietnamese nationalism against France or recognise how that had been historically directed at imperial China. Nixon’s carpet-bombing of Cambodia in needless extension of the Vietnam conflict was to cause the rise to power of Pol Pot and his vicious Khmer Rouge (to remove whom Vietnam attacked, causing China to attack Vietnam in 1979).
Nixon was in Beijing in February 1972 ostensibly to seek Chinese cooperation in ending the Vietnam War, as well as opening an Eastern Front in the Cold War against the USSR. Nixon fancied himself a Metternich-like statesman whose wisdom and brilliance would redesign the international order for a century. What was plain to unsentimental observers was that his underlying purpose was greedy and hardly statesmanlike, namely, winning re-election in November 1972 by outflanking domestic left-wing criticism using photos of having been toasted by Mao himself. That Nixon was no Machiavelli, Metternich or Bismarck but more likely just delusional and paranoid came to be revealed in his subsequent political debacle over Watergate.
The US attitude towards China’s 1959-1962 aggression against India changed drastically because of Nixon’s Beijing visit. Tibet’s people and culture had not been attacked and brutalised by Chiang Kaishek’s Nationalist Army nor by India’s soldiers ~ the Mao-Zhou Communist war machine, fresh from their Korean adventures, did that. There would have been no border conflict between China and India today in 2008 if Communist China had not first invaded and occupied Tibet.
All such fundamental facts used to be perfectly clear to the Americans as to everyone else. India’s Defence Ministry’s excellent official history of the 1962 war acknowledges the vital aid sent by President Kennedy with the help of Ambassador Galbraith. Ten years later, in 1972, Nixon and Kissinger in Beijing changed all that completely and did a U-turn against India using the dubious book of a single journalist as cover for their dissimulation:
“ZHOU: …. Actually the five principles (of peaceful coexistence) were put forward by us, and Nehru agreed. But later on he didn’t implement them. In my previous discussions with Dr Kissinger, I mentioned a book by Neville Maxwell about the Indian war against us, which proves this.
NIXON: I read the book.
KISSINGER: I gave it to the President.
NIXON: I committed a faux pas ~ Dr Kissinger said it was ~ but I knew what I was doing. When Mrs Gandhi was in my office before going back, just before the outbreak of the (1971) war, I referred to that book and said it was a very interesting account of the beginning of the war between India and China. She didn’t react very favourably when I said that. (Zhou laughs)
ZHOU: Yes, but you spoke the truth. It wasn’t faux pas. Actually that event was instigated by Khrushchev. He encouraged them. In looking at 1962, the events actually began in 1959. Why did he go to Camp David? In June of that year, before he went to Camp David, he unilaterally tore up the nuclear agreements between China and the Soviet Union. And after that there were clashes between Chinese and Indian troops in the western part of Sinkiang, the Aksai Chin area. In that part of Sinkiang province there is a high plateau. The Indian-occupied territory was at the foot of the Karakorums, and the disputed territory was on the slope in between.
KISSINGER: It’s what they call Ladakh.
NIXON: They attacked up the mountains.
ZHOU: We fought them and beat them back, with many wounded. But the TASS Agency said that China had committed the aggression against India…..They just don’t want to listen to reason. Anyway, the TASS Agency account had the effect of encouraging India. And also Maxwell mentioned in the book that in 1962 the Indian Government believed what the Russians told them that we, China, would not retaliate against them. Of course we won’t send our troops outside our borders to fight against other people. We didn’t even try to expel Indian troops from the area south of the McMahon Line, which China doesn’t recognize, by force. But if (Indian) troops come up north of the McMahon Line, and come even further into Chinese territory, how is it possible for us to refrain from retaliating? We sent three open telegrams to Nehru asking him to make a public reply, but he refused. He was so discourteous; he wouldn’t even do us the courtesy of replying, so we had no choice but to drive him out. You know all the other events in the book, so I won’t describe them, but India was encouraged by the Soviet Union to attack.
NIXON: I would like to ask the Prime Minister a question with regard to Bangladesh recognition. We have delayed recognition though Britain and other countries have done so.
ZHOU: France has also recognised Bangladesh.
NIXON: Before we make a decision on that, we have tried to find the attitude of (Zulfikar Ali) Bhutto. And Bhutto indicated he does not object to recognition. In fact he could see that we would have some advantage in not leaving the field clear to the Soviet Union in that region. It is our understanding that India is supposed to withdraw all its forces from Bangladesh by the 24th of March. And based on what we have for consideration, we have for consideration the possibility of recognising Bangladesh about that time….”
“ZHOU: …. we truly wish to see (India) truly withdraw their troops in East Pakistan, now called Bangladesh. We wish to see them truly do this and not just with words. Of course they can only do that superficially, because if they get some Bengali forces to remain and join Mujibar Rahman, there would be no way to be sure because the Bengalis all look the same. But that would trouble to the future of India and Mrs Gandhi herself. The Indians said they have no territorial ambitions, but the development of events is that they have remained in their place and refused to withdraw. Once again we can only cite the events of Indian aggression in the 1962 war. At that time our troops pressed to the foothills quite close to Tezpur in Assam, and when they reached that place, Chairman Mao ordered that all troops should turn back. We turned back to the Indians ~ this is in Maxwell’s book ~ and we withdrew all troops back north of the so-called McMahon Line because one must show one can be trusted and must not wait for others to act…. India should withdraw its troops from the areas it is occupying in West Pakistan, and Pakistan should also withdraw from the lesser areas it occupies in India. Bhutto agrees. These two things, at least, the Indian side should abide by. If the US recognises Bangladesh after this situation is brought about, then we believe this would raise the prestige of the US in the United Nations.
After all, what you want is to bring about the withdrawal of all troops from Bangladesh and West Pakistan. Also, you will be able to encourage Mr Bhutto and give him some assistance. That is what they need. You said your actions should be parallel to ours, and we don’t mind that. We said this both to Yahya, the former President, and to the present President. Both of us owe something to Yahya, although he didn’t show much statesmanship in leading his country, for (bridging) the link between our two countries.
NIXON: He is a bridge.
ZHOU: We should not forget and we cannot forget, especially that Dr Kissinger was able through him to come secretly for talks here. And when a man makes a contribution to the world, we should remember him.
KISSINGER: Actually the President sent a message to Bhutto that he should treat Yahya well in retirement and we would not look favourably on any retribution. It was a personal message from Pakistan.
ZHOU: …. At the time of the ceasefire they (the Pakistanis) still had 80,000 troops in East Pakistan. It was not a situation in which they couldn’t keep fighting….. Yahya should have concentrated his troops to win a victory, and once the Indians had suffered a defeat they would have stopped because West Bengal was not very secure either. So at that time even our Vice Foreign Minister still believed they could win the war. Bhutto too…. .
KISSINGER: (Reading from a cable) Mr President, you were speaking of military shipments. We have information that the Soviet Union has shipped since November 150 tanks from Poland and 100 armored personnel carriers from Czechoslovakia. They were shipped in two ships each month in November and December. In January a third ship was to bring military equipment to India.
NIXON: To India?
KISSINGER: To India.
NIXON: The problem is to find some way that West Pakistan can find some military equipment and assistance. On our side, what we will do is to supply substantial amounts of economic assistance to West Pakistan. That would enable West Pakistan to ~ we would think in the interest of its defence ~ to acquire arms from other sources. As a matter of fact, that is the tragedy of our policy in India. We supplied almost 10 billion dollars in assistance to India in the last 20 years ~ very little was military assistance, it was economic ~ and that relieved India so it could purchase very substantial amounts of arms from the Soviet Union, and also manufacture arms. That was not our intent, but that’s what happened. With regard to our aid to India on this point ~ economic assistance ~ we are going to move in a very measured way. I am resisting considerable pressure from the public and the press to rush in and resume economic assistance at former levels. We are going to wait and see what India does with regard to the border problem and our relations generally.
ZHOU: And India actually is a bottomless hole. (Nixon laughs)
NIXON: When the Prime Minister referred to the problem India has with Bangladesh, as I look at India’s brief history, it has had enough trouble trying to digest West Bengal. If now it tries to digest East Bengal it may cause indigestion which could be massive.
ZHOU: That’s bound to be so. It is also a great pity that the daughter (Madame Gandhi) has also taken as her legacy the philosophy of her father embodied in the book Discovery of India (in English). Have you read it?
KISSINGER: He was thinking of a great India empire?
ZHOU: Yes, he was thinking of a great Indian empire ~ Malaysia, Ceylon, etc. He would probably also include our Tibet. When he was writing that book in a British prison, but one reserved for gentlemen in Darjeeling. Nehru told me himself that the prison was in Sikkim, facing the Himalayan mountains. At the time I hadn’t read the book, but my colleague Chen Yi had, and called it to my attention. He said it was precisely the spirit of India which was embodied in the book. Later on when I read it I had the same thought.
NIXON: …. Germany and Japan, received US aid…. why (they) have done so well, it is because they have qualities of drive and are willing to work hard, whereas some other countries we have helped do not have this quality. This brings me to the point: it is not the help that is provided a country that counts, it is whether the people of that country have the will to use this help. If they don’t have that, the money just goes down a rathole. A pretty good example is aid to India. (Zhou laughs)… India is not able to do much with aid because as compared with Japan, it does not have the drive, or the spirit of determination that the Japanese people have…..”
Genocide
Every Bangladeshi knows the causal role Z A Bhutto had in Pakistan’s civil war yet it is upon the word of such a man that Nixon’s recognition of their nation seemed based. The famous “Archer Blood telegram” by the American Consul-General in Dhaka reporting the genocidal Yahya-Tikka assault on East Pakistan starting March 25 1971 meant nothing to Nixon and Kissinger. Benazir retained her charm in Washington’s power circles because she was Bhutto’s daughter. Similarly, as recently as the 1999 Kargil conflict, Bill Clinton flatteringly referred to China for advice on how to deal with India and Pakistan.
Perversely enough, many in New Delhi, Kolkata etc express so much confused love for both China and the United States that they have accepted as their own the biased baseless opinions about India expressed by Nixon, Kissinger and the Communist Chinese. They would do well to read instead the Defence Ministry’s excellently researched historical account of the 1962 war, which the Government of India should not only publish properly at once but have translated into Mandarin as well.
Dr Manmohan Singh has as recently as 29 November 2007 expressed the opinion: “The type of leadership that China has produced since the days of Deng, I think, is the greatest asset that China has”. Dr Singh might have said, but did not, that China’s greatest asset has been in fact the preservation of Confucian values despite decades of communist tyranny and destruction. With such deep misapprehension about post-1949 China on the part of India’s present Head of Government, it may be unlikely that New Delhi or Kolkata acquires a realistic view of our neighbour or of a healthy China-India relationship in the 21st Century.
To Clarity from Confusion on Indo-US Nuclear Deal
August 19, 2007 — drsubrotoroy(Author’s Note September 3 2008: This article “Need for Clarity” published in The Statesman last year was one of several I have published on the subject; see also, for example, “Towards an Energy Policy”, “India’s Energy Interests” , “Against Quackery” all published first in The Statesman in 2006 and 2007; also “India and ‘Energy Security'” which was my lecture to a KAF conference on the subject. It seems quite prescient in that it anticipated by a few months the “secret” letter from the US Executive Branch to the Legislative Branch, released by the Washington Post today . India’s UPA Government has put forward a junior spokesman from the Congress Party to waffle around with a purported explanation. )
Need for Clarity
A poorly drafted treaty driven by business motives is a recipe for international misunderstanding
First published in The Sunday Statesman, August 19 2007, Editorial Page Special Article
by
SUBROTO ROY
Confusion prevails over the Indo-US Nuclear Deal. Businessmen, bureaucrats, politicians, diplomats, scientists and now the public at large have all joined in the cacophony in the last two years.
On Wednesday August 15, America’s foreign ministry made the clearest most unequivocal statement possible as to the official American Government interpretation of the Indo-US nuclear deal: “The proposed 123 agreement has provisions in it that in an event of a nuclear test by India, then all nuclear co-operation is terminated, as well as there is provision for return of all materials, including reprocessed material covered by the agreement” (Sean McCormack). Yet our Prime Minister had told Parliament two days earlier: “The agreement does not in any way affect India’s right to undertake future nuclear tests, if it is necessary”. What is going on? Our politics are in uproar, and it has been suggested in these pages that the country go to a General Election to allow the people to speak on the matter. Clearly, we need some clarity.
Let us start at the beginning. How did it all originate? The private US nuclear industry prevailed upon India’s government bureaucrats and businessmen over several years that nuclear power is the way forward to solving India’s “infrastructure” problems. They would sell us, in words of the Manmohan-Montek Planning Commission’s energy adviser, “six to eight lightwater reactors” (especially as they may not be able to sell these anywhere else). Our usual prominent self-seeking retired bureaucrats started their waffling about the importance of “infrastructure”.
Then Manmohan Singh felt his foreign travels as PM could be hardly complete without a fife-and-drum visit to the White House. But before he could do so, Dabhol would have to be cleared up since American business in India was on a self-moratorium until GE and Bechtel were paid settlements of some $140-160 million each by the Governments of India and Maharashtra. GE’s CEO for India kindly said afterwards “India is an important country to GE’s global growth. We look forward to working with our partners, customers, and State and Central Governments in helping India continue to develop into a leading world economy”.
Also, before Manmohan’s USA trip, the Confederation of Indian Industry registered as an official Washington lobbyist and spent half a million dollars lobbying American politicians for the deal. (“Why?” would be a good question.)
So Dr Singh was able to make his White House visit, accompanied by US business lobbies saying the nuclear deal can generate $100 billion worth of new American business in India’s energy-sector alone. It is only when business has lubricated politics in America that so much agreement about the India-deal could arise. The “bottom-line” is that six to eight reactors must be sold to India, whatever politics and diplomacy it takes.
Now Dr Singh is not a PM who is a Member of the Lower House of Parliament commanding its confidence. He says his Government constitutes the Executive and can sign treaties on India’s behalf. This is unwise. If he signs a treaty and then the Congress Party loses the next General Election, a new Executive Government can use his same words to rescind the same treaty. What is sauce for the goose is sauce for the gander. One reason we are so confused is that India has not signed very many bilateral treaties, and there is barely a noted specialist in international law anywhere in the country. Dr Singh’s original mentor, PN Haksar, had gone about getting a treaty signed with the USSR back in 1971 which tided us over a war, though the USSR itself collapsed before that treaty ended.
Signing a treaty is much more than signing an international MOU. It requires a national consensus or a least a wide and deep understanding on the part of the public and the political class as to what necessitates the treaty. That plainly does not exist at present. Most people in India do not even know how nuclear power is generated, nor how small and insignificant nuclear power has been in India.
Natural uranium is 99.3 per cent of the U-238 isotope and 0.7 per cent the radioactive U-235 isotope. Nuclear power generation requires “enriched uranium” or “yellow cake” to be created in which U-235 has been increased from 0.7 per cent to 4 to 5 percent. (Nuclear bombs require “highly enriched” uranium with more than 90 per cent of U-235.) Yellow cake is broken into small pieces, put in metal rods placed in bundles, which are then bombarded by neutrons causing fission. In a reactor, the energy released turns water into steam, which moves turbines generating electricity. While there is no carbon dioxide “waste” as in burning fossil fuels, the “spent” rods of nuclear fuel and other products constitute grave radioactive waste, almost impossible to dispose of.
India’s 14 “civilian” nuclear reactors presently produce less than 4% of our total power. 70% of our power arises from burning fossil fuels, mainly coal. Much of the rest arises from hydro. We have vast hydroelectric potential in the North and Northeast but it would take a lot of serious political, administrative and civil engineering effort to organise all that, and there would not be any nice visits to Washington or Paris involved for politicians and bureaucrats.
Simple arithmetic says that even if all our principal energy sources stayed constant and only our tiny nuclear power sector grew by 100%, that would still hardly increase by very much our energy output overall. Placing a couple of expensive modern lightwater reactors around Delhi, a couple around Mumbai and a few other metros will, however, butter already buttered bread quite nicely and keep all those lifts and ACs running.
The agreed text of the “treaty” looks, from a legal standpoint, quite sloppily and hurriedly written ~ almost as if each side has cut and paste its own preferred terms in different places with a nod to the other side. For example, there is mention of “WMD” initially which is repeated as “weapons of mass destruction” just a little later. There is solemn mention of the “Government of India” and “Government of the United States of America” as the “Parties”, but this suddenly becomes merely “United States” and “India” in the middle and then reverts again to the formal usage.
Through the sloppiness comes scope for different interpretations. The Americans have said: try not to test, you don’t need to, we don’t test any more, and you have to know that if you do test, this deal is over, in fact it gets reversed. We have said, okay, we won’t test, and if we do test we know it is over with you but that does not mean it is over with others. Given such sloppy diplomacy and treaty-making, the scope for mutual misunderstanding, even war, remains immense long after all the public Indian moneys have found their way into private pockets worldwide. Will a future President Jeb Bush or Chelsea Clinton send F-22 bombers to bomb India’s nuclear facilities because India has carried out a test yet declined to return American equipment? Riding a tiger is not something generally to be recommended.
The answer to our present conundrum must be patience and the fullest transparency. What is the rush? If it is good or bad for us to buy six or eight new American reactors now, it will remain good or bad to do so a year or two from now after everyone has had a thorough think about everything that is involved. What the Manmohan-Montek Planning Commission needed to do first of all was a thorough cost-benefit analysis of India’s energy requirements but such elementary professionalism has been sorely lacking among our economists for decades.
On Indian Nationhood (2007)
May 25, 2007 — drsubrotoroyOn Indian Nationhood
From Tamils To Kashmiris And Assamese And Mizos To Sikhs And Goans
First published in The Statesman, Editorial Page
May 25 2007
By Subroto Roy
In the decades before 1947, imperialist critics of Indian nationalism accused the movement of being less about creating Indian nationhood than about supplanting British rule with local Indian oligarchies. Sydenham, for example, in the upper house of Britain’s Parliament in August 1918, gleefully quoted from the “Madras Dravidian Hindu Association” (forerunners of today’s DMK etc): “We shall fight to the last drop of our blood any attempt to transfer the seat of authority in this country from British hands to so-called high-caste Hindus, who have ill-treated us in the past and will do so again but for the protection of British laws.” Also quoted were “Namasudras of Bengal”, allegedly numbering “ten million men”, protesting “gross misrepresentation” by “so-called high-caste leaders” of the desirability of “Home Rule or self-government”. Besides caste and class there was always religion too by which India’s inhabitants could be classified and divided, and it must have delighted Sydenham to quote the “South Indian Islamic League” saying “Nothing should be done which will weaken British authority in any manner whatsoever, and hand over the destinies of the Moslem community to a class which has no regard for their interests and no respect for their sentiments”.
Home Rule League
Sydenham was attacking the Montagu-Chelmsford Report which had stated that India had “a core of earnest men who believe sincerely and strive for political progress; around them a ring of less educated people to whom a phrase or a sentiment appeals; and an outside fringe of those who have been described as attracted by curiosity to this new thing, or who find diversions in attacking a big and very solemn Government as urchins might take a perilous joy at casting toy darts at an elephant.”
Annie Besant, herself an Englishwoman, was, along with BG Tilak and MA Jinnah, a pioneer of Indian nationalism at the time and headed the new Indian Home Rule League on the Irish pattern. The League stated its membership at 52,000. Sydenham multiplied that by five and asked if a quarter million could purport to rule 244 millions in an Indian democracy. Where, he demanded, was the “voice that cannot yet be heard, the voice of the peoples of India”? The imperialist jibe was that the British Raj would be replaced at best by a “Vakil Raj” of “high-caste” Hindus and at worst by anarchy and bloodshed.
Thirty years later India’s was partitioned and independent under Attlee’s Labour Party. Churchill took over the imperialist mantle and found solace in the new India agreeing to remain in Britain’s “Commonwealth”, saying that India doing so as a Republic did not impair “the majesty of the Crown or the personal dignity of the King”.
The ghosts of Churchill and Sydenham today would heartily cheer our Republic’s current President APJ Abdul Kalam agreeing to receive the “King Charles II Medal” from the Royal Society, and our current PM Manmohan Singh accepting honorary British degrees also while in office. Britain’s Crown Prince has proposed a cricket match between India and Pakistan to mark the 60th anniversary of 1947, and what, after all, could be less inappropriate to mark the event in British eyes? All that Indian nationalism would have been firmly put in its place.
Now Pakistan mostly goes unmentioned in the history of Indian nationalism because the new Pakistanis as of 14 August 1947 hardly felt or even wished to be independent of the British. Instead they longed only to acquire control over any kind of Muslim-majority Government that they could, and as much of the resources and joint military assets of the old India they could get their hands on.
The Kashmir dispute and India-Pakistan conflict have not been ones between Hindus and Muslims, regardless of what the BBC, CNN etc make themselves believe. As much as for any other reason, Kashmir escalated out of control because of British irresponsibility during the process of disintegration of the old Indian Army between the two new Dominions. Newly demobilised Mirpuri soldiers who had formed loyal British battalions were drawn into the cycle of Partition-related communal violence and reprisals in Punjab, which inevitably spilt over into Jammu and culminated in the attack on J&K State that commenced from Pakistan’s NWFP in October 1947 ~ plunging J&K into civil war with Sheikh Abdullah and Bakshi Ghulam Mohammad’s National Conference allied to the new secular India and Sardar Ibrahim’s Muslim Conference allied to the new and soon to be Islamic Pakistan. Field Marshal Auchinlek, the Supreme Commander of both Indian and Pakistani Armed Forces, had the decency to resign and abolish the so-called “Supreme Command” as soon as he realised his own forces were at war with one another.
It would not be too inaccurate to say Pakistan and Britain continued in a neo-colonial relationship throughout the 1950s and 1960s ~ all the way until Ayub Khan (who had been warmly entertained at Chequers during the Christine Keeler-Profumo matter), overplayed his hand by attacking India in 1965. That war followed by the East Pakistan cyclone in 1969 brought to a head the inherent political contradictions of the Pakistani state accumulated until that time, and soon led to Bangladesh’s creation in 1971. Britain has had no real interest in Bangladesh but as Pakistan had allowed dual nationality with Britain, Britain found itself with a lot of Bangladeshi immigrants whose “Indian” restaurants give modern Britons today something to look forward to every weekend.
Britain and its American ally continued to have deep interests in Pakistan, mostly because of the geopolitical importance of Pakistani real estate and the generally obsequious and compliant nature of the Pakistani military and diplomatic elite. All that began to change fundamentally when the real declaration of Pakistani independence occurred in the world with the AQ Khan nuclear bombs exploding in 1998 followed by the September 11 2001 attacks upon the USA.
Nationalism today
As for ourselves in India, we have developed some coherent and recognisable design of a modern political economy with a Union Government and more than two dozen State Governments, and we have abolished the imperialist lackeys known as the “princes”. Our Governments at Union and State levels change peacefully by periodic elections under the 1950 Constitution. This in itself would be seen as an astonishing democratic achievement relative to where we were one hundred years ago at the time of the Morley-Minto policies. Thanks to Jawaharlal Nehru, we have had universal franchise since 1952 (at a time when the USA still had its Jim Crow laws against black citizens) ~ yet the imperialist jibe of an infinitesimally small elite purporting to represent hundreds of millions of India’s people remains to be addressed.
It would be interesting to know how many descendants of the 52,000 members of Annie Besant’s Home Rule League remain in India and how many have emigrated to the USA, Britain, Australia etc. The children of our top military, bureaucratic, business, professional and academic elite have cheerfully led an exodus out of the country. E.g. the son of a former commanding general of the Indian Army’s Artillery Regiment is now a British businessman and member of Tony Blair’s new House of Lords. Indian Nationhood in the 21st Century no longer has to include Bangladeshis and Pakistanis who have ended up seeking to develop their own nationalisms, but it remains hard enough to try to include everyone else ~ from Tamils to Kashmiris and from Assamese and Mizos to Sikhs and Goans. Cleaning up our government accounting and sorting out our public finances nationwide so as to establish a sound money for everyone to use for the first time in sixty or seventy years, is among the first steps in defining our common goals as an independent nation.
(Postscript: The original text stated Independence and Paritition came “forty years” after the only date mentioned until that point in the text, which is of the 1918 Montagu-Chelmsford period. Unconsciously, I was counting from the Morley-Minto period of 1906-1908 which was the constitutional precedent to Montagu-Chelmsford.)
India and Her Neighbours
May 15, 2007 — drsubrotoroyWe & Our Neighbours
Pakistanis And Bangladeshis Would Do Well To Learn From Sheikh Abdullah
by Subroto Roy
First published in The Statesman May 15 2007, Editorial Page Special Article, http://www.thestatesman.net
Pakistan and Bangladesh, unlike ourselves in India, have yet to properly establish elementary constitutional institutions. “Individuals may form communities, but it is institutions alone that can create a nation”, said Benjamin Disraeli. The continual political chaos on the streets of Pakistan and Bangladesh ~ not just in recent weeks but in recent years and decades ~ indicate such institutions are still lacking or stillborn there. Tear gas, water cannon and hordes of armed policemen to charge at enraged stone-throwing crowds are not part of any solution but part of the political problem itself.
One main purpose of constitutional institutions has to do with peaceful transfer of power from one political party to its adversary. Mulayam Singh Yadav has just transferred political power to Mayawati in Uttar Pradesh, an Indian State more populous than either Pakistan or Bangladesh. Not long ago Lalu Prasad Yadav did the same to Nitish Kumar in Bihar, and Atal Behari Vajpayee to an appointee of Sonia Gandhi for all India itself. Modern democratic institutions are precisely about such peaceful transfers of power after voters have acted periodically to try to “throw the rascals out”.
Honeymoon period
It would be foolish to suppose an incoming Government of UP, Bihar or all India itself will be very much better than the one it displaces. But certainly in its first few “honeymoon” months or weeks at least, it will not be any worse. The tail-end of any scheduled democratic government, whether in India, Britain, the USA or elsewhere, is quite a disgusting sight, as those in their last days of power grab whatever they can from office before departure without any pretence of shame or embarrassment. Serious decision-making in the public interest would have long ago ceased. Almost anything new would be better.
At the same time, among those coming into power there will be some earnest wish at least to make some small difference for the better ~ a wish that will surely disappear within weeks of entering office after which the old cynicism and corruption will take hold again, and it will be the same ugly business as usual. But certainly, voters can expect slightly fresh air for a brief time after they have thrown one party out of power and chosen to bring in another. That is as about as good as democracy gets in modern practice.
Of India’s dozen or more larger States, we have, in the sixth decade of our Constitution, quite a few in which bipartisan democratic processes have been taking shape. UP was not one of them, and it is to Mayawati’s credit that she has broken the pattern of hung assemblies and now heads a majority government. Bihar too had seemed in the monolithic grip of Lalu Yadav until Nitish Kumar broke it, though the latter’s honeymoon period is now long over and it is business quite as usual there. Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and even J&K each have a noticeable bipartisan nature developing with at least one “national” party present to be counted. Tamil Nadu has been bipartisan but in an unhealthy way based on the personality cults of antagonistic leaders rather than any political principles or class-interests ~ which is a pity as the old Madras once had seemed a source of some new rationality in Indian politics. West Bengal’s voters have been definitely bipartisan, the communist vote being no more than that of the Congress and Trinamul combined. But for decades the local Congress has been notoriously sold down the river to its communist adversary by the Congress “leadership” in Delhi, and that has allowed an entrenched and wholly corrupted communist cultural and political mindset to rule in Kolkata. The Basu-Bhattacharjee Government was palpably bewildered over the Singur and Nandigram events because of their self-induced delusion about the economic and political realities of the State.
Throughout India though, periodic elections have acquired enough legitimacy to be accepted as the means of peaceful change of government. And with bipartisan politics there is a tendency for the median voter to be wooed at election-time.
We have of course many other continuing problems in our political economy ~ most notorious of which is the rotten state of our public finances and the continuous massive deficit finance that has ruined our paper currency and banking system ever since Indira Gandhi’s rule, coinciding with the start of Manmohan Singh’s career as an economic bureaucrat and Pranab Mukherjee’s as a politician in the early 1970s. Our acceptance of the democratic way has to an extent depended on our notoriously irresponsible macroeconomic policies ~ since every State and Union Government entity has been allowed to face no effective binding financial budget-constraint, and all its perverse decision-making can flow eventually into the swamp that is our Public Debt which constitutes the asset-side of the domestic banking system. India’s cardinal problem then becomes one of how to improve our macroeconomics without losing our democracy ~ something the Sonia-Manmohan-Pranab Congress, the BJP/RSS and the Communists are all equally clueless about.
Across our borders, our Pakistani and Bangladeshi cousins were cut from the same constitutional cloth as ourselves, namely the 1935 Government of India Act and the Montague-Chelmsford reforms before that. But after Jinnah’s death they refused to admit this and instead embarked on trying to write and implement a Constitution for a new Caliphate. The initial demand was “That the sovereignty in Pakistan belongs to God Almighty alone and that the Government of Pakistan shall administer the country as His agent”. In Rashid Rida and Maulana Maududi’s words, Islam becomes “the very antithesis of secular Western democracy. The philosophical foundation of Western democracy is the sovereignty of the people. Lawmaking is their prerogative and legislation must correspond to the mood and temper of their opinion… Islam… altogether repudiates the philosophy of popular sovereignty and rears its polity on the foundations of the sovereignty of God and the viceregency (Khilafat) of man.” (Rosenthal, Islam & the Modern National State, Cambridge 1965). Pakistan’s constitutionalists thus have faced an impossible battle to overcome the ontological error of assuming that any mundane government can be in communication with God Almighty.
J&K’s Constitution
Now Sheikh Mohammad Abdullah was as pious a Muslim as any but was far more modern in his 5 November 1951 speech to J&K’s Constituent Assembly: “You are the sovereign authority in this State of Jammu & Kashmir; what you decide has the irrevocable force of law”. Referring to the American and French Constitutions, he said the “basic democratic principle” was of the “sovereignty of the nation”. “We should be clear about the responsibilities that this power invests us with. In front of us lie decisions of the highest national importance which we shall be called upon to take. Upon the correctness of our decisions depends not only the happiness of our land and people now, but the fate as well of generations to come.”
Can a modern conclave of Pervez Musharraf, Nawaz Sharif, Benazir Bhutto and Chaudhry Iftikhar Ahmed decide or declare any better for Pakistan today? Or one of Khaleda, Hasina and whichever cabal of generals and bureaucrats happens to head Bangladesh at present?
If Pakistan and Bangladesh each chose to restart with the modern-minded constitutional example Sheikh Abdullah set more than a half century ago in J&K, they may find their political problems less severe in due course. It is a long road ahead.
India and “Energy Security”
May 7, 2007 — drsubrotoroyFirst published in India’s Energy Security edited by Anant Sudarshan and Ligia Noronha, Konrad Adenauer Stiftung, New Delhi 2007
“On the Political Economy of India’s Energy Policy: One Citizen’s Viewpoint”
by
Subroto Roy
For the idea of “energy security” to have meaning, “energy insecurity” must hold meaning as well. Looking back a generation, the average American, European and Japanese citizen became anxious and insecure when the cartel power of the oil exporting countries was first exercised, and energy prices quadrupled. The idea of the US Government accumulating a “strategic reserve” of petroleum originated due to the oil crisis, and amounted to no more than a buffer-stock or commodity price-stabilisation scheme so “cheap gasoline” could be had always, and lifestyles would not be suddenly inconvenienced, and hence presidential popularity ratings would not suddenly drop.
In many ways energy insecurity has been a creation of bad design. Hawaii is a good example of this. Hawaii’s renowned climate is cooled by the magnificent trade-winds which blow all year long except in September. Architecture suitable to those trade-winds would have created homes a few stories high with windows which could be opened. Instead, Honolulu has become a city of high-rises and skyscrapers in the middle of the Pacific Ocean — many with New York-style permanently closed windows and centralised airconditioning.
Energy Insecurity, and hence Energy Security, may be notions mostly relevant to advanced Western economies. North American, European and Japanese homes, lifestyles, architectures and urban sprawls are all highly capital-intensive and inelastically dependant on domestic or imported energy. The reason a vague undefined notion of “Energy Security” tends to make New Delhi anxious is because many inside the Delhi Beltway live in dreamlands or fantasy-worlds where they would like to imitate Western lifestyles in their personal lives. But New Delhi is not Europe or America and certainly India is not New Delhi.
There are hundreds of millions of Indians in rural India. What is the appropriate National Energy Policy for them? It quite simply is for there to be genuine electrification of India’s 600,000 villages (where more than 70% of the rural Indian population still have no electric lighting even according to Government data), as well as better trains, better all-weather feeder-roads to reach bus routes and primary schools, and conditions to arise for technological change and normal prosperity among ordinary people, so those who are today transporting a whole family of four on a bicycle, are able in a few years to do so on a motor-scooter, and some years after that perhaps in a small private car. Economic theory speaks of preferences, resources and technologies. Preferences define and give rise to the demand-side; resources and technologies define and give rise to the supply-side. Relative prices (which include interest-rates, reflecting the force of the present relative to the future) tend to intermediate equilibria between demand and supply conditions. In policy-making, private preferences for public goods and services must somehow become translated through a tolerable political process into reasonable public preferences. It must have seemed a good idea privately to someone to create skyscrapers with closed windows in Honolulu forgetting the trade winds and ignoring the energy-dependence of the Hawaiian Islands, yet in retrospect that may seem to have been publicly unwise. Similarly, India is a coal-abundant coal-exporting and diesel-importing country yet we got rid of all our steam locomotives and replaced these with diesel engines – if there were enough reasons to do so, I at least remain ignorant of what they were. One problem with our energy policy-making that has emerged in the current nuclear deal-making with American businessmen and politicians, is that it has seemed to lack rational assessments being made of relative costs and benefits in the Indian case of nuclear/fossil fuel/renewable energy, especially hydroelectric energy. Indeed it reveals the same lack of transparency as other policy-making in this country – like the $12 billion worth of commercial aircraft from Boeing and Airbus bought for our bankrupt nationalized airlines.
Moving from preference-formation to resources and technologies, it will be recalled that no economist of any school of thought anywhere ever backed the Club of Rome/“Limits to Growth” idea a generation ago that mankind was doomed in some sense to run out of resources. There are always alternatives, each with a relative cost attached to it, and there are always new and unpredictable opportunities and ingenuities arising which dynamically change the set of alternatives on offer at a given time. Prices and costs tend to adjust when possible to make myriad individual decisions consistent with one another, and in fact, futures, forward and option markets for petroleum products are among the most active and well-traded that there are in the world. Design improvements in nuclear reactors will also improve productivity; e.g. “fast breeder” reactors “breed” more fissile material than they use, and may get 100 times as much energy from a kilogram of uranium as existing reactors do. We in India also have one innovatively designed thorium reactor under construction.
Coming to the nuclear deal, the plausible part of the Government of India’s official line on the Indo-US nuclear deal is that removing these international restrictions will — through importation of new technologies, inputs, fuel etc — improve the functioning of the 14 existing nuclear plants that are going to be designated as “civilian”. However, those purchasing decisions involved in enhancing India’s efficiency gains must be made by the Government’s nuclear scientists on technical grounds of improving the working of our existing nuclear infrastructure.
It would be a different animal altogether to be purchasing new nuclear reactors on a turnkey basis from American, French or any other foreign businessmen in a purported attempt to improve India’s “energy security”. The central question over such massive foreign purchases no longer would be the technical one of using the Indo-US deal to improve efficiency or productivity of our existing inefficient and even crippled nuclear infrastructure. Instead it would become a question of calculating social costs and benefits of our newly investing in nuclear power relative to other sources like hydroelectric power. The contribution of nuclear power to India’s electricity production has been close to negligible. Among India’s energy sources, the largest growth-potential has remained hydroelectric. Even if all other sources of electricity remained constant, and our civilian nuclear capacity alone was made to grow by 100% under the deal that Dr Manmohan Singh and Mr Montek Singh Ahluwalia have been promoting, that would still make up less than 8% of total Indian electricity produced.
In 2004, the International Energy Agency’s estimated that the new energy capacity required by rising economic growth in 2020 will derive 1400 GW from burning coal (half of it in China and India), 470 GW from burning oil, 430 GW from hydro, and 400 GW from renewable sources like solar or wind power. Because gas prices are expected to remain low worldwide, construction of new nuclear reactors for electricity will mostly remain unprofitable. By 2030, new energy expected to be required worldwide is 4700 GW, of which only 150 GW is expected from new nuclear plants which in any case will replacing existing plants due to be retired. I am afraid the thought cannot be avoided that a proper cost-benefit analysis may reveal that the reason why potential American, French and other sellers of new nuclear reactors to India are becoming so keen on India using civilian nuclear energy is that they are unable to sell these reactors under free market principles elsewhere in the world economy. There is enough circumstantial evidence that the current nuclear deal-making has been promoted mostly by big business lobbies and has had little to do with anything else. The nuclear deal was promoted by the US-India Business Council and the US-India CEO Forum. The Confederation of Indian Industry registered as an official lobbyist in Washington, and went about spending half a million dollars lobbying American politicians for the nuclear deal. After President Bush’s visit to India, the US Foreign Commercial Service reportedly said American engineering firms, equipment suppliers and contractors faced a $1,000 billion opportunity in India, and the US Chamber of Commerce said the nuclear deal can cause $100 billion worth of new American business in India’s energy-sector alone.
If the Indo-US nuclear deal helps India improve or maintain its existing nuclear infrastructure, well and good. If in fact the underlying motivation of the local and foreign business lobbies driving the deal has been to sell India nuclear reactors on a turnkey basis at a time when nuclear energy is uneconomical elsewhere in the world because of low gas prices, then India’s ordinary citizens may demand to know from the Government whether the deal is principally aimed at allowing such importation of new nuclear reactors, and if so, why such an expensive alternative is being considered. Thus must include a realisation that while the transactions, organisation and political costs of getting new hydroelectric power investments off the ground are high, it is hydroelectric and not nuclear power where India’s real future potential exists. As a general rule, I put it to you that we need to be less worried about “Energy Security” anywhere and more worried about thoughtless irresponsible corrupt governments everywhere. There is no shortage of energy or resources as such anywhere in the world; what should be making us feel insecure is the shortage of wisdom in political decision-making. That there is everywhere.
Maharashtra’s Money
April 24, 2007 — drsubrotoroyMaharashtra Govt Finance 2004 Table
Maharashtra’s Money: Those Who Are Part Of The Problem Are Unlikely To Be A Part Of Its Solution
first published in The Statesman April 24 2007, Editorial Page
by Subroto Roy
Mr Percy Mistry, according to the World Bank’s official chronology, worked there with Moeen Qureshi, and S Javed Burki. Mr Qureshi was doyen of Pakistani bureaucrats in Washington and something of a king-maker back home, briefly becoming Pakistan’s PM himself; Mr Burki briefly became Pakistan’s Finance Minister and is an author in the book Foundations of Pakistan’s Political Economy created by WE James and myself in the 1980s in the USA. Although Mr Mistry claims no special expertise about India’s monetary economy or public finances, he was appointed by Finance Minister P. Chidambaram to head an official committee that has given an opinion on a crucial monetary issue facing the country today, namely, the rupee’s convertibility. Mr Mistry apparently authored the report but resigned before its release, making it unclear who is responsible for its contents.
Mr Mistry has glossed over India’s present fiscal circumstances, said nothing of the limitless waste, fraud and abuse of the public purse the Sonia-Manmohan Government have been indulging in (like their Vajpayee-Advani predecessor) yet declared the rupee should be freed in 2008 ~ telling Business Standard a convertible rupee will allow people like “Ratan” and “Kumar” to raise capital in India for their foreign purchases, and not have to go to London as they must do now, poor things. All this in a report purporting to be a plan to make Mumbai an “international financial centre”, which is a different subject altogether.
Mr Mistry thus becomes a certifiable member of the “Dream Team” of Dr Singh, Mr Chidambaram, Mr Montek Ahluwalia, Mr Deepak Parekh and their big business/big labour/big media friends across political parties. Dreaming involves constructs in which normal logic and facts have no place. In the waking world, India is a labour-rich, capital-scarce country where wages are lower and interest-rates are higher respectively than in labour-scarce, capital-rich Western countries; hence India will be importing not exporting capital. In the real world too, Mumbai is not an off-shore island-resort outside India (like the so-called SEZs are going to be from a legal standpoint) but happens to be located in Maharashtra, whose public finances urgently require hard investigation and sober thought.
Now there used to be a “Bombay State” coinciding with the old Bombay Presidency plus “princely states” plus Marathi-majority districts of MP and Hyderabad and excluding Kannada-majority districts to Mysore. On May 1 1960, after much agitation, this became the new States of Gujarat and Maharashtra. There was talk of making Bombay city a Union Territory but the Marathis would have none of it. In fact, within a few weeks, Maharashtra reverted to calling itself “Bombay State” and it was not until the end of the year the Government of India officially declared it must be called Maharashtra.
The same quest for, or confusion about, cultural and political identity continues in recent times and may be at the root of the Shiv Sena’s erratic political behaviour which rocks Maharashtra politics so frequently. “Bombay” may be “Mumba Bai” or “Mumba Devi” but it had not been a Marathi town any more than Calcutta had been a Bengali town. Bombay’s traders and businessmen descended there while it developed after the decline of Surat, where the British initially came to trade in the 17th Century. Modern Bombay retains some of its “all-India” character and even today you cannot make money in its markets unless you speak Gujarati. Marathi-speakers have tended to wish Maharashtra was “Maratha-rashtra” reminiscent of the great Shivaji Bhonsla (1627-1680) but others have read the name only as “Great State”.
This continuing identity crisis had its most devastating costly impact through the Dabhol-Enron fiasco. As recently as March 4 2007, Chief Minister Vilasrao Deshmukh said frankly “We could not generate a single megawatt of electricity in the last 10 years due to the Enron issue”, adding demand for electric power had been growing in the State at 10% per annum.
Indeed, before the 2005-2006 nuclear or any other deal could be contemplated with the Americans, the US-India Business Council, the American business lobbyist (and recent guest and soon-to-be host of the CPI-M’s Buddhadeb Bhattacharya), insisted India pay up fully for the Dabhol-Enron fiasco. Maharashtra and its sovereign guarantor the Government of India, duly paid out at least $140-$160 million ($14-$16 crore) to each General Electric and Bechtel Corporation in “an amicable settlement”. It was only then that Dr Manmohan Singh could be hosted in the White House and in turn play host to President George W. Bush.
Without entering the intricacies of the fiasco, it may be still asked who was responsible. And in retrospect the finger must point both at the Mahajan-Munde BJP/ Thakeray-Joshi Shiv Sena, and at the Sharad Pawar Government and Manmohan-Montek Union Finance Ministry at the time. The BJP-Shiv Sena declared an intent to “throw Enron into the Arabian Sea” and thus vitiated the atmosphere with the Americans. Americans are shrewd and practical people in commercial matters and accounted for such contingencies in their deal-making, tidily earning their money anyway, winning the arbitration awards in due course. Maharashtra’s identity confusion was exemplified by Rebecca Mark having to visit Bal Thakeray before a policy flip-flop could be permitted.
If the basic technical cause Enron’s electricity became too expensive was that it was denominated in dollar prices and the rupee depreciated rapidly during and after the deal-making, then the financial responsibility for the fiasco must be ultimately traced to India’s Finance Minister in the early 1990s, namely Dr Singh, and his chief acolyte and Finance Secretary Mr Ahluwalia. Maharasthtra is not a sovereign country, and it was the Union Finance Ministry’s responsibility to oversee the necessary cost-benefit and project appraisal analyses, and these if properly done would have accounted for exchange-rate depreciation scenarios. It is no wonder the World Bank later refused to finance the project because they had done their studies better. The same kind of cavalier unprofessional attitude in spending scarce foreign moneys earned by India’s public has been displayed now more than a decade later by the Manmohan-Montek duo, though on a vastly larger scale, in regard to the planned purchase of nuclear reactors from Russia, the USA etc on a turnkey basis.
Maharashtra may be a Great State but its public finances are in as great a shambles as any other. The table for 2003-2004 (before the Enron payments were made) reveals the very high continuing public indebtedness, and the same pattern as the budgets of West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh described in these columns earlier. A closer look would reveal, e.g., that Rs 814.36 crore (Rs. 8.14 billion) were spent in collecting Rs1,205.97 crore. (Rs. 12.05 billion) of “Vehicle Tax”! There is much that Mumbai’s and Maharashtra’s and India’s citizens have to ponder over and act upon before serious thought can be put to restoring the integrity of India’s money. In that process, those who have been part of the problem are unlikely to be part of its solution.
Govt. of Maharashtra Finances 2003-04
EXPENDITURE ACTIVITIES: RsBn (Hundred Crore)
governance & local governance 18.19 2.58%
judiciary 2.96 0.42%
police (including vigilance etc) 19.81 2.81%
prisons 0.86 0.12%
bureaucracy 27.97 3.97%
collecting land revenue & taxes 42.25 6.00%
government employee pensions 26.36 3.74%
schools, colleges, universities, institutes 93.74 13.31%
health, nutrition & family welfare 23.42 3.33%
water supply & sanitation 10.22 1.45%
roads, bridges, transport etc. 12.96 1.84%
electricity 16.96 2.41%
irrigation, flood control, environ, ecology 70.79 10.05%
agricultural subsidies, rural development 41.30 5.86%
industrial subsidies 2.60 0.37%
capital city development 6.25 0.89%
social security, SC, ST, OBC, lab.welfare 25.40 3.61%
tourism 0.89 0.13%
arts, archaeology, libraries, museums 0.75 0.11%
miscellaneous -0.47 -0.07%
debt amortization & debt servicing 261.03 37.07%
total expenditure 704.22
INCOME SOURCES:
tax revenue 285.52
operational income 35.49
grants from Union 22.70
loans recovered 4.82
total income 348.53
GOVT. BORROWING REQUIREMENT (total expenditure minus total income) 355.70
financed by:
new public debt issued 317.02
use of Trust Funds etc 38.68
355.70
from author’s research and using C&AG data
On Land-Grabbing
January 14, 2007 — drsubrotoroyON LAND-GRABBING
Dr Singh’s India, Buddhadeb’s Bengal, Modi’s Gujarat have notorious US, Soviet and Chinese examples to follow ~ distracting from the country’s real economic problems
By SUBROTO ROY
First published in The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, Jan 14 2007
AT a business meet on 12 January 2005, Dr Manmohan Singh showered fulsome praise on Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee as “dynamic”, “the Nation’s Best Chief Minister”, whose “wit and wisdom”, “qualities of head and heart”, “courage of conviction and passionate commitment to the cause of the working people of India” he admired, saying “with Buddhadeb Babu at the helm of affairs it appears Bengal is once again forging ahead… If today there is a meeting of minds between Delhi and Kolkata, it is because the ideas that I and Buddhadebji represent have captured the minds of the people of India. This is the idea of growth with equity and social justice, the idea that economic liberalization and modernization have to be mindful of the needs of the poor and the marginalized.”
With such support of a Congress Prime Minister (as well as proximity to Pranab Mukherjee), Mr Bhattacharjee could hardly have feared the local Congress and Trinamul would pose any threat in the 2006 Assembly Elections despite having more potential voters between them than the CPI-M.
Dr Singh returned to the “needs of the poor and the marginalized” at another business meet on 8 January 2007 promising to “unveil a new Rehabilitation Policy in three months to increase the pace of industrialisation” which would be “more progressive, humane and conducive to the long-term welfare of all stakeholders”, while his businessman host pointedly stated about Singur “land for industry must be made available to move the Indian manufacturing sector ahead”.
The “meeting of minds between Delhi and Kolkata” seems to be that agriculture allegedly has become a relatively backward slow-growing sector deserving to yield in the purported larger national interest to industry and services: what the PM means by “long-term welfare of all stakeholders” is the same as the new CPI-M party-line that the sons of farmers should not remain farmers (but become automobile technicians or IT workers or restaurant waiters instead).
It is a political viewpoint coinciding with interests of organised capital and industrial labour in India today, as represented by business lobbies like CII, FICCI and Assocham on one hand, and unions like CITU and INTUC on the other. Business Standard succinctly (and ominously) advocated this point of view in its lead editorial of 9 January as follows: “it has to be recognised that the world over capitalism has progressed only with the landed becoming landless and getting absorbed in the industrial/service sector labour force ~ indeed it is obvious that if people don’t get off the land, their incomes will rise only slowly”.
Land is the first and ultimate means of production, and the attack of the powerful on land-holdings or land-rights of the unorganised or powerless has been a worldwide phenomenon ~ across both capitalism and communism.
In the mid-19th Century, white North America decimated hundreds of thousands of natives in the most gargantuan land-grab of history. Defeated, Chief Red Cloud of the Sioux spoke in 1868 for the Apache, Navajo, Comanche, Cheyenne, Iroquois and hundreds of other tribes: “They made us many promises, more than I can remember, but they never kept any except one: they promised to take our land, and they took it.”
Half a century later, while the collapse of grain prices contributed to the Great Depression and pauperisation of thousands of small farmers in capitalist America in the same lands that had been taken from the native tribes, Stalin’s Russia embarked on the most infamous state-sponsored land-grab in modern history: “The mass collectivisation of Soviet agriculture (was) probably the most warlike operation ever conducted by a state against its own citizens…. Hundreds of thousands and finally millions of peasants… were deported… desperate revolts in the villages were bloodily suppressed by the army and police, and the country sank into chaos, starvation and misery… The object of destroying the peasants’ independence…was to create a population of slaves, the benefit of whose labour would accrue to industry. The immediate effect was to reduce Soviet agriculture to a state of decline from which it has not yet recovered… The destruction of the Soviet peasantry, who formed three quarters of the population, was not only an economic but a moral disaster for the entire country. Tens of millions were driven into semi-servitude, and millions more were employed as executants…” (Kolakowski, Main Currents of Marxism).
Why did Stalin destroy the peasants? Lenin’s wishful “alliance between the proletariat and the peasantry” in reality could lead only to the peasants being pauperised into proletarians. At least five million peasants died and (Stalin told Churchill at Yalta) another ten million in the resultant famine of 1932-1933. “Certainly it involved a struggle ~ but chiefly one between urban Communists and villagers… it enabled the regime to obtain much of the capital desired for industrialization from the defeated village… it was the decisive step in the building of Soviet totalitarianism, for it imposed on the majority of the people a subjection which only force could maintain” (Treadgold, 20th Century Russia).
Mr Bhattacharjee’s CPI-M is fond of extolling Chinese communism, and the current New Delhi establishment have made Beijing and Shanghai holiday destinations of choice. Dr Singh’s Government has been eager to create hundreds of “Special Economic Zones” run by organised capital and unionised labour, and economically privileged by the State. In fact, the Singur and Nandigram experiences of police sealing off villages where protests occur are modelled on creation of “Special Economic Zones” in China in recent years.
For example, Chinese police on 6 December 2005 cracked down on farmers and fishermen in the seaside village of Dongzhou, 125 miles North East of Hong Kong. Thousands of Dongzhou villagers clashed with troops and armed police protesting confiscation of their lands and corruption among officials. The police immediately sealed off the village and arrested protesters. China’s Public Security Ministry admitted the number of riots over land had risen sharply, reaching more than seventy thousand across China in 2004; police usually suppressed peasant riots without resort to firing but in Dongzhou, police firing killed 20 protesters. Such is the reality of the “emergence” of China, a totalitarian police-state since the Communist takeover in 1949, from its period of mad tyranny until Mao’s death in 1976, followed by its ideological confusion ever since.
Modern India’s political economy today remains in the tight grip of metropolitan “Big Business” and “Big Labour”. Ordinary anonymous individual citizens ~ whether housewife, consumer, student, peasant, non-union worker or small businessman ~ have no real voice or representation in Indian politics. We have no normal conservative, liberal or social democratic party in this country, as found in West European democracies where the era of land-grabbing has long-ceased. If our polity had been normal, it would have known that economic development does not require business or government to pauperise the peasantry but instead to define and secure individual property rights and the Rule of Law, and establish proper conditions for the market economy. The Congress and BJP in Delhi and CPI-M in Kolkata would not have been able to distract attention from their macroeconomic misdeeds over the decades ~ indicated, for example, by increasing interest-expenditure paid annually on Government debt as a fraction of tax revenues (see Table). This macroeconomic rot originated with the Indira Gandhi-PN Haksar capriciousness and mismanagement, which coincided with the start of Dr Singh’s career as India’s best known economic bureaucrat.
Land, Liberty & Value
December 31, 2006 — drsubrotoroyLAND, LIBERTY & VALUE
Government must act in good faith treating all citizens equally ~ not favouring organised business lobbies and organised labour over an unorganised peasantry
By SUBROTO ROY
First published in The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Special Article, December 31 2006
EVERY farmer knows that two adjacent plots of land which look identical to the outsider may be very different in character, as different as two siblings of the same family. Adjacent plots may differ in access to groundwater and sunlight, in minerals and salts, in soil, fertilisers, parasites, weeds or a dozen other agronomic factors. Most of all, they will differ in the quality and ingenuity of thought and labour that has gone into their care and cultivation over the years, perhaps over generations.
John Locke said: “Whatsoever that (a man) removes out of the state that Nature hath provided and left it in, he hath mixed his labour with and joined to it something that is his own, and thereby makes it his property… For this labour being the unquestionable property of the labourer, no one but he can have a right to what that once joined to, at least where there is enough and as good left in common for others” (Second Treatise of Government). Plots of land are as specific as the families that have “mixed” their labour with them. Locke wrote of labour being something “unquestionably” the labourer’s own property; in the same libertarian vein, Robert Nozick opened Anarchy, State and Utopia saying “Individuals have rights, and there are things no person or group may do to them (without violating their rights)”.
But as we recognise the universal sanctity of the individual person and his/her private property, we have to start qualifying it. If you purchase a field, forest or estate through which runs a pathway traditionally used by the public to get from one side to the other then even as the new owner you may not have a right to forbid the public’s use of the pathway. By extension, it is clear the State, the community of which you are a citizen, may approach you and demand there should be and will be a public road or thoroughfare through your property in the common interest. Such is the sovereign’s right of “eminent domain” recognised throughout the world, not only in times of war or natural disaster but also in normal times where private property may be taken for public use. The individual’s right to free use of his/her property is circumscribed as a result.
What may be certainly expected though in all matters is that the State will act in good faith, i.e., that it has conducted proper technical surveys and cost-benefit analyses as well as transparent public hearings, and has honestly decided that the road must be constructed using this route and no other. The doctrine of eminent domain implies that while the right to private property may be basic, it is not absolute, as indeed no right is, not even the right to one’s own life. In India, one key difference between the landmark Golaknath (AIR 1967 SC 1643) and Kesavananda Bharati (AIR 1973 SC 1461) rulings had to do precisely with the former recognising the right to property being fundamental as in our original 1950 Constitution, while the latter consented to the Indira Parliament’s denial of this.
When private property is taken, fair compensation must be paid. For example, the American Constitution says “no private property may be taken for public use without just compensation”. What is just compensation? Typically it would be the “fair market value” — but that must be properly adjudged accounting for the best future use of the land, not merely the historical or traditional past use of the land.
Consider, in a mature urban real-estate market, a plot made vacant because a warehouse located on it has accidentally burned down. What is the value of the plot now? Another warehouse could be built, but other bids could come in too for construction of offices or residential flats or a multi-storey garage. The plot’s value would differ depending on which use it is ultimately put to. And this value would be ascertained by calculating the expected cash flows into the future from each of these possibilities, discounted appropriately to account for the fact the future is less valuable than the present, with the highest value alternative being chosen. That is how a mature private real-estate market works in theory, though in practice there would be zoning and environmental restrictions to account for the traditional nature of the neighbourhood as well as possible pollution by effluent waste etc.
In India, Government departments and ministries have inherited prime urban real estate from British times. Amidst the highest value real estate in Kolkata, Bangalore, Delhi etc. will be found a military camp or flats built for military personnel, having nothing whatsoever to do with furtherance of the nation’s defences today. The appalling state of government accounting and audit of our public property and institutions includes the fact that neither the Union nor State Governments and municipalities have the faintest idea of assets, including real estate, that they own. These public assets are frequently open to abuse by managerially uncontrolled government employees.
Fallacies even more curious seem to be currently at work in Indian policy-making, whether by this or that political party. The “eminent domain” doctrine requires a public purpose to exist for acquisition of private property by the State: e.g. construction of a road, bridge, dam, airport or some other traditional public good which is going to be used by the public. In India as elsewhere, “land reform” did involve taking an absentee landlord A’s land and distributing it to B, C, D and E who worked as peasants on it. But nowhere else outside formerly communist China has land been forcibly taken from peasants B, C, D and E and handed over to this or that private capitalist in name of economic development (in a reverse class war)!
Eminent domain doctrine requires good faith on part of the State with respect to its citizens and that implies treating all citizens’ interests equally – not e.g. favouring an organised business lobby or organised industrial labour over the unorganised peasantry uneducated in the wiles of city people.
Also, there is no reason why Government should be interested in a particular product-mix emerging out of a given private factory (such as the so-called inflation-unadjusted “Rs one lakh car” instead of telecom equipment or garments or textiles). Dr Manmohan Singh’s statement last week that he wishes to see “employment-intensive” industries merely added to Government confusion: from Henry Ford to Japanese “lean business” today, everyone knows the direction of change of technology in the automobile industry has been towards robotics, making modern manufacturing less and less manpower-intensive! The Tatas themselves underwent a major downsizing and restructuring in the last decade, hiving off industries not considered part of their “core competence”.
Traditional agriculture of Singur’s sort represents the most labour-intensive employment-generating kind of rural economy. While such rural life may appear unsatisfying to the urban outsider, there is, as Tolstoy, Rabindranath, Gandhi and others knew, subtle happiness, contentment and tranquility there absent in alienated industrial sprawls. “Surplus” labour occurs in agriculture because of technological improvements in quality and delivery of agricultural inputs as well as new education and awareness (Theodore W. Schultz,Transforming Traditional Agriculture). It is mostly seasonal and all hands are used during the harvest when even urban migrants flock back to help. Industry did not leave Bengal in the 1960s and 1970s because of Mamata Banerjee but because of urban unrest, the culture of gheraos and lockouts, and bad regulations of the labour and capital markets associated largely with Ms Banerjee’s Left Front adversaries.
The basic fiction the Union and State Governments have made themselves believe is that their idea of an industrialisation plan is necessary for economic development. It is not. Real economic problems in West Bengal and elsewhere are financial to do with State budgets. “Debt overhang is there” is how the RBI Governor apologetically put it last week. Interest payments on the West Bengal State public debt consume larger and larger fractions of the revenue: these payments were at Rs 13 Bn in 1995 but grew to Rs. 92 Bn by 2004, and may jump to Rs 200 Bn in the next decade. The communists have been in power thirty years and no one but they are responsible. Making the State’s budget healthy would require tackling the gargantuan bureaucracy, slashing ministerial extravagance (foreign trips, VIP security) etc. It is much easier to hobnob with the rich and powerful while tear-gassing the peasants.
New Foreign Policy? (8-9 Oct 2006)
October 9, 2006 — drsubrotoroyNEW FOREIGN POLICY? “Kiss Up, Kick Down”?
Seven phases of Indian foreign policy may be identifiable since Nehru; the current phase seems to involve subservience to the strong, jingoism otherwise
by Subroto Roy
First published in The Sunday Statesman 8 Oct 2006, The Statesman 9 Oct 2006 Editorial Page Special Article
The outlines of a new tri-partisan Indian foreign policy may be becoming discernible. That it is “new” or that it commands near unanimity among the Congress, BJP and “Left” and their respective friends in the Indian media and political classes, does not make it sound or robust in any way. In fact, its basis in the history, geography and economics of India is wholly inadequate, and it is also entirely divorced from any clearly enunciated new Indian political ethics for the modern world.
The new policy, which may be fairly dubbed the Jaswant-Manmohan policy after the BJP and Congress politicians who have been its putative authors and leading practitioners, is as likely as not to lead to an India that is no longer a free decision-maker in any meaningful way in world affairs by 2047, one hundred years after Independence. Our great grandchildren may well be taught that for some decades in Indian history a sovereign unitary republic actually existed which then came to be effectively lost.
Indeed the new policy may amount to being less a coherent new doctrine of India’s role in international relations than a mere change in attitude on the part of politicians, bureaucrats and their intelligentsia friends: from seeming universally arrogant in the world to becoming pliant and subservient towards those world powers perceived (accurately or inaccurately) as strong, combined with a vainglorious jingoism towards all others. It is an application to international diplomacy and politics of the classic bureaucratic principle of “kiss up, kick down” in an organisation, and may reflect the fact the two main institutions the Mughals and British used to run their empires were the bureaucracy and military ~ both of which have grown and continued to run New Delhi (and Islamabad) afterwards, co-opting whatever domestic political development that has arisen. There is plenty of wishful waffling too about India becoming a “great power” or being a “swing state in the global balance of power”, and about how well the economy is supposedly doing ~ as if what Government spokesmen say about the economy is to be believed at face-value. Indian Leftists and their fellow-travellers ~ as great lovers themselves of bureaucracy, collectivist groupthink and propaganda on the USSR or PRC pattern, and fearful or envious of all individual criticism, creativity and achievement – have taken to the same principle like fish to water.
The first phase of Indian foreign policy was Nehruvian in that it began with Nehru’s Fabian misperception of Stalin’s USSR, and ended with the military debacle he led the country into at the hands of Zhou’s “human wave” armies in the mountains of Ladakh and NEFA.
A second phase was Kashmir-centric, overlapping with the first insofar as it may be traced to Karan Singh’s iniquitous dismissal of Sheikh Abdullah’s first Government, but really beginning after Nehru’s death with the Ayub-Abdullah summit, and being marked by Ayub’s 1965 attack in J&K ~ Shastri’s riposte reaching the Ichogil Canal signalled that no longer would war over J&K be confined to J&K.
A third phase was forced on India by the Pakistani civil war that led to Bangladesh’s creation, and was marked by the Indira/ Haksar alliance with Brezhnev’s USSR, as well as by Pokhran-I.
A fourth phase of Indian foreign policy may be identified in the late 1970s and 1980s, marked by rebellion of the fundamentalist Sikhs whom Indira and Sanjay Gandhi had provoked, which led in due course to her assassination. The turmoil that followed in Punjab and North India was financed by anti-Indian Sikhs from Vancouver,California and Britain, with gleeful help from the Pakistanis, and Indian diplomats had their hands full in trying to counter that phenomenon. It was during this phase of domestic Indian turmoil that New Delhi wholly missed the seismic changes occurring in the USSR, East Europe and international relations generally, and completely failed to predict its consequences for India.
The phase came to end when the Narasimha Rao Government (upon advice of a well-known communist cabal in the IFS and JNU) instantly showered praise on the anti-Yeltsin coup in August 1991. When Yeltsin returned to power, the new anti-communist Russians took their revenge on New Delhi, exacting hard dollars for the soft rouble-trade of friendlier times.
A fifth phase may be seen in retrospect as one of relative success.The main plank of Indian foreign policy in the late 1980s and early 1990s was to get Pakistan designated a “terrorist state” in American eyes, as well as to warn of the dangers of a Pakistani nuclear bomb. It had been prompted by the end of American involvement in the Afghan war, which caused the ISI to shift the jihadis to J&K, and the Indian policy was destined not to succeed. No matter how hard Kanwal Sibal tried in 1992-1993 as Minister-Political in the Washington Embassy to tell the Americans that their Pakistani friends were dangerous, he was destined to fail as the MEA had entirely failed to realise how far ahead the Pakistanis were in their lobbying power in Washington ~ the Pakistani super-elite has been entrenched among the K-Street lobbyists and in expensive real-estate along the Potomac River for more than two generations. Yet after the 9/11 attacks several years later, the Indians were able to look back at that fifth phase and say to the Americans, “We told you so”.
In the late 1990s came a short-lived sixth phase of Pokhran-II and the Lahore bus-trip, which may be credited as Vajpayee successes, and also contained the Kargil War and Kandahar hijacking, which were more dubious. This overlapped with the last and currently continuing seventh phase of Indian foreign policy with Jaswant Singh breaking the ice with the Americans when they had recovered from the fact the CIA’s failures included not foreseeing Pokhran-II; it coincided too with Osama bin Laden’s declarations of jihad against the USA. The Americans enlisting themselves on the side of the Northern Alliance to defeat the Taliban after 9/11 was beneficial from an Indian standpoint since Afghanistan had been effectively lost to secular Indian influence for two decades, and the Taliban had shown themselves no friends of India during the Kandahar hijacking.
But the BJP’s anti-Muslim thought processes quickly took over, as did its proximity to organised business lobbies. When Iraq was attacked and occupied in 2003, there was hardly a whimper from the BJP leadership, and instead their businessmen friends started to fly to Amman hopeful of “reconstruction” contracts. The Sonia/ Manmohan Congress/Leftist combine has effectively continued and expanded that trend, though now the business lobbies have been much more muted and subtle, especially in their backroom dealings and payoffs with respect to the nuclear deal. There is also an occasional burst of anti-Americanism from leftists though it is hard of course to beg for American foreign investment in Marxist-run areas while also being sincere in quaint street demos or agitprop.
Running through the new foreign policy is a fiction that it is driven by a new economic motivation to improve development and mass well-being in India. The bizarre idea of creating hundreds of so-called “Special Economic Zones” (reminiscent of 17th and 18th Century colonial fortifications) illustrates this. India’s ordinary anonymous masses ~ certainly the 850 million people entirely outside the organised sector ~ have little or nothing to do with any of this. Benefits will accrue only to the ten million Indian nomenclatura controlling or having access to the gaping exit holes to the outside world in the new semi-closed economy with its endless deficit finance paid for by unlimited printing of an inconvertible domestic currency.
It is as fallacious to think private investment from foreign or domestic businessmen will support public “infrastructure” creation as it is to think foreign exchange reserves are like tax revenues in being available for Government expenditure on “infrastructure”. Such fallacies are intellectual products of either those who know no economics at all or those who have forgotten whatever little they might have been once mistaught in their youth. What serious economics does say is that Government should generally have nothing to do with any kind of private business, and instead should focus on properly providing public goods and services, encourage competition in all avenues of economic activity and prevent or regulate monopoly, and see to it all firms pay taxes they are due to pay.
That is it. It is as bad for Government to be pampering organised foreign or domestic business or organised labour with innumerable subsidies, as has been happening in India for decades, as it is to make enterprise difficult with red tape and hurdles. Businessmen are grown ups and should be allowed to freely risk their capital and make their profits or their losses without public intervention.
An economics-based policy would have single-mindedly sought to improve the financial condition of every governmental entity in the country, with the aim of improving the provision of public goods and services to all 1,000 million Indians. If and when budgets of all governmental entities become sound, foreign creditors would automatically line up before them with loans to sell, and ambitious development goals can be accomplished. As long as public budgets (and public accounts) remain in an outrageous shambles, nothing can be in fact achieved and only propaganda, corruption and paper-money creation results instead. Whatever economic growth does occur is due to new enterprise and normal technological progress, and is mostly despite and not because of New Delhi’s bureaucrats (see “The Dream Team: A Critique”, The Statesman 6-8 January 2006).
The first aspect of the new Indian foreign policy has been for Government to become wholly ingratiating towards any and all “First World” members visiting India who may deign to consider any kind of collaboration whatsoever. The long line of foreign businessmen and heads of government having photo-ops with the Indian PM began with Vajpayee and has continued with Manmohan, especially when there is a large weapons’ or commercial aircraft or other purchase to be signed. The flip-side has been ministerial and especially Prime Ministerial trips abroad ~ from Vajpayee’s to a Singapore golf-cart immediately after commiserating Gujarat, to Manmohan receiving foreign honorary doctorates while still holding public office.
Subservience to foreign business interests in the name of economic policy extends very easily to Indian naval, military or diplomatic assets being used to provide policing or support services for the great powers as and when they may ask for it. Hence, Indian naval forces may be asked by the Americans to help fight pirates in the Indian Ocean, or escort this vessel or that, or India may be asked to provide refuelling or base facilities, or India may be requested to vote against Iran, Venezuela or whomever here or there. But there would be absolutely no question of India’s role in international politics being anything greater than that of a subaltern or comprador whose response must be an instant “Ji, Huzoor”. The official backing of the Tharoor candidacy was as futile and ridiculous as the quest for UN veto-power or the willingness to attend G-8 summits as an observer.
While subservience towards the First World’s business and military interests is the “kiss up” aspect of the new foreign policy, an aggressive jingoism towards others is the “kick down” aspect. One influential voice among the media friends of the new foreign policy states it as follows: “The search for `equity oil’ has been the single most important new element of Indian economic diplomacy in recent years… Equity oil raises India’s stakes in the stability of regimes or even individuals who preside over these resources… the big question is how far would India go in defence of `regime stability’ elsewhere? And if it’s assets fall into hostile hands, would India be prepared to consider promoting `regime change’?” Just as surely as a pacifist Fabian socialist Nehru misperceived Stalin’s USSR, New Delhi’s new capitalistic jingoists have misperceived the Cheney-Rumsfeld grab for “equity oil” and have even defined Bush-Blair adventurism as being “the side of the angels”. How they must love to want to project Indian military force ~ paratroopers in the Maldives perhaps, though they need to recall what happened with the LTTE too!
Multiple Jallianwalla Bagh massacres may have been occurring in front of us in Iraq, Afghanistan and Balochistan, and there may soon be an attack on Iran too. New Delhi’s new “kiss up, kick down” attitude has rendered India’s once-dignified and sober voice silent, our eyes closed or our face turned away.
The obvious alternative to bureaucratic “kiss up, kick down” would be “kick up, kiss down” loved by all individualists and anti-bureaucrats. In other words, it would be for India to take each case and circumstance in international politics on its merits; be seen to stand up seriously to the powerful in world politics wherever and whenever necessary; seek to protect those who may be vulnerable to international or other brutality in world affairs, while getting on properly with the mundane business of ordinary government and commerce at all other times. That mundane business may call for a gradual withdrawal of India from all or most of the fancy, corrupt international bureaucracies in New York, Washington, Geneva etc, focussing calmly but determinedly instead on improved administration and governance at home. Such was what Rajiv Gandhi was advised in January 1991 (see “Memos to Rajiv,” The Statesman 31 July-2 August 1991; Freedom First October 2001), when for one futile moment he even formed a peaceful bridge between the Americans and Saddam during the first Gulf War. The New Delhi establishment may be too intoxicated with power and insecure intellectually to be able to reflect on such sober alternatives.
India’s Energy Interests
August 28, 2006 — drsubrotoroyOUR ENERGY INTERESTS
Subroto Roy
First published in The Sunday Statesman, August 27 2006, The Statesman August 28 2006, Editorial Page Special Article


Americans are shrewd and practical people in commercial matters, and expect the same of people they do business with. Caveat emptor, “let the buyer beware”, is the motto they expect those on the other side of the table to be using. Let us not think they are doing us favours in the nuclear deal ~ they are grown-ups looking after their interests and naturally expect we shall look after our own and not expect charity while doing business. Equally, let us not blame the Americans if we find in later years (long after Manmohan Singh and Montek Ahluwalia have exited from India’s stage) that the deal has been implemented in a bad way for our masses of ordinary people.
That said, there is a remarkable disjoint between India’s national energy interests (nuclear interests in particular), and the manner in which the nuclear deal is being perceived and taken to implementation by the two sides. There may be a fundamental gap between the genuine positive benefits the Government of India says the deal contains, and the motivations American businessmen and through them Indian businessmen have had for lobbying American and Indian politicians to support it. An atmosphere of being at cross-purposes has been created, where for example Manmohan Singh is giving answers to questions different from the questions we may want to be asking Montek Ahluwalia. The fundamental gap between what is being said by our Government and what may be intended by the businessmen is something anyone can grasp, though first we shall need some elementary facts.
In 2004, the International Energy Agency estimated the new energy capacity required by rising economic growth in 2020 will derive 1400 GW from burning coal (half of it in China and India), 470 GW from burning oil, 430GW from hydro, and 400 GW from renewable sources like solar or wind power. Because gas prices are expected to remain low worldwide, construction of new nuclear reactors for electricity will be unprofitable. By 2030, new energy expected to be required worldwide is 4700GW, of which only 150GW is expected from new nuclear plants, which will be in any case replacing existing plants due to be retired. Rational choice between different energy sources depends on costs determined by history and geography. Out of some 441 civilian reactors worldwide, France has 59 and these generate 78 per cent of its electricity, the rest coming from hydro. Japan has 54 reactors, generating 34% of its electricity from them. The USA has 104 reactors but generates only 20 per cent of its electricity from them, given its vast alternative sources of power like hydro. In India as of 2003, installed power generating capacity was 107,533.3MW, of which 71 per cent came from burning fuels. Among India’s energy sources, the largest growth-potential is hydroelectric, which does not involve burning fuels ~ gravity moves water from the mountains to the oceans, and this force is harnessed for generation. Our hydro potential, mostly in the North and North-East, is some 150,000MW but our total installed hydro capacity with utilities was only 26,910MW (about 18 per cent of potential). Our 14 civilian nuclear reactors produced merely 4 per cent or less of the electricity being consumed in the country. Those 14 plants will come under “international safeguards” by 2014 under the nuclear deal.
It is extremely likely the international restrictions our existing nuclear plants have been under since the 1970s have hindered if not crippled their functioning and efficiency. At the same time, the restrictions may have caused us to be innovative too. Nuclear power arises from fission of radioactive uranium, plutonium or thorium. India has some 8 million tonnes of monazite deposits along the seacoast of which half may be mined, to yield 225,000 tonnes of thorium metal; we have one innovatively designed thorium reactor under construction. Almost all nuclear energy worldwide today arises from uranium of which there are practically unlimited reserves. Fission of a uranium atom produces 10 million times the energy produced by combustion of an atom of carbon from coal. Gas and fossil fuels may be cheap and in plentiful supply worldwide for generations to come but potential for cheap nuclear energy seems practically infinite. The uranium in seawater can satisfy mankind’s total electricity needs for 7 million years. There is more energy in the uranium impurity present in coal than can arise from actually burning the coal. There is plenty of uranium in granite. None of these become profitable for centuries because there is so much cheap uranium extractable from conventional ores. Design improvements in reactors will also improve productivity; e.g. “fast breeder” reactors “breed” more fissile material than they use, and may get 100 times as much energy from a kilogram of uranium as existing reactors do. India has about 95,000 tonnes of uranium metal that may be mined to yield about 61,000 tonnes net for power generation. Natural uranium is 99.3 per cent of the U-238 isotope and 0.7 per cent of the radioactive U-235 isotope. Nuclear power generation requires “enriched uranium” or “yellow cake” to be created in which U-235 has been increased from 0.7 per cent to 4 to 5 percent. (Nuclear bombs require highly enriched uranium with more than 90 per cent of U-235.) Yellow cake is broken into small pieces, put in metal rods placed in bundles, which are then bombarded by neutrons causing fission. In a reactor, the energy released turns water into steam, which moves turbines generating electricity. While there is no carbon dioxide “waste” as in burning fossil fuels, the “spent” rods of nuclear fuel and other products constitute grave radioactive waste, almost impossible to dispose of.
The plausible part of the Government of India’s official line on the Indo-US nuclear deal is that removing the international restrictions will ~ through importation of new technologies, inputs, fuel etc ~ improve functioning of our 14 existing civilian plants. That is a good thing. Essentially, the price being paid for that improvement is our willingness to commit that those 14 plants will not be used for military purposes. Fair enough: even if we might become less innovative as a result, the overall efficiency gains as a result of the deal will add something to India’s productivity. However, those purchasing decisions involved in enhancing India’s efficiency gains must be made by the Government’s nuclear scientists on technical grounds of improving the working of our existing nuclear infrastructure.
It is a different animal altogether to be purchasing new nuclear reactors on a turn-key basis from American or any other foreign businessmen in a purported attempt to improve India’s “energy security”. (Lalu Yadav has requested a new reactor for Bihar, plus of course Delhi will want one, etc.) The central question over such massive foreign purchases would no longer be the technical one of using the Indo-US deal to improve efficiency or productivity of our existing nuclear infrastructure. Instead it would become a question of calculating social costs and benefits of our investing in nuclear power relative to other sources like hydroelectric power. Even if all other sources of electricity remained constant, and our civilian nuclear capacity alone was made to grow by 100 per cent under the Manmohan-Montek deal-making, that would mean less than 8% of total Indian electricity produced.
This is where the oddities arise and a disjoint becomes apparent between what the Government of India is saying and what American and Indian businessmen have been doing. A “US-India Business Council” has existed for thirty years in Washington as “the premier business advocacy organization promoting US commercial interests in India.… the voice of the American private sector investing in India”. Before the nuclear or any other deals could be contemplated with American business, the USIBC insisted we pay up for Dabhol contracted by a previous Congress Government. The Maharashtra State Electricity Board ~ or rather, its sovereign guarantor the Government of India ~ duly paid out at least $140-$160 million each to General Electric and Bechtel Corporations in “an amicable settlement” of the Dabhol affair. Afterwards, General Electric’s CEO for India was kind enough to say “India is an important country to GE’s global growth. We look forward to working with our partners, customers, and State and Central Governments in helping India continue to develop into a leading world economy”.
Also, a new “US-India CEO Forum” then came about. For two Governments to sponsor private business via such a Forum was “unprecedented”, as noted by Washington’s press during Manmohan Singh’s visit in July 2005. America’s foreign ministry announced it saying: “Both our governments have agreed that we should create a high-level private sector forum to exchange business community views on key economic priorities…” The American side includes heads of AES Corporation, Cargill Inc., Citigroup, JP Morgan Chase, Honeywell, McGraw-Hill, Parsons Brinckerhoff Ltd, PepsiCo, Visa International and Xerox Corporation. The Indian side includes heads of Tata Group, Apollo Hospitals Group, Bharat Forge Ltd, Biocon India Group, HDFC, ICICI One Source, Infosys, ITC Ltd, Max India Group and Reliance Industries. Presiding over the Indian side has been Montek Ahluwalia, Manmohan’s trusted aide ~ and let it be remembered too that the Ahluwalias were Manmohan’s strongest backers in his failed South Delhi Lok Sabha bid. (Indeed it is not clear if the Ahluwalias have been US or Indian residents in recent years, and if it is the former, the onus is on them to clear any perception of conflict of interest arising in regard to roles regarding the nuclear deal or any other official Indo-US business.)
Also, before the Manmohan visit, the Confederation of Indian Industry registered as an official lobbyist in Washington, and went about spending half a million dollars lobbying American politicians for the nuclear deal. After the Manmohan visit, the US Foreign Commercial Service reportedly said American engineering firms, equipment suppliers and contractors faced a $1,000 billion (1 bn =100 crore) opportunity in India. Before President Bush’s visit to India in March 2006, Manmohan Singh signed vast purchases of commercial aircraft from Boeing and Airbus, as well as large weapons’ deals with France and Russia. After the Bush visit, the US Chamber of Commerce said the nuclear deal can cause $100 billion worth of new American business in India’s energy-sector alone. What is going on?
Finally, the main aspect of Manmohan Singh’s address to America’s legislature had to do with agreeing with President Bush “to enhance Indo-US cooperation in the field of civilian nuclear technology”. What precisely does this mean? If it means the Indo-US nuclear deal will help India improve or maintain its existing nuclear infrastructure, well and good. There may be legitimate business for American and other foreign companies in that cause, which also helps India make the efficiency and productivity gains mentioned. Or has the real motivation for the American businessmen driving the deal (with the help of the “CEO Forum” etc) been to sell India nuclear reactors on a turn-key basis (in collaboration with private Indian businessmen) at a time when building new nuclear reactors is unprofitable elsewhere in the world because of low gas prices? India’s citizens may demand to know from the Government whether the Manmohan-Montek deal-making is going to cause importation of new nuclear reactors, and if so, why such an expensive alternative is being considered (relative to e.g. India’s abundant hydroelectric potential) when it will have scant effect in satisfying the country’s energy needs and lead merely to a worsening of our macroeconomic problems. Both Manmohan Singh and Montek Ahluwalia have been already among those to preside over the growth of India’s macroeconomic problems through the 1980s and 1990s.
Lastly, an irrelevant distraction should be gotten out of the way. Are we a “nuclear weapons” state? Of course we are, but does it matter to anything but our vanity? Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev had control over vastly more nuclear weapons and they declared together twenty years ago: “A nuclear war cannot be won and must not be fought”, which is how the Cold War started to come to an end. We need to remind ourselves that India and Pakistan are large, populous countries with hundreds of millions of materially poor, ill-informed citizens, weak tax-bases, humongous internal and external public debts (i.e. debt owed by the Government to domestic and foreign creditors), non-investment grade credit- ratings in world financial markets, massive annual fiscal deficits, inconvertible currencies, nationalized banks, and runaway printing of paper-money. Discussing nuclear or other weapon-systems to attack one other with is mostly a pastime of our cowardly, irresponsible and yes, corrupt, elites.
The Politics of Dr Singh (2006)
May 21, 2006 — drsubrotoroyPreface April 25 2009: This article of mine has become a victim of bowdlerization on the Internet by someone who seems to support Dr Singh’s political adversaries. I should say, therefore, as I have said before that there is nothing personal in my critical assessment of Dr Singh’s economics and politics. To the contrary, he has been in decades past a friend or at least a colleague of my father’s, and in the autumn of 1973 visited our then-home in Paris at the request of my father to advise me, then aged 18, before I embarked on my undergraduate studies at the London School of Economics. My assessments in recent years like “The Politics of Dr Singh” or “Assessing Manmohan” etc need to be seen along with my “Assessing Vajpayee: Hindutva True and False”, “The Hypocrisy of the CPI-M”, “Against Quackery”, “Our Dismal Politics”, “Political Paralysis” etc. (Also “Mistaken Macroeconomics”, June 2009). Nothing personal is intended in any of these; the purpose at hand has been to contribute to a full and vigorous discussion of the public interest in India.
Postscript 2 Sep 2013: See especially Did Jagdish Bhagwati “originate”, “pioneer”, “intellectually father” India’s 1991 economic reform? Did Manmohan Singh? Or did I, through my encounter with Rajiv Gandhi, just as Siddhartha Shankar Ray told Manmohan & his aides in Sep 1993 in Washington? Judge the evidence for yourself. And why has Amartya Sen misdescribed his work? India’s right path forward today remains what I said in my 3 Dec 2012 Delhi lecture!
also from 2014: https://independentindian.com/2014/08/07/haksar-manmohan-and-sonia/
THE POLITICS OF DR SINGH
by
Subroto Roy
First published in The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Special Article, May 21 2006
Manmohan Singh matriculated during Partition, and earned bachelor’s and master’s degrees in economics from Punjab University in 1952 and 1954. He then went to Cambridge to read for the BA over two years. The pro-communist Joan Robinson and Nicholas Kaldor were dominant influences in Cambridge economics at the time. Mark Tully reports Dr Singh saying in 2005 he fell under their influence. “At university I first became conscious of the creative role of politics in shaping human affairs, and I owe that mostly to my teachers Joan Robinson and Nicholas Kaldor. Joan Robinson was a brilliant teacher, but she also sought to awaken the inner conscience of her students in a manner that very few others were able to achieve. She questioned me a great deal and made me think the unthinkable. She propounded the left wing interpretation of Keynes, maintaining that the state has to play more of a role if you really want to combine development with social equity. Kaldor influenced me even more; I found him pragmatic, scintillating, stimulating. Joan Robinson was a great admirer of what was going on in China, but Kaldor used the Keynesian analysis to demonstrate that capitalism could be made to work.”
Now, in fact, what was going on in China at that time was the notorious catastrophe caused by Mao Zedong known initially as the “Little Leap Forward” (with a Stalin-like collectivization of agriculture) and then as the “Great Leap Forward”. Mao later apologised to China’s people for his ignorance of microeconomic principles, admitting he “had not realised coal and steel do not move of their own accord but have to be transported”. If what Robinson was extolling to young Indians at Cambridge like Amartya Sen and Manmohan Singh in the mid 1950s was Mao’s China, it was manifest error.
As for Kaldor, the Canadian economist Harry Johnson independently reported that “being a man who rolls with the times fairly fast”, Kaldor “decided early on that capitalism actually was working. So for him the problem was, given that it works, it cannot possibly work because the theory of it is right. It must work for some quite unsuspected reason which only people as intelligent as himself can see.” Like Robinson, Kaldor made a handful of fine contributions to economic theory. But in policy-making he exemplified the worst leftist intellectual vanity and “technocratic” arrogance.
Returning to India, Manmohan Singh was required to spend three years at Chandigarh. In 1960, he left for Nuffield College to work for an Oxford DPhil on the subject of Indian exports. He returned to Chandigarh as required by government rules for another three years, and in 1966 left again until 1969, this time as a bureaucrat at the new UNCTAD in New York run by Raul Prebisch. A book deriving from his doctoral thesis was published by Clarendon Press in 1964.
In 1969, Dr Singh returned to India becoming Professor of International Trade at the Delhi School of Economics. A technical survey of mainstream Indian economic thinking done by his colleagues Jagdish Bhagwati and Sukhamoy Chakravarty published in the American Economic Review of 1969, made footnote references to his book in context of planning and protectionism, but not in the main discussion of Indian exports which at the time had to do with exchange-rate overvaluation.
After Indira Gandhi’s March 1971 election victory, Dr Singh came to the attention of Parameshwar Narain Haksar, who launched his career in bureaucracy after inviting him to write a political paper “What to do with the victory”. Haksar had been an Allahabad lawyer married into the Sapru family. In London as a student he was a protégé of R. Palme Dutt and Krishna Menon, and openly pro-USSR. He was close to the Nehrus, and Jawaharlal placed him in the new Foreign Service. He was four years older than Indira and later knew her husband Feroze Gandhi who died in 1960. By May 1967 Haksar was Indira’s adviser, and became “probably the most influential and powerful person in the Government” until 1974, when there was a conflict with her younger son. But Haksar’s influence continued well into the 1990s. His deeds include nationalization of India’s banks, the Congress split and creation of the Congress(I), and politicisation of the bureaucracy including the intelligence services. High quality independent civil servants became politically committed pro-USSR bureaucrats instead. Professionalism ended and the “courtier culture” and “durbar” politics began.
Haksar and T. N. Kaul were key figures negotiating the August 1971 “Treaty of Peace, Friendship and Cooperation” with the USSR, which was to run 25 years except the USSR collapsed before then. Indira had hosted Richard Nixon two years previously, and the Nixon-Kissinger attempt to get close to Zhou En Lai’s China using Pakistan’s Z. A. Bhutto and Yahya Khan (coinciding with Pakistan’s civil war) were undoubtedly factors contributing to India’s Soviet alliance.
As Haksar’s protégé, Dr Singh’s rise in the economic bureaucracy was meteoric. By 1972 he was Chief Economic Adviser and by 1976 Secretary in the Finance Ministry. The newly published history of the Reserve Bank shows him conveying the Ministry’s dictates to the RBI. In 1980-1982 he was at the Planning Commission, and in 1982-1985 he was Reserve Bank Governor (when Pranab Mukherjee was Finance Minister), followed by becoming Planning Commission head, until taking his final post before retirement heading the “South-South Commission” invented by Julius Nyerere of Tanzania, from August 1987 until November 1990 in Geneva.
Dr Singh joined Chandrashekhar’s Government on 10 December 1990, when Rajiv Gandhi was Leader of the Opposition yet supporting Chandrashekhar “from the outside”, and left when new elections were announced in March 1991. The first time his name arose in context of contemporary post-Indira Congress Party politics was on 22 March 1991 when M K Rasgotra challenged the present author to answer how Manmohan Singh would respond to proposals being drafted for a planned economic liberalisation of India by the Congress Party authorised by Rajiv since September 1990 (viz., “Memos to Rajiv” The Statesman 31 July-2 August 1991 republished here as “Three Memoranda to Rajiv Gandhi”; “The Dream Team: A Critique” The Statesman 6-8 January 2006 also republished here; see also “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform” published elsewhere here, and in abbreviated form in Freedom First, October 2001).
Rajiv was assassinated on 21 May 1991, resulting in Narasimha Rao (who had been ill and due to retire) becoming PM in June 1991. Dr Singh told Tully: “On the day (Rao) was formulating his cabinet, he sent his Principal Secretary to me saying, `The PM would like you to become the Minister of Finance’. I didn’t take it seriously. He eventually tracked me down the next morning, rather angry, and demanded that I get dressed up and come to Rashtrapati Bhavan for the swearing in. So that’s how I started in politics”. In the same conversation, however, Dr Singh also said he learnt of “the creative role of politics” from Robinson, and hence he must have realised he actually became politically committed when he began to be mentored by Haksar — Indira Gandhi’s most powerful pro-communist bureaucrat. Before 1991, Dr Singh may be fairly described as a statist anti-liberal who travelled comfortably along with the tides of the pro-USSR New Delhi political and academic establishment, following every rule in the bureaucratic book and being obedient in face of arbitrary exercise of political and economic power. There is no evidence whatsoever of him having been a liberal economist before 1991, nor indeed of having originated any liberal economic idea afterwards. The Congress Party itself in May 2002 passed a resolution saying the ideas of India’s liberalisation had originated with neither him nor Narasimha Rao.
Indeed, the 1970s and 1980s saw onset of the worst macroeconomic policies with ruination and politicisation of India’s banking system, origins of the Rs 30 trillion (Rs 30 lakh crore) public debt we have today, and the start of exponential money supply growth and inflation. Along with Pranab Mukherjee, Dr Singh, as the exemplary Haksarian bureaucrat, must accept responsibility for having presided over much of that. If they are to do anything positive for India now, it has to be first of all to undo such grave macroeconomic damage. This would inevitably mean unravelling the post-Indira New Delhi structure of power and privilege by halting deficit finance and corruption, and enforcing clean accounting and audit methods in all government organisations and institutions. Even the BJP’s Vajpayee and Advani lacked courage and understanding to begin to know how to do this, allowing themselves to be nicely co-opted by the system instead. Rajiv might have done things in a second term; but his widow and her coalition government led by Dr Singh, who exemplified India’s political economy of the 1970s and 1980s, appear clueless as to the macroeconomic facts, and more likely to enhance rather than reverse unhealthy fiscal and monetary trends.
Revisionist Flattery of Indira Gandhi
May 7, 2006 — drsubrotoroyInder Malhotra’s Indira Gandhi : A Review Article
by Subroto Roy
First published in The Statesman May 7 2006
Indira Priyadarshini Nehru was fortunate to have been a handsome woman born to an eminent and indulgent father and grandfather. Despite her lack of higher education or significant worldly wisdom or experience, she acquired enough of an aura of being born to rule that she became Congress Party President in 1959 at age 41, and India’s most dramatic Prime Minister from 1966-1977 and again from 1980-1984 when she was assassinated. She was lucky too that the Zoroastrian man she married did not have one of the many long and colourful surnames Indian Zoroastrians can have, but coincidentally shared the same surname as modern India’s founder. Hence arose the iconic name and personage known as Indira Gandhi.
“The evil that men do lives after them, the good is often interred with their bones”, said Shakespeare. Indira Gandhi’s one and paramount good deed as India’s leader and indeed as a world leader of her time was to have fought a war that was so rare in international law for having been unambiguously just. And she fought it flawlessly. The cause had been thrust upon her by an evil enemy’s behaviour against his own people, an enemy supported by the world’s strongest military power with pretensions to global leadership. Victims of the enemy’s wickedness were scores of millions of utterly defenceless, penniless human beings. Indira Gandhi did everything right. She practised patient but firm diplomacy on the world’s stage to avert war if it was at all possible to do. She chose her military generals well and took their professional judgement seriously as to when to go to war and how to win it. Finally, in victory she was magnanimous to the enemy that had been defeated. Children’s history-books in India should remember her as the stateswoman who freed a fraternal nation from tyranny, at great expense to our own people. As a war-leader, Indira Gandhi displayed extraordinary bravery, courage and good sense.
Unfortunately, this was the only arena in which these virtues of hers came to be expressed. India’s serious history-books, beyond those written for or read by children, need to record that her sheer ignorance of the fundamentals of domestic statecraft as well as her caprice, arrogance and hubris caused permanent harm to India’s polity in innumerable dimensions from which we have yet long to recover. On advice first of her childhood acquaintance, the proto-communist P. N. Haksar, and later of her ruffian unprincipled younger son Sanjay, she single-handedly destroyed India’s nascent parliamentary traditions, federalism, the Rule of Law, and its most important political party; the integrity of the civil services, judiciary, police, intelligence services and other public institutions; as well as monetary and fiscal prudence Beside this, she and her younger son Sanjay contributed to destroying communal harmony and political stability in the Punjab, while she and later her older son Rajiv contributed to do the same in Kashmir. She exulted in the personality cult, courtier culture and durbar politics of her father and grandfather.
Many pertinent questions about the personal and political life of Indira Gandhi have remained to be answered by any serious modern biographer. Her relationships with her husband and his rival for her time and affections, her father, remain in darkness, as does, after their deaths, her relationship between 1967- 1974 with Haksar, her key adviser. Her capacity and her failures as a mother to two very different sons also remain unclear. Her own lack of education was transmitted to them and neither succeeded at what he studied to be, though at least Rajiv became a gentleman. Her father had been an indifferent husband to Kamala and she an indifferent wife to Feroze — the most important thing her sons may have done with their lives was to have married women she did not choose for them, and then to have become well-loved spouses themselves. As mother-in-law, her petulant bullying of the young Sikh widow of Sanjay, mother of an infant child at the time, remains to be contrasted with her apparent warmth and generosity towards her Italian-born elder daughter-in-law. All such questions would be ones of feminine gossip or TV-soap operas in case of any ordinary woman but assume political significance for Indians because of the inordinate impact she, her father, her sons and their widows have had on India’s modern history. Why all of India’s national-level politics have acquired a gossipy joint-family tone about them is because she projected onto them no high and universally known political principles whatsoever, but merely her own personal experiences and desire for popularity.
The book at hand provides almost no new fact or insight on any relevant extant personal or political question about Indira Gandhi at all. The one exception has to do with a brief discussion of her relationship with Lal Bahadur Shastri which reveals her naked ambition most clearly, though the author is too ingratiating to wish to draw such a conclusion himself. He meekly deflects blame for her faults onto exogenous random shocks like monsoon failures, the rise in petroleum prices or other uncontrollable international events, or the ill-will of others. The most fawning apologists and cultists are quoted with approval: Sanjay was merely “inept”, the Emergency was brought on by its victims and not such a bad thing really, the Shah Commission resembled “a Chinese people’s court”, Maneka was a “rebellious chit of a girl”, etc. Two decades later, we must expect the greatest detachment and calm objectivity in any serious treatment of this complex stateswoman’s life. What we have instead received — at a time when Rajiv’s widow is in power in Delhi and Haksar’s protégé is her PM, while The Mitrokhin Archives II are published — is a clear attempt at revisionist flattery, complete with Indira’s face smiling at us at the start of every chapter and old propaganda photos from the PIB. This is deeply unfortunate coming from the National Book Trust. Indeed, neither she nor her father deserve further inquiry and reflection today more than do their respective spouses, Feroze Gandhi and Kamala Nehru, both of whom died prematurely.
Lessons for India from Nepal’s Revolution
April 26, 2006 — drsubrotoroyLessons for India from Nepal’s Revolution
Subroto Roy
The Statesman, frontpage, April 26 2006
King Gyanendra of Nepal has lost legitimacy in the eyes of almost all his people. His days as a monarch are numbered. It is as inevitable as night follows day that his dynasty is over, and Nepal will sooner or later become a secular Republic. The practical questions that follow include what is to be done with him and his family, that is, which country should they seek exile in and at what pension, to whom exactly should sovereignty in Nepal pass immediately and in the long term, how may needless bloodshed, civil chaos and mayhem come to be avoided, and how soon can a viable democratic republic and a healthy economy and society emerge.
Salus populi suprema lex: the good of the people is the supreme law. And the good of the people in Nepal today requires Gyanendra to depart (that is, for exile in Britain), after abdicating in favour of his son ~ or better still his infant grandson, placing a Regent acceptable to the Seven-Party Alliance in charge of calling a Constituent Assembly as everyone and especially the Maoists have demanded.
The Government and people of India seem strangely ignorant or indifferent about what is happening right next door to us, even when that door is open. While the people of Nepal almost stormed their Bastille, we witnessed instead the bizarre televised parade of politicians and Bollywood personalities to visit another celebrity in hospital (we should be thankful they have not been allowed anywhere near him).
Our Prime Minister/foreign minister, with his “national security advisor” sitting next to him, flew off to a brief spring holiday in Europe to discuss importation of uranium and BMWs and other such posh things. The Congress Party has said the Prime Minister may have expressed “his own views” on the subject of supporting King Gyanendra’s Friday offer but that the Government of India always supported “multiparty democracy” and the Congress Party supported the government! Have people become even more detached from reality here? If it is the case the Prime Minister has become so utterly consumed by personal hubris that he is making impromptu remarks contrary to his own government’s policies, then it may be time for him to realise he has filled his quota of foreign trips and put in his papers. At the very least, MK Narayanan has been derelict in his duties by joining the Prime Minister in the European spring rather than remaining in India watching Nepal. The Prime Minister has been so negligent as his own foreign minister (for example, handing over his America policy to personal diplomacy by his favoured aide, Mr Montek Singh Ahluwalia) that he is making the country almost miss the foreign minister who had to be fired, an unfortunate thought!
In the last six months, Nepal’s non-Maoist opposition coalesced and the Maoists declared a unilateral cease-fire. India remained preoccupied with the vanities of its own petty dynasties. Why we Indians, despite our pretensions as the world’s largest democracy (in reality, the world’s largest voting public), may have been so dull and ignorant with respect to Nepal’s “trinamul” democratic movement is that we have never had any kind of revolution ourselves.
Revolution is anathema to the pompous bureaucrats of New Delhi, just as it is to the pompous generals of Islamabad. Partition was the one all-consuming trauma experienced by the Indian and Pakistani ruling classes, and they are simply unable to understand populist rebellions of the kind now being seen in Nepal or seen under Sheikh Mujib in East Pakistan almost 40 years ago. The Indira Gandhi brand of populism practised by India’s “democratic leaders” has to do with renting crowds and giving speeches while waving to the TV cameras, always making sure to fly back to air-conditioned comfort in Lutyens Delhi by the end of the day if at all possible. Lutyens Delhi is Royal India, and Royal India secretly sympathises with all Royalty and pseudo-Royalty. Ours has become a democracy upside down where it is not a question of how the interests of the people of India should be represented in New Delhi but how New Delhi’s interests can come to be projected upon the people of India.
In Nepal on the other hand, the questions now precisely have to do with the most difficult issues of sovereignty, political legitimacy and representation. The forced exile of the Shah of Iran was followed by the return of Ayatollah Khomeini from Qom and the brutality and bloodshed of the Islamic Revolution. The exile of Sihanouk of Cambodia was followed by the horrors of the Khmer Rouge. Can mass bloodshed and class war be averted if the exile of King Gyanendra is followed by a Maoist takeover in Nepal? The Maoists are indisputably led by Pushpa Kamal Dahal (Prachanda) who does not appear to be a murderous Pol Pot and has been projected as principled and statesmanlike. But will he be able to control his own creation or could he himself be swept aside? “Revolution is not a tea party” said Mao Zedong. There are at least two other proximate models that are more benign. One was the forced exile of Ferdinand Marcos and his odious family to the USA in 1986, leading to Mrs Benito Aquino becoming President of the Philippines. She and Fidel Ramos had led ordinary people to the most peaceful bloodless revolution ever seen until then, and coined the term “People Power”. Democracy has had its problems here but has survived intact ever since. Another relevant model has to do with the forced departure for Bombay of Hari Singh of Jammu and Kashmir (who pretended to “abdicate” in favour of his young son though in fact no such alternative existed in international law). Sheikh Abdullah knew his constitutional politics well enough and then led J&K to a reasonable Constituent Assembly. Our Pakistani cousins, cut from the same political cloth as ourselves, embarked haplessly saying “That the sovereignty in Pakistan belongs to God Almighty alone and that the Government of Pakistan shall administer the country as His agent”. In the words of Rashid Rida and Maulana Maududi, Islam becomes “the very antithesis of secular Western democracy. The philosophical foundation of Western democracy is the sovereignty of the people. Lawmaking is their prerogative and legislation must correspond to the mood and temper of their opinion… Islam… altogether repudiates the philosophy of popular sovereignty and rears its polity on the foundations of the sovereignty of God and the viceregency (Khilafat) of man.” Sheikh Abdullah by contrast told the J&K Constituent Assembly: “You are the sovereign authority in this State of Jammu & Kashmir; what you decide has the irrevocable force of law. The basic democratic principle of sovereignty of the nation, embodied ably in the American and French Constitutions, is once again given shape in our midst. I shall quote the famous words of Article 3 of the French Constitution of 1791: `The source of all sovereignty resides fundamentally in the nation. Sovereignty is one and indivisible, inalienable and imprescriptable. It belongs to the nation.’ We should be clear about the responsibilities that this power invests us with. In front of us li e decisions of the highest national importance which we shall be called upon to take. Upon the correctness of our decisions depends not only the happiness of our land and people now, but the fate as well of generations to come.”
The fact the young son of Hari Singh then caused or contributed to a putsch against Abdullah is among the most regrettable events contributing to the misfortunes of J&K’s recent history. Nepal is going through its own French Revolution in which Gyanendra is no longer able to claim the “Divine Right of Kings” simply because his people have permanently withdrawn their acceptance of his legitimacy.
In the circumstances, Nepalese of all political colours would do very well to remember that the greatest of them in the history of mankind was a Hindu prince who became the founder of Buddhism. As the Himalayan home of Hindus and Buddhists and many others, the Nepalese Revolution could be among the most exemplary in being peaceful without bloodshed. The aim of Indians and all other friends of Nepal must be to seek to ensure that.
Iran’s Nationalism (2006)
April 6, 2006 — drsubrotoroyIRAN’S NATIONALISM
Is America close to breaking its pledged word?
First published in The Statesman Editorial Page, 6 April 2006
by
Subroto Roy
Ayatollah Khomeini was the Ho Chi Minh of Iran. Ho was both a communist and a Vietnamese nationalist, but America’s Presidents from Eisenhower to Nixon failed to see the latter. Khomeini was both a devout Shia Muslim and an Iranian nationalist yet America’s Presidents from Carter to W. Bush refused to see his Revolution being as much about Iranian nationalism as about creating an Islamic Republic. As a general rule, Western countries allow for nationalism among other Western countries but not among non-Western countries. Immanuel Kant’s dictum of treating everyone as an end in himself/herself and not as a means towards one’s own ends, is applied in intra-Western international relations but often not when the West deals with others. But Indians did not have to be communists to sympathise with Vietnam’s struggle against first France and then America, and Indians do not have to be Shia Muslims to sympathise with Iran’s struggle against an impending Anglo-American aggression. The opaque Manmohan- Montek deal-making with America on behalf of India’s people may need to be set aside in such a context — while it might benefit several dozen businesses on both sides and several hundred bureaucrats may become even fatter with bribes, it may have next to nothing to do with any dimension of India’s national interests.
US pledge 1981, policy 2006
On January 19 1981, the Government of the United States signed what came to be called the Algiers Accord, the first point of which stated: “Non-Intervention in Iranian Affairs: The United States pledges that it is and from now on will be the policy of the United States not to intervene, directly or indirectly, politically or militarily, in Iran’s internal affairs.” This was part of a comprehensive truce between Khomeini’s Iran and the USA in regard to the war-like conditions then prevailing between them. That pledge now seems about to be broken. British newspapers reported on April 2 2006 that the Blair Government is holding “secret talks” with its own Chief of Defence Staff, Chief of Defence Intelligence and others to discuss “an American-led attack, designed to destroy Iran’s ability to develop a nuclear bomb… if Tehran’s leaders fail to comply with United Nations demands to freeze their uranium enrichment programme.” This is despite the British foreign minister saying last month “that a military attack against Iran was ‘inconceivable’”. America’s “National Security Strategy” dated March 16 2006 states the policy clearly: “We may face no greater challenge from a single country than from Iran. For almost 20 years, the Iranian regime hid many of its key nuclear efforts from the international community. Yet the regime continues to claim that it does not seek to develop nuclear weapons. The Iranian regime’s true intentions are clearly revealed by the regime’s refusal to negotiate in good faith; its refusal to come into compliance with its international obligations by providing the IAEA access to nuclear sites and resolving troubling questions; and the aggressive statements of its President calling for Israel to ‘be wiped off the face of the earth’. The United States has joined with our EU partners and Russia to pressure Iran to meet its international obligations and provide objective guarantees that its nuclear program is only for peaceful purposes. This diplomatic effort must succeed if confrontation is to be avoided. As important as are these nuclear issues, the United States has broader concerns regarding Iran. The Iranian regime sponsors terrorism; threatens Israel; seeks to thwart Middle East peace; disrupts democracy in Iraq; and denies the aspirations of its people for freedom. The nuclear issue and our other concerns can ultimately be resolved only if the Iranian regime makes the strategic decision to change these policies, open up its political system, and afford freedom to its people. This is the ultimate goal of U.S. policy. In the interim, we will continue to take all necessary measures to protect our national and economic security against the adverse effects of their bad conduct. The problems lie with the illicit behavior and dangerous ambition of the Iranian regime, not the legitimate aspirations and interests of the Iranian people. Our strategy is to block the threats posed by the regime while expanding our engagement and outreach to the people the regime is oppressing.“
Attack scenario
In one scenario, America will make a surprise cruise-missile attack on Iranian buildings “suspected” of producing biological weapons. If the Iranians respond in any way other than total submission, it will be sufficient to launch a major bombing of Iran’s military facilities using B-2 bombers based in Diego Garcia, England and other American bases, possibly using nuclear “earth penetrating” weapons to attack underground facilities. Of course it is not impossible the British and Americans are merely setting up a bluff to scare the Iranians into complying without a fight, but the existence of aggressive war plans and preparations cannot be doubted.
Now it is possible the Americans will say they are not bound by the pledge made in the Algiers Accord in January 1981 to not intervene in Iran’s affairs. In breach of all diplomatic law, 66 Americans had been taken captive by Iranians seizing the American Embassy on November 4 1979. Six others escaped with the help of the Canadian and Swedish embassies. Of the 66, 13 women and black Americans were released two weeks later; one man was released due to ill-health in July 1980. The remaining 52 including two women and one black American were released on January 20 1981 by the terms of the Algiers Accord just before Ronald Reagan took over as President of the United States. Eight American military personnel were killed on April 25 1980 in a failed attempt to rescue them. The official designations of the 52 (who had been held captive for 444 days) included 10 military attachés; 6 “communications and electronics specialists”; 8 political and administrative officers, and 12 diplomatic/consular staff. In addition there were 12 guards and 4 others. Even if the US Embassy in Tehran was a den of spies as the Iranians claimed, the Revolutionary Government could have ordered them all to leave and to have ended diplomatic relations in accordance with international law. What explained Iranians’ anger for them to have violated international law so brazenly? That was the age before terrorism, and nor was Iran a player in the conflict between Israel and the Arabs.
Iran’s anger stemmed from having felt being used by Britain, America and Soviet Russia for half a century before the 1979 Khomeini Revolution – from having been merely means towards their ends in violation of the Kantian dictum. It was almost as if Britain and America had said to Iran and the entire Middle East, “We invented the internal combustion engine and the automobile which uses it, and we also discovered the petroleum that runs it; the mere fact you happen to sit on this petroleum does not make you own it; we own it too and we will take it by force whenever necessary.” During the Cold War, the USSR followed suit, and now after the Cold War has ended, the new Russia is a Western ally in the same kind of attempted domination over non-Western countries like Iran (or Pakistan and India, who get sold a lot of useless weapons to fight each other with).
Mossadeq the democrat
Specifically, if the January 1981 Algiers Accord was signed by the USA under duress, the Iranians could say that Iran had been cheated into signing the 25 year agreement of September 1954 with an international oil consortium led by the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company. Iran would receive 50% profit on all Iranian oil exported, after paying the AIOC ₤25 million in compensation for having nationalised it in 1951 under the democratic government of Mohammad Mossadeq which had broken off diplomatic relations with Britain. Mossadeq was overthrown by an Anglo-American coup détat in August 1953, and replaced by the compliant General Fazlollah Zahedi and Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi. Arthur Millspaugh, an American invited by the Iranians to help their public finances, once wrote: “Persia cannot be left to herself, even if the Russians were to keep their hands off politically. …Persia has never yet proved its capacity for independent self-government.” Millspaugh’s 1925 book titled America’s Task in Persia seems to have remained the handbook of Western policy towards Iran. Khomeini’s Revolution was its antithesis.

Towards an Energy Policy
April 2, 2006 — drsubrotoroyNote: This article may have initiated the public debate on the economics of the Indo-US nuclear deal. It was published as a Special Article on the Editorial Page of The Sunday Statesman of April 2 2006 but it failed to be uploaded at the website http://www.thestatesman.net because there had been a fire on March 31 2006. The politicians who led the parliamentary debate in 2006 subsequently made reference to it.
See also republished elsewhere here e.g. “India’s Energy Interests”, “India and Energy Security”, “Need for Clarity”/”From Confusion to Clarity”, “Against Quackery”, “Jimmy Carter and the Indo-US Nuclear Deal””, NuksaanFaida Analysis”.
“Towards an Energy Policy”
by Subroto Roy
First published in
The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article 2 April 2006
When was the last time we heard a thorough, well informed debate in Parliament about India’s long-term energy needs and policy-alternatives? The answer is never. Just as Pakistan tends to be run by Islamabad’s generals, we tend to be run by New Delhi’s bureaucrats; both are a legacy of the Raj which was run by small numbers of pompous civil servants and soldiers. Bureaucrats keep as much decision-making information as they can to themselves, give it to Parliament only under duress and then too in garbled opaque form, and share it voluntarily with the public never at all. A bureaucrat of conscience who shares vital information transparently becomes a “whistleblower”, and may risk his/her life and career because assorted mafias invariably surround all government contracting, and, like vampire bats, cannot stand the light of day shed upon them.
The problem with the Manmohan/Montek deal-making with the USA on behalf of India’s people has less to do with rational assessments not having been made of the relative costs and benefits of e.g. nuclear/fossil fuel/renewable energy, as it has to do with the fact it reflects the same lack of transparency (and is accompanied by the same politically correct propaganda) as has existed in other policy-making – like the $12 billion worth of commercial aircraft from Boeing and Airbus bought for our bankrupt nationalized airlines, or spending untold billions of borrowed dollars on new weapons from France, Russia, Britain or whomever to fight unknown enemies in unimagined wars, or throwing newly printed paper-money at every government project that any fool or knave cares to mention.
To be fair, the UPA/Communist dispensation of the public’s largesse is no worse than that of the NDA/RSS. Both are part of New Delhi’s own “Inside-the-Beltway” syndrome, and turn up at the same celebrity wedding-receptions and iftehar parties. Neither minds too much when the other is in power so long as they can keep their government accommodation. Our fundamental political problem may be the absence of any serious party of Left or of Right which is secular, scientific, liberal, nationalist, clean, law-abiding, and fiscally prudent.
Since no national debate on energy-policy has been offered by New Delhi, ordinary citizens will have to create such a debate for themselves. What follows constitutes a few of the barest facts needed to start such an analysis of India’s alternative energy scenarios and their respective costs.
Hydroelectric power does not involve burning any fuels. Instead, the gravitational force of the movement of water from the mountains to the oceans is harnessed to generate electricity. But hydroelectric projects (like the Narmada Dam) can displace people, who must be then compensated and resettled. Burning of organic “fossil fuels” like coal, gas and oil, causes atmospheric oxygen to turn into carbon dioxide, which may affect climate in unknown ways. In 2004, the International Energy Agency’s estimated the new energy capacity worldwide required by rising economic growth in the year 2020 will derive 1400 GW from burning coal (half of it in China and India), 470 GW from burning oil, 430GW from hydro, and 400 GW from renewable sources (like solar or wind power). On the Agency’s assumptions, gas prices will remain low, making construction of new nuclear plants for electricity uneconomical. By 2030, new energy expected to be required worldwide is 4700GW, of which only 150GW is expected from new nuclear plants — which will be replacing existing nuclear plants due to be retired. (Such is the scenario before any new nuclear plants were going to be exported by e.g. USA to India).
Now the fission of an atom of uranium produces perhaps 10 million times the energy produced by combustion of an atom of carbon from coal. Gas and fossil fuels may be cheap and in plentiful supply worldwide for generations to come but the potential for cheap energy from nuclear sources seems practically infinite. Nuclear power can arise from fission of radioactive uranium, plutonium or thorium. India has perhaps 8 million tonnes of monazite deposits along the seacoast of which half may be mined, to yield 225,000 tonnes of thorium metal; we have one innovatively designed thorium reactor under construction. But almost all nuclear energy worldwide today arises from uranium, and there are practically unlimited reserves of that. There is so much uranium in sea water that mankind’s total electricity needs can be satisfied for 7 million years. There is more energy in the uranium impurity present in coal than can arise from actually burning the coal. There is plenty of uranium in granite. None of these sources will become profitable for centuries because there is so much cheap uranium possible to be extracted from conventional ores. In 2001, uranium cost about US$20 per kg or so, translating to US$0.0004 per kwh of electricity. The known reserves of uranium that can be profitably sold at $120 per kg are enough for at least a hundred years. Design improvements in reactors will also improve productivity; e.g. “fast breeder” reactors “breed” more fissile material than they use, and may get 100 times as much energy from a kilogram of uranium as existing reactors do. India has about 95,000 tonnes of uranium metal which may be mined to yield about 61,000 tonnes net for power generation.
Natural uranium is 99.3 percent of the U-238 isotope and 0.7 percent of the radioactive U-235 isotope. Nuclear power requires “enriched uranium” or “yellow cake” in which U-235 has been increased from 0.7 percent to 4 to 5 percent, and that “separation” process is expensive. (Nuclear bombs require highly enriched uranium with more than 90% of U-235). Yellow cake is broken into small pieces, put in metal rods placed in bundles, which are then bombarded by neutrons causing fission. In nuclear bombs, the fission occurs in a small space, and the blast that results kills all life for miles around it by sucking up all the atmospheric oxygen, besides causing firestorms, shock waves and radioactivity. In a civilian reactor, the energy released turns water into steam, which moves turbines powering the generation of electricity. However, while there is no carbon dioxide “waste” as in burning fossil fuels, the “spent” rods of nuclear fuel and other products constitute grave radioactive waste, which is hard if not impossible to dispose of. Many countries like the USA just bury their nuclear waste in remote thinly populated desert areas.
Rational choice between energy sources depends on costs determined by history and geography. France has 59 of the 441 or so civilian nuclear reactors in the world, and generates 78% of its electricity from them, 22% from hydroelectricity. Japan has 54 reactors and generates 34% of its electricity from them. The USA has 104 reactors but generates only 20% of its electricity from them, principally because it has vast alternative sources of energy. In India, installed power generating capacity as of 2003 was 107,533.3MW, of which 71% was from burning fossil fuels. Hydroelectric potential is 150,000MWe. In 2003, total installed hydro capacity with utilities was 26,910MWe (about 18% of the potential). More than 70% of India’s hydroelectric potential is in the North and NorthEast regions put together.
India’s 14 nuclear reactors produce less than 4% of the total electricity being consumed in the country. Even if all other sources of electricity remained constant, and our civilian nuclear capacity alone was made to grow by 100% under the Manmohan-Montek deal with the USA, that would mean less than 8% of total Indian electricity produced. So the first question India’s citizens must ask is why such a fuss has been created about the Manmohan-Montek deal with America. Clearly, the Government of India must come wholly clean with all the facts and analysis it has available on the whole problem of India’s energy future in all its complexity and detail. If and when it does so, we may simply find that the fault lies not in the stars but in ourselves. Whether the US-India nuclear deal stands or falls, it will have scant effect in satisfying the country’s energy needs.
Logic of Democracy (2006)
March 30, 2006 — drsubrotoroyLOGIC OF DEMOCRACY
by
SUBROTO ROY
First published in The Statesman,
Editorial Page Special Article, March 30 2006
Parliament may unanimously vote for a bill on the “Office of Profit” issue but this will have to be consistent with the spirit and letter of the Constitution and with natural law if it is not to be struck down by the Supreme Court. It is thus important to get the logic right.
India is a representative and not a direct democracy. We the people constitute the Electorate who send our representatives periodically to legislative institutions at national, state and local levels. These representatives, namely, Lok Sabha and Legislative Assembly Members and municipal councilors, have a paid job to do on behalf of all their constituents, not merely those who voted for them. They are supposed to represent everyone including those who voted against them or did not vote at all.
In view of this, if the question is asked: “Was India’s interest served by Sonia Gandhi peremptorily resigning as the Lok Sabha Member from Rae Bareli and then immediately declaring she will fight a fresh election from there?”, the answer must be of course that it was not. Mrs Gandhi had been elected after an expensive process of voting and she had a duty to continue to represent all of Rae Bareli’s people (not just her party-supporters) for the duration of the 14th Lok Sabha. Instead she has given the impression that Rae Bareili is her personal fiefdom from where she must prove again how popular she is as its Maharani.
What needed to be done instead was to abolish the so-called “National Advisory Council” which, like the “Planning Commission” is yet another expensive extra-constitutional body populated by delusional self-styled New Delhi worthies. The NAC has been functioning as Mrs Gandhi’s personal Planning Commission, and she lacked the courage to scrap it altogether — just as Manmohan Singh lacks the courage to tell Montek Ahluwalia to close down the Planning Commission (and make it a minor R&D wing of the Ministry of Finance).
Lok Sabha’s duties
What are Lok Sabha Members and State MLAs legitimately required to be doing in caring for their constituents? First of all, as a body as a whole, they need to elect the Government, i.e. the Executive Branch, and to hold it accountable in Parliament or Assembly. For example, the Comptroller and Auditor General submits his reports directly to the House, and it is the duty of individual legislators to put these to good use in controlling the Government’s waste, fraud or abuse of public resources.
Secondly, MPs and MLAs are obviously supposed to literally represent their individual constituencies in the House, i.e. to bring the Government and the House’s attention to specific problems or contingencies affecting their constituents as a whole, and call for the help, funds and sympathy of the whole community on their behalf.
Thirdly, MPs and MLAs are supposed to respond to pleas and petitions of individual constituents, who may need the influence associated with the dignity of their office to get things rightly done. For example, an impoverished orphan lad once needed surgery to remove a brain tumour; a family helping him was promised the free services of a top brain surgeon if a hospital bed and operating theatre could be arranged. It was only by turning to the local MLA that the family were able to get such arrangements made, and the lad had his tumour taken out at a public hospital. MPs and MLAs are supposed to vote for and create public goods and services, and to use their moral suasion to see that existing public services actually do get to reach the public.
Rajya Sabha different species
Rajya Sabha Members are a different species altogether. Most if not all State Legislative Councils have been abolished, and sadly the present nature of the Rajya Sabha causes similar doubts to arise about its utility. The very idea of a Rajya Sabha was first mooted in embryo form in an 1888 book A History of the Native States of India, Vol I. Gwalior, whose author also advocated popular constitutions for the “Indian India” of the “Native States” since “where there are no popular constitutions, the personal character of the ruler becomes a most important factor in the government… evils are inherent in every government where autocracy is not tempered by a free constitution”.
When Victoria was declared India’s “Empress” in 1877, a “Council of the Empire” was mooted but had remained a non-starter even until the 1887 Jubilee. An “Imperial Council” was now designed of the so-called “Native Princes”, which came to evolve into the “Chamber of Princes” which became the “Council of the States” and the Rajya Sabha.
It was patterned mostly on the British and not the American upper house except in being not liable to dissolution, and compelling periodic retirement of a third of members. The American upper house is an equal if not the senior partner of the lower house. Our Rajya Sabha follows the British upper house in being a chamber which is duty-bound to oversee any exuberance in the Lok Sabha but which must ultimately yield to it if there is any dispute.
Parliament in India’s democracy effectively means the Lok Sabha — where every member has contested and won a direct vote in his/her constituency. The British upper house used to have an aristocratic hereditary component which Tony Blair’s New Labour Government has now removed, so it has now been becoming more like what the Rajya Sabha was supposed to have been like.
The corruption of our body-politic originated with the politicisation of the bureaucracy thirty five years ago by Indira Gandhi and PN Haksar. The Rajya Sabha came to be ruined with the “courtier culture” and “durbar politics” that resulted. This bad model which the Congress Party created and followed was imitated by the Congress’s political opponents too. Our Rajya Sabha has now tended to become a place for party worthies who have lost normal elections, superannuated cinematic personalities, perpetual bureaucrats still seeking office, and similar others. The healthiest course of action for Indian democracy may be to close it down completely for a few years, then recreate it ab initio based on its original purposes and intent (but this may not be constitutionally possible to do).
Holding Executive accountable
It is a forgotten platitude that in a representative democracy what elected legislators are supposed to be doing is represent the interests of the Electorate. Along with the Judiciary, the Legislative Branch is supposed to control the Executive Government, which is the natural oppressor of the Electorate. That is why the Legislature must be independent of the Executive — which is the precise intent behind Article 102 (a) of the Constitution of India: “A person shall be disqualified for being chosen as, and for being, a member of either House of Parliament… if he holds any office of profit under the Government of India or the Government of any State…”
In other words, if you are a Lok Sabha MP or State MLA who is supposed to be a part of the august House which has elected the Executive Government and by whom that Government is supposed to be held accountable, then it is a clear conflict of interest if you are yourself in the pay of that Government. As a legislator, you are either in the Executive or you are not. If you are in the Executive, you are liable to be held accountable by the House. If you are not in the Executive, you are duty-bound as an ordinary Member of the House to hold the Executive accountable. The logic is ultimately as clear and simple as that.
It is inevitable that the delineation of the appropriate boundaries between Legislature and Executive will have to be pronounced upon by the Judiciary. The “Office of Profit” issue has opened an opportunity for a Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court to speak on the rights and duties of the Legislative and Executive Branches of Government. And no Constitution Bench has ever spoken unwisely.
Atoms for Peace (or War)
March 5, 2006 — drsubrotoroyAtoms for Peace (or War)
by Subroto Roy
First published in The Sunday Statesman, March 5 2006 Editorial Page Special Article,
“Atoms for Peace” was Dwight D. Eisenhower’s 1953 speech to the UN (presided over by Jawaharlal Nehru’s sister) from which arose the IAEA. Eisenhower was the warrior par excellence, having led the Allies to victory over Hitler a few years earlier.
Yet he was the first to see “no sane member of the human race” can discover victory in the “desolation, degradation and destruction” of nuclear war. “Occasional pages of history do record the faces of the ‘great destroyers’, but the whole book of history reveals mankind’s never-ending quest for peace and mankind’s God-given capacity to build.” Speaking of the atomic capacity of America’s communist adversary at the time, he said: “We never have, and never will, propose or suggest that the Soviet Union surrender what rightly belongs to it. We will never say that the peoples of the USSR are an enemy with whom we have no desire ever to deal or mingle in friendly and fruitful relationship.” Rather, “if the fearful trend of atomic military build-up can be reversed, this greatest of destructive forces can be developed into a great boon, for the benefit of all mankind…. if the entire body of the world’s scientists and engineers had adequate amounts of fissionable material… this capability would rapidly be transformed into universal, efficient and economic usage”. Eisenhower’s IAEA would receive contributions from national “stockpiles of normal uranium and fissionable materials”, and also impound, store and protect these and devise “methods whereby this fissionable material would be allocated to serve the peaceful pursuits of mankind.…to provide abundant electrical energy in the power-starved areas of the world… to serve the needs rather than the fears of mankind.” When Eisenhower visited India he was greeted as the “Prince of Peace” and a vast multitude threw rose petals as he drove by in an open limousine.
Now, half a century later, Dr Manmohan Singh read a speech in Parliament on February 27 relating to our nuclear discussions with America. But it seems unclear even his speech-writers or technical advisers knew how far it was rhetoric and how far grounded in factual realities. There is also tremendous naivete among India’s media anchors and political leaders as to what exactly has been agreed by the Americans on March 2.
Churchill once asked what might have happened if Lloyd George and Clemenceau told Woodrow Wilson: “Is it not true that nothing but your fixed and expiring tenure of office prevents you from being thrown out of power?” The same holds for George W. Bush today. Wilson made many promises to the world that came to be hit for a six by US legislators. In December 2005, Edward Markey (Democrat) and Fred Upton (Republican) promised to scuttle Bush’s agreements with India, and once the pleasant memories of his India visit fade, Bush may quite easily forget most things about us. All the Americans have actually agreed to do is to keep talking.
It needs to be understood that submarine-launched ballistic missiles are the only ultimate military deterrent. Land and air forces are all vulnerable to a massive first-strike. Only submarines lurking silently for long periods in waters near their target, to launch nuclear warheads upon learning their homeland had been hit by the enemy, act as a deterrent preventing that same enemy from making his attack at all. Indeed, the problem becomes how a submarine commander will receive such information and his instructions during such a war. (For India to acquire an ICBM capability beyond the MRBM Agni rockets is to possess an expensive backward technology — as retrograde as the idea India should spend scarce resources sending manned moon missions half a century after it has already been done. The secret is to do something new and beneficial for mankind, not repeat what others did long ago merely to show we can now do it too.) A nuclear-armed submarine needs to be submerged for long periods and also voyage long distances at sea, and hence needs to be nuclear-powered with a miniature version of a civilian nuclear reactor aboard in which, e.g. rods of enriched uranium are bombarded to release enough energy to run hydroelectric turbines to generate power. Patently, no complete separation of the use of atomic power for peace and war may be practically possible. If India creates e.g. its own thorium reactors for civilian power (and we have vast thorium reserves, the nuclear fuel of the future), and then miniaturised these somehow to manufacture reactors for submarines, the use would be both civilian and military. In 1988 the old USSR leased India a nuclear-powered submarine for “training” purposes, and the Americans did not like it at all. In January 2002, Russia’s Naval Chief announced India was paying to build and then lease from 2004 until 2009 two nuclear-powered Akula-class attack submarines, and Jaswant Singh reportedly said we were paying $1 thousand crore ($10 bn) for such a defence package. Whether the transaction has happened is not known. Once we have nuclear submarines permanently, that would be more than enough of the minimum deterrent sought.
Indeed, India’s public has been barely informed of civilian nuclear energy policy as well, and an opportunity now exists for a mature national debate to take place — both on what and why the military planning has been and what it costs (and whether any bribes have been paid), and also on the cost, efficiency and safety of the plans for greater civilian use of nuclear energy. Government behaviour after the Bhopal gas tragedy does not inspire confidence about Indian responses to a Three Mile Island/Chernobyl kind of catastrophic meltdown.
That being said, the central question remains why India or anyone else needs to be nuclear-armed at all. With Britain, France or Russia, there is no war though all three are always keen to sell India weapons. Indeed it has been a perennial question why France and Britain need their own deterrents. They have not fought one another for more than 100 years and play rugby instead. If Russia was an enemy, could they not count on America? Or could America itself conceivably become an enemy of Britain and France? America owes her origins to both, and though the Americans did fight the British until the early 1800s, they have never fought the French and love the City of Paris too much ever to do so.
Between China and India, regardless of what happened half a century ago, nuclear or any war other than border skirmishes in sparse barren lands is unlikely. Ever since Sun Yat-sen, China has been going through a complex process of self-discovery and self-definition. An ancient nation where Maoism despoiled the traditional culture and destroyed Tibet, China causes others to fear it because of its inscrutability. But it has not been aggressive in recent decades except with Taiwan. It has threatened nuclear war on America if the Americans stand up for Taiwan, but that is not a quarrel in which India has a cogent role. China (for seemingly commercial reasons) did join hands with Pakistan against India, but there is every indication the Chinese are quite bored with what Pakistan has become. With Pakistan, our situation is well-known, and there has been an implicit equilibrium since Pokhran II finally flushed out their capacity. Had India ever any ambition of using conventional war to knock out and occupy Pakistan as a country? Of course not. We are barely able to govern ourselves, let aside try to rule an ideologically hostile Muslim colony in the NorthWest. Pakistan’s purported reasons for acquiring nuclear bombs are spurious, and cruelly so in view of the abject failures of Pakistan’s domestic political economy. Could Pakistan’s Government use its bombs against India arising from its own self-delusions over J&K? Gohar Ayub Khan in 1998-1999 threatened to do so when he said the next war would be over in two hours with an Indian surrender. He thereby became the exception to Eisenhower’s rule requiring sanity. An India-Pakistan nuclear exchange is, unfortunately, not impossible, leaving J&K as Hell where Jahangir had once described it as Heaven on Earth.
America needs to end her recent jingoism and instead rediscover the legacy of Eisenhower. America can lead everyone in the world today including Russia, China, Israel, Iran and North Korea. But she can do so only by example. America can decommission many of her own nuclear weapons and then lead everyone else to the conference table to do at least some of the same. Like the UN, the IAEA (and its NPT) needs urgent reform itself. It is the right time for serious and new world parleys towards the safe use of atoms for peace and their abolition in war. But are there any Eisenhowers or Churchills to lead them?
Separation of Powers: India, the USA, Pakistan
February 13, 2006 — drsubrotoroySEPARATION OF POWERS (2006)
Montesquieu’s Spirit of the Laws outlined a doctrine that applies to India, the USA and all constitutional democracies: there is no monopoly of political wisdom.
By SUBROTO ROY
First published in The Sunday Statesman, The Statesman Editorial Page,
Special Article Feb 12-13 2006
The Speaker’s noble office is that of the single member of the House, traditionally chosen by unanimity, whose task it is to self-effacingly maintain order in Parliamentary debate and proceedings, so that the House’s work gets done. C’est tout. Once chosen Speaker, he ipso facto retires from partisan politics for life. The Speaker neither contributes to the substance of Parliamentary debate (except in the rare case of a tie) nor has to feel personally responsible for Parliament’s conduct.
Our Parliament has tended to become so dysfunctional since Indira Gandhi and her sycophants destroyed its traditions 30 years ago, that supervising its normal work is an onerous enough task for even the finest of Speakers to handle.
The Lok Sabha’s incumbent Speaker has tended to see himself as the champion of Parliament. He need not. He does not command a majority in the Lok Sabha; the Government Party does. We have had the oddest peculiarity unfolding in India at present where the person who does command the Lok Sabha’s majority, and therefore who would be normally defined as Prime Minister of India, has chosen to nominate someone who is not a member of the Lok Sabha to act as Prime Minister, i.e. to command the Lok Sabha’s majority. (The Rajya Sabha was and remains irrelevant to most things important to Indian democracy, regardless of its narcissism and vanity). Someone with access to 10 Janpath should have told Sonia Gandhi in May 2004 that if she did not wish to be PM and wanted to gift the job to someone else, she should do so to someone who, like herself, had been elected to the Lok Sabha, like Pranab Mukherjee (elected for the first time) or Kamal Nath or Priya Ranjan (both veterans).
Manmohan Singh, a former Lok Sabha candidate, may as Finance Minister have been able to progress much further with economic reforms. But sycophancy has ruled the roost in the Congress’s higher echelons, and nobody had the guts to tell her that. Indeed as early as December 2001, Congress leaders knew that in the unlikely event they won the polls, Manmohan Singh would likely be PM by Sonia Gandhi’s choice (though he was not expected to last long at the top), and yet he did not contest the Lok Sabha polls in 2004.
The Government of the day, not the Speaker, is Parliament’s champion in any discussion with the Supreme Court over constitutional rights and Separation of Powers. And the Government has in fact quietly and sensibly requested the Supreme Court to set up a Constitutional Bench for this purpose. Such a Constitutional Bench shall have cause to ask itself how far Kesavananda Bharati needs to be tweaked if at all to accommodate the contention that Parliament has a right to judge its own members. The Court may well likely say that of course Parliament has a right to judge its own members but even that right is not an absolute right, (nothing is). Even Parliament’s right to judge its own members must be in accordance with natural law, with principles of justice, with due and clearly defined processes. E.g. the established Privileges Committee and not the ad hoc Bansal Committee had to do the needful.
Imagine a hypothetical case of fantastic fiction where half a dozen independent MPs are elected to a future Lok Sabha, and then take it upon themselves to expose corruption and shenanigans of all major political parties. Our fantastic super-heroes become whistleblowers within Parliament itself while remaining totally incorruptible as individuals — like Eliot Ness’s team who jailed Al Capone and other gangsters, and came to be depicted in Hollywood’s The Untouchables. These Untouchables would come to be feared and despised by everyone from Communists on one side of the political spectrum to Fascists on the other. They would upset everybody precisely because they were so clean and were not purchasable. The Government and Opposition of the day might wellgang up to expel such troublemakers and even fabricate charges to do so. (Now there’s a script for a Bollywood movie!)
What our Supreme Court’s Constitutional Bench decides now in the matter at hand will determine the fate of our super-heroes in such a future fantasia. The present case is a polar opposite — where MPs have been caught on camera with their sordid fingers in the cookie-jar, and then made to walk the plank immediately by their peers. Yet natural law applies here as it will to our fantastic future fighters, and this is what the Bench would have to speak on.
Why the present situation continues to be disconcerting is because the whole country heard all the holier-than-thou protestations, yet everyone continues to take a very dim view of what they see of politicians’ behaviour. There remain strong suspicions that only a few very tiny tips of very large icebergs were or can be caught on camera. Large-scale deals and contracts involve payments into invisible bank accounts, not petty cash into pockets or even suitcases filled with cash sloshing around Delhi.
What we have desperately needed in the situation is modern prime ministerial leadership which could intelligently and boldly guide national debate in the right direction on the whole matter of probity in public life. Why a distinguished parliamentarian like the Speaker has found himself in the limelight is because neither the de jure nor de facto Prime Ministers of India are anywhere to be seen thinking on their feet on these central issues of constitutional procedure and practice. They tend to use prepared scripts and may be temperamentally disinclined to do what has been called for by these unscripted circumstances. (Indeed the much-maligned H. D. Deve Gowda could be alone among the bevy of recent PMs who has been able to think on his feet at all.)
Collapse Before Executive Power
In the meantime, the United States is going through its own Separation of Powers’ crisis. As explained in these columns previously, the American system is distinctly different from the British, and our own system is midway between them. Yet similar principles may be discerned to apply or fail to be applied in all.
Winston Churchill once perspicaciously observed:
“The rigid Constitution of the United States, the gigantic scale and strength of its party machinery, the fixed terms for which public officers and representatives are chosen, invest the President with a greater measure of autocratic power than was possessed before (the First World War) by the Head of any great State. The vast size of the country, the diverse types, interests and environments of its enormous population, the safety-valve function of the legislatures of fifty Sovereign States, make the focussing of national public opinion difficult, and confer upon the Federal Government exceptional independence of it except at fixed election times. Few modern Governments need to concern themselves so little with the opinion of the party they have beaten at the polls; none secures to its supreme executive officer, at once the Sovereign and the Party Leader, such direct personal authority.”
America’s Legislative Branch has, on paper, strong powers of advice and consent to control errors, excesses or abuse of power by the Executive President. But (with rare and courageous exceptions like Sen. Robert C. Byrd of West Virginia) the Legislature cravenly collapsed before the father-son Bush presidencies in regard to the Middle East wars of recent years. America’s once-revered federal judiciary has also tended to lose its independence of mind with overt politicisation of judicial appointments in recent decades.
Bush the First went to war against Saddam Hussein (a former American ally against Islamic Iran) at least partly with an eye to winning re-election in 1992 (which he would have done as a result but for a random shock known as Ross Perot; Bill Clinton became the beneficiary). Bush the Second obsessively wished to follow up on the same, to the point of misjudging the real threat to America from Bin Laden and fabricating a false threat from an emasculated Saddam.
America’s Legislature palpably failed to control her Presidents. Now, late in the day, after all the horses have bolted, the Senate Judiciary Committee began tepid hearings on February 5 2006 into whether the President authorized laws to be broken with impunity in regard to wire-tapping some 5,000 citizens (doubtless mostly non-white and Muslim) without judicial warrants. Republican Senator Arlen Specter, the Committee’s Chairman, has said he believes the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act has been “flatly” violated, and “strained and unrealistic” justifications are now being offered. Bush’s men, from his Vice President and Attorney General to political intelligence operatives, have brazenly placed in the dustbin the traditional principle fiat justitia pereat mundus — let justice be done even if the world perishes — saying that the Sovereign can do just as he pleases to save the realm from external enemies as he might perceive and define them to be.
What this kind of collapse in current American practice reveals is a new aspect unknown at the time of Montesquieu’s Spirit of the Laws. In the modern world, Separation of Powers involves not merely constitutional institutions like Executive, Legislature and Judiciary but also the normal civil institutions of a free and open society, especially academic institutions and the press. In America, it has been not merely the Legislature and Judiciary which have tended to collapse before Executive Power in regard to the recent Middle East wars, but the media and academia as well.
“Embedded reporters” and Fox TV set the tone for America’s official thought processes about Iraq and the Muslim world — until it has become too late for America’s mainstream media or academics to recover their own credibility on the subject. On the other hand, unofficial public opinion has, in America’s best traditions, demonstrated using vast numbers of Internet websites and weblogs, a spirited Yankee Doodle individuality against the jingoism and war-mongering of the official polity.
Neither the press nor academia had collapsed the same way during America’s last major foreign wars in Vietnam and Cambodia forty years ago, and it may be fairly said that America’s self-knowledge was rather better then than it is now, except of course there were no Internet websites and weblogs.
Our Pakistani Cousins
Across the border from us, our Pakistani cousins are, from a political and constitutional point of view, cut from the same cloth as ourselves, namely the 1935 Government of India Act, and the Montague-Chelmsford and Morley-Minto reforms earlier. However, ever since Jinnah’s death, they have refused to admit this and instead embarked haplessly on what can only be called an injudicious path of trying to write a Constitution for a new Caliphate. The primary demand of the main scholars influencing this process was “That the sovereignty in Pakistan belongs to God Almighty alone and that the Government of Pakistan shall administer the country as His agent”. By such a view, in the words of Rashid Rida and Maulana Maududi, Islam becomes “the very antithesis of secular Western democracy. The philosophical foundation of Western democracy is the sovereignty of the people. Lawmaking is their prerogative and legislation must correspond to the mood and temper of their opinion… Islam… altogether repudiates the philosophy of popular sovereignty and rears its polity on the foundations of the sovereignty of God and the viceregency (Khilafat) of man.” (Rosenthal, Islam & the Modern National State, Cambridge 1965.) Pakistan’s few modern constitutionalists have been ever since battling impossibly to overcome the ontological error made here of assuming that any mundane government can be in communication with God Almighty. In the meantime, all normal branches of Pakistan’s polity, like the electorate, press, political parties, Legislature and Judiciary, have remained at best in ill-formed inchoate states of being — while the Pakistan Armed Forces stepped in with their own large economic and political interests and agendas to effectively take over the country and the society as a whole, on pretext of protecting Pakistan from India or of gaining J&K for it. Pakistan’s political problems have the ontological error at their root. Pakistan’s political parties, academics and press, have with rare exceptions remained timid in face of the militaristic State — directing their anger and frustration at an easier target instead, namely ourselves in India. The Pakistan Government’s way of silencing its few political, academic or press dissidents has been to send them into comfortable exile abroad.
Sheikh Abdullah Contrasted
Pakistan’s perpetual constitutional confusion deserves to be contrasted with the clarity of Sheikh Mohammad Abdullah’s thinking, e.g. his 5 November 1951 speech to the Constituent Assembly of J&K: “You are the sovereign authority in this State of Jammu & Kashmir; what you decide has the irrevocable force of law. The basic democratic principle of sovereignty of the nation, embodied ably in the American and French Constitutions, is once again given shape in our midst. I shall quote the famous words of Article 3 of the French Constitution of 1791:- ‘The source of all sovereignty resides fundamentally in the nation. Sovereignty is one and indivisible, inalienable and imprescriptable. It belongs to the nation.’ We should be clear about the responsibilities that this power invests us with. In front of us lie decisions of the highest national importance which we shall be called upon to take. Upon the correctness of our decisions depends not only the happiness of our land and people now, but the fate as well of generations to come.”
Contrasting the Pakistani views of constitution-making with those of Sheikh Abdullah may help to explain a great deal about where we are today on the delicate and profound subject of J&K. (See “Solving Kashmir”, The Statesman, December 1—3, 2005)
India’s current debate about Separation of Powers needs to keep at a distance the clear negative examples of our American friends, who have brought upon themselves in recent times a craven collapse of Legislature, Judiciary, press and academia to the Executive President (as Churchill had seemed to predict), as well as of our Pakistani cousins who have continued with general political and civil collapse for half a century. Because our universities are all owned by the State, India’s academics, from Communist to Fascist, have tended to be servile towards it. In respect of the press, the power of independent newspapers has been dwindling, while the new TV anchors have created their own models of obsequiousness and chummery towards New Delhi’s ruling cliques of the day. It thus becomes India’s Supreme Court which remains the ultimate guardian of our Constitution and the safest haven of our very fragile freedoms — besides of course our own minds and hearts.


Diplomatic Wisdom (2006)
January 31, 2006 — drsubrotoroyDIPLOMATIC WISDOM
by Subroto Roy
Editorial page, The Statesman, January 31 2006
Indian diplomacy has, almost accidentally, shown some wisdom. The King of Saudi Arabia should have been long ago invited to be Chief Guest on Republic Day. His Majesty immediately reciprocated with the most gracious words possible: “I consider myself to be in my second homeland. The relationship between India and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is an historic one, we have been old friends and, God willing, this visit will renew these historic ties”. Indeed the King should be invited to make a full State visit in the near future travelling all over India, including Srinagar Valley ; where Khruschev and Bulganin went in 1955!
India has the second largest population of Muslim believers in the world after Indonesia, and it is only right the Keeper of the Holy Places of Islam should see for himself that India is indeed dar-ul-aman, not the dar-ul-harb that the propaganda of the Pakistanis and their terroristic protégés have made it out to be in Saudi and Gulf power circles.
Kalam and the King
The Vajpayee Government deserves a little credit for the present success, because it was they who caused the fact that His Majesty Faisal Ibn Abdullah Ibn Muhammad Al-Saud was hosted by an Indian rocket scientist born in a Muslim family in an impecunious fishing village of Tamil Nadu. The King and his princes would not have failed to feel the poignancy in that. India is also the second largest country of Shiá Islam after Iran, and Ayatollah Khatami was Chief Guest a few years ago when he was President of Iran. It has been argued in these columns (“Solving Kashmir”, The Statesman, December 1-3, 2005) that the solution to J&K requires Indian diplomacy with Iran and Afghanistan as well ; which, incidentally, will make the hollowness of Pakistan’s claims in J&K most obvious.
Now the President of the United States is due to visit India shortly. George W Bush is the third Republican President to come to India after Dwight D. Eisenhower and Richard Nixon. His predecessor Bill Clinton came as a single man at the end of his second term, on holiday from a rocky marriage, to dance with Rajasthani women and indulge his love of Indian food. Before Clinton in 2000, the last American President to visit was Jimmy Carter in 1978, who gave a stirring speech to Parliament about democracy after Morarji Desai had defeated Indira Gandhi’s Emergency. George Bush, also in his second term, will come to India amid controversy.
“You’re a good man”, Bush condescendingly said to Manmohan Singh in Washington, half-remembering that morning’s intelligence briefing memo. Had our PM been more experienced of the world he could have replied equally loudly: “Thanks, you’re not so bad yourself. Let’s chop some wood next time”. It is almost definite there will be no agreement on the nuclear collaboration deal, and that the dispute erupting over Iran may have enlarged itself. Platitudes will be exchanged but the fact that the President has chosen to combine his visit to India with a visit to his buddies in the Pakistani Government will not go unnoticed in the MEA.
“Balance of power” has been the motif of Anglo-American foreign policy in Asia at least ever since the Arabs were induced to revolt against the Turks by Allenby and Lawrence, followed by pitting Iran and the Arabs against each other. The same goes for India and Pakistan. Also, our rather uncouth Communists have vowed to make their presence felt in street-protests and boycotts of Parliament when Bush comes.
FDR & Martin Luther King Jr
In this tense atmosphere, where the summit may actually falter rather badly on substance, Manmohan Singh will need to make some important symbolic gestures. Going to meet the Saudi King at the airport was an appropriate gesture. Clinton had expected the Indian PM to meet him too, and was visibly disappointed to land in the middle of the night only amidst the lights of the TV cameras. The Bushes should be met at the airport by our PM and his spouse. The President is our honoured guest and guests are to be treated like gods.
In the same vein, four boulevards across India’s largest cities deserve to be named after four American heroes: Franklin Delano Roosevelt, Martin Luther King Jr., Dwight D. Eisenhower and Abraham Lincoln. The first two were Democrats, the latter two Republicans.
Naming a boulevard in New Delhi after FDR would belatedly acknowledge his small, spontaneous yet critical and principled role in support of Indian independence that, shockingly, remains unrecognised in India. Britain could not expect American support against German and Japanese imperialism while expecting the Americans not to support Indian aspirations for national freedom. India’s own academic historians, mostly under influence of either Communist or RSS methodologies, have failed even to produce objective biographies of major national leaders, let aside candid accounts of British rule, the development of the Indian nation-state, the Transfer of Power or Partition.
The same intellectual sloppiness has extended to economics too, and underlies the gross misunderstanding of India’s monetary and fiscal histories as was outlined recently in these columns. It has required a young American scholar, Dinyar Patel, writing in an official American Government publication to outline Roosevelt’s role during India’s independence (Span, March 2005).
Where FDR helped India’s struggle for freedom, Martin Luther King Jr adopted India’s method to lead America’s blacks (“Negroes” and “coloureds” as they were then called) to freedom within their own country. MK Gandhi had corresponded with Tolstoy after beginning his campaign of passive resistance to unjust South African laws, and he read Henry Thoreau’s essay on civil disobedience when he was already in jail for that very same offence. Many years later, the young Alabama preacher put to use Gandhi’s example of courageous peaceful defiance of injustice in his own sweet land of liberty. On receiving the Nobel Peace Prize on 10 December 1964, King said: “Non-violence is the answer to the crucial political and moral question of our time – the need for man to overcome oppression and violence without resorting to violence and oppression. Civilisation and violence are antithetical concepts. Negroes of the United States, following the people of India, have demonstrated that non-violence is not sterile passivity, but a powerful moral force which makes for social transformation”. Of course, King like Gandhi would have been appalled by the religious, colour, caste and racial prejudices of contemporary Indians, Pakistanis etc today, and naming a boulevard in King’s name may do more for our own moral well-being than anything else.
Eisenhower and Lincoln
As for Dwight Eisenhower and Abraham Lincoln, the former may well be seen in later centuries as the greatest of 20th Century American Presidents as the latter was of the 19th. Though they had nothing to do with India, naming boulevards after them would remind Indians of the existence of great men in world history.
Jyoti Basu’s Communists once named streets in Kolkata after Lenin and Ho Chi Minh, and still pay annual obeisance at Lenin’s statue with clenched fists and garlands. Ho Chi Minh was a great nationalist and may have deserved an Indian street but it was a cheap and gratuitous insult by the Communists to name the very street on which the American Consulate stood after the Vietnamese leader who was then their enemy. The Americans were mature enough at the time to ignore it and not pull out their Consulate from Kolkata — the very same Consulate that is so highly in demand with Basu’s successor, Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee.
Under influence of the well-known academic apologists for Communist China, Bhattacharjee has been recently extolling the virtues of Mao Zedong and Zhou Enlai too – apparently ignorant of the 40 million Chinese that Mao killed and apparently forgiving Zhou’s hatred of and perfidy against India. Before any further such nonsense occurs, we should name roads after FDR, King, Eisenhower and Lincoln, and the time to do it would be when George W. Bush makes his visit.
Unaccountable Delhi: India’s Separation of Powers’ Doctrine
January 13, 2006 — drsubrotoroyUNACCOUNTABLE DELHI
India’s Separation Of Powers’ Doctrine
First published in The Statesman Jan 13 2006 Editorial Page Special Article,
By Subroto Roy

The Speaker does not like the fact the High Court has issued notices questioning the procedure he followed in expelling MPs from Parliament. Sonia Gandhi’s self-styled “National Advisory Council” has demanded control over disbursement of 100,000,000,000 rupees of public money. The Manmohan Singh Government plans to quietly ignore the Supreme Court’s finding that it had breached India’s Constitution in imposing President’s Rule in Bihar. All three issues have to do with application of India’s Separation of Powers Doctrine, i.e. the appropriate delimitation of Constitutional powers between our Legislature, Executive and Judiciary.
A constitutional crime was attempted in India during the Indira-Sanjay Gandhi political “Emergency” declared on 26 June 1975. On 10 November 1975 (a time of press censorship) a 13-judge Bench of the Supreme Court met to hear the Government plead for overrule of Kesavananda Bharati (A.I.R. 1973 S.C. 1461), a landmark Nani Palkhivala once called “the greatest contribution of the Republic of India to constitutional jurisprudence”. Within two days, the Government had failed in the Court, and Kesavananda held. What was upheld? That while India’s Parliament was sovereign and could amend the Constitution, the amending power may not be used to alter or destroy “the basic structure or framework of the Constitution”. And the Supreme Court decides for itself whether Parliament has exceeded its legitimate power to amend.
Basic structure
Palkhivala’s description of what constitutes the “basic structure or framework” of India’s Constitution is excellent enough: “the rule of law, the right to personal liberty and freedom from arbitrary arrest and imprisonment, the right to dissent which implies the freedom of speech and expression and a free press are… a part of the basic structure of a free democracy, and it is these priceless human freedoms which cannot be destroyed by Parliament in exercise of its amending power. Thus Kesavananda’s case ensures that tyranny and despotism shall not masquerade as constitutionalism.”
Palkhivala argued that, if anything, the aspects of Kesavananda that needed to be set aside were those that had over-ruled Golaknath (A.I.R. 1967 S.C. 1643) which said Parliament should not be held to have the power to abridge any fundamental right, indeed any amended article which abrogates any fundamental right is invalid.
Dicey said “In the principle of the distribution of powers which determines its form, the constitution of the United States is the exact opposite of the English constitution.” Kesavananda Bharati showed the midway point between the two in constitutional jurisprudence anywhere in the world. We are like the Americans and unlike the British first in being a Republic, and secondly in having an explicit written Constitution. We are like the British and unlike the Americans in being a parliamentary democracy where the Executive Branch of Government, namely the Prime Minister and his/her Cabinet is elected from within the Legislative Branch of Government, namely, Parliament, and must at all times retain the confidence of the latter, specifically the Lok Sabha, the House of the People.
The American Executive Branch has a directly-elected President who chooses his administration, and it is commonplace for him to not have the confidence of the Upper or Lower House of the Legislature, to the point that one recent president had to undergo impeachment proceedings and barely survived. There is no constitutional crisis in America if the Legislature loathes the President and wishes him out. The American President and his Executive Branch stay in office until the last minute of his fixed term.
PM answers to Parliament
In our system, the Prime Minister answers at all times to Parliament. Parliament in India’s democracy has normally meant the House of the People — where every member has contested and won a direct vote in his/her constituency. India’s current Lok Sabha has set a constitutional precedent not seen in more than a hundred years anywhere in electing an Executive led by someone not a member. The British Upper House used to have an aristocratic hereditary component which Mr Blair’s New Labour Government has removed, making it more like what the Rajya Sabha was supposed to be — except that by now our Rajya Sabha has tended to become a place for party worthies who have lost normal elections, superannuated cinematic personalities, perpetual bureaucrats still seeking office, and others who really should be at home helping to raise the grandchildren. Parliament may not have fully recovered its health ever since that constitutional crime committed against the Republic known as the Indira-Sanjay “Emergency” (and at least one member of Sanjay’s coterie wields much power today).
Crimes and misdemeanours
The Supreme Court’s finding that the Government breached the Constitution by imposing President’s Rule in Bihar is a finding not of a constitutional crime but of a constitutional misdemeanour. (For reasons given already in these columns on 20 October 2005, it has nothing to do with the President, who merely embodies the sovereignty of our Republic.) For an Executive Order or Legislative Act to be found by a competent Court as being unconstitutional means merely that it does not have to be obeyed by citizens. In the Bihar case, the Supreme Court found this consequence irrelevant because new elections were already in process, the result of which would come from the most authentic democratic voice possible, namely, the same people who elect the House of the People in the first place. India’s Executive has been found to have committed a constitutional misdemeanour, for which it needed to apologise to the Court and Parliament (who are its constitutional co-equals) and then ask the latter to renew its confidence — in which event, life goes on. If confidence was not renewed, the Government would fall and a new Government would have to be formed. But we do not have yet the idea of a backbench revolt —mainly because all the front benches themselves have tended to be in such confusion and disarray with regard to parliamentary traditions, processes and functions.
The Supreme Court as the ultimate protector of the Constitution would be well within its prerogative to oversee whether a Parliamentary Speaker has acted appropriately. Consider a hypothetical case. Once elected, a Speaker is supposed to have no party-affiliation ever more for the rest of his/her life. Suppose, hypothetically, a controlled experiment found a Speaker systematically biased in favour of his/her own former party-members and against their opponents. Where but the Courts could such arbitrariness be effectively remonstrated against? Even if the incumbent Speaker impossibly imagines himself the personal embodiment of the Legislative Branch, he is not beyond the Constitution and therefore not beyond India’s Separation of Powers’ Doctrine.
The Opposition had alleged that the Speaker failed to follow procedure which required the culprits in the expulsion case be referred to the Privileges Committee. But beyond that the Opposition was too confused and guilt-ridden to pursue the matter during the dying moments of Parliament’s Winter Session. In the clear light of day, the issue has now ended up in the Courts. If the Supreme Court eventually rules the Speaker had in fact failed to follow Parliament’s own procedures (and hence breached Constitutional practices), the Speaker would need to apologise to the Courts and the House that elected him, and perhaps offer to fall on his sword.
Finally, for the “National Advisory Council”, a wholly unelected body, to demand a say for itself over spending Rs. 100 billion in State and Union Government budget-making, would be another constitutional misdemeanour — unless its members are merely on the personal staff of the Hon’ble Member representing Rae Bareili, who may of course introduce whatever legislation on money-bills that any other Lok Sabha Member may do.
The Dream Team: A Critique (2006)
January 8, 2006 — drsubrotoroyThe Dream Team: A Critique
by Subroto Roy
First published in The Statesman and The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, January 6,7,8, 2006
(Author’s Note: Within a few weeks of this article appearing, the Dream Team’s leaders appointed the so-called Tarapore 2 committee to look into convertibility — which ended up recommending what I have since called the “false convertibility” the RBI is presently engaged in. This article may be most profitably read along with other work republished here: “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform”, “Three Memoranda to Rajiv Gandhi”, “”Indian Money & Banking”, “Indian Money & Credit” , “India’s Macroeconomics”, “Fiscal Instability”, “Fallacious Finance”, “India’s Trade and Payments”, “Our Policy Process”, “Against Quackery”, “Indian Inflation”, etc)
1. New Delhi’s Consensus: Manmohantekidambaromics
Dr Manmohan Singh has spoken of how pleasantly surprised he was to be made Finance Minister in July 1991 by PV Narasimha Rao. Dr Singh was an academic before becoming a government economic official in the late 1960s, rising to the high office of Reserve Bank Governor in the 1980s. Mr Montek Singh Ahluwalia now refers to him as “my boss” and had been his Finance Secretary earlier. Mr Ahluwalia was a notable official in the MacNamara World Bank before being inducted a senior government official in 1984. Mr P Chidambaram was PVNR’s Commerce Minister, and later became Finance Minister in the Deve Gowda and Gujral Governments. Mr Chidamabaram is a Supreme Court advocate with an MBA from Harvard’s Business School. During 1998-2004, Dr Singh and Mr Chidambaram were in Opposition but Mr Ahluwalia was Member-Secretary of the Vajpayee Planning Commission. Since coming together again in Sonia Gandhi’s United Progressive Alliance, they have been flatteringly named the “Dream Team” by India’s pink business newspapers, a term originally referring to some top American basketball players.
Based on pronouncements, publications and positions held, other members or associates of the “Dream Team” include Reserve Bank Governor Dr YV Reddy; his predecessor Dr Bimal Jalan; former PMO official Mr NK Singh, IAS; Chief Economic Advisers Dr Shankar Acharya and Dr Ashok Lahiri; RBI Deputy Governor Dr Rakesh Mohan; and others like Dr Arvind Virmani, Dr Isher Ahluwalia, Dr Parthasarathi Shome, Dr Vijay Khelkar, Dr Ashok Desai, Dr Suman Bery, Dr Surjit Bhalla, Dr Amaresh Bagchi, Dr Govind Rao. Honorary members include Mr Jaswant Singh, Mr Yashwant Sinha, Mr KC Pant and Dr Arun Shourie, all economic ministers during the Vajpayee premiership. Institutional members include industry chambers like CII and FICCI representing “Big Business”, and unionised “Big Labour” represented by the CPI, CPI(M) and prominent academics of JNU. Mr Mani Shankar Aiyar joins the Dream Team with his opinion that a gas pipeline is “necessary for the eradication of poverty in India”. Mr Jairam Ramesh explicitly claimed authoring the 1991 reform with Mr Pranab Mukherjee and both must be members (indeed the latter as Finance Minister once had been Dr Singh’s boss). Dr Arjun Sengupta has claimed Indira Gandhi started the reforms, and he may be a member too. External members include Dr Jagdish Bhagwati, Dr. TN Srinivasan, Dr Meghnad Desai, Dr Vijay Joshi, Mr Ian Little, Dr Anne O. Krueger, Dr John Williamson, IMF Head Dr R Rato, and many foreign bank analysts who deal in Bombay’s markets. Harvard’s Dr Larry Summers joins with his statement while US Treasury Secretary in January 2000 that a 10% economic growth rate for India was feasible. His Harvard colleague Dr Amartya Sen — through disciples like Dr Jean Dreze (adviser to Sonia Gandhi on rural employment) — must be an ex officio member; as an old friend, the Prime Minister launched Dr Sen’s recent book while the latter has marked Dr Singh at 80% as PM. Media associates of the Dream Team include editors like Mr Aroon Purie, Mr Vinod Mehta, Dr Prannoy Roy, Mr TN Ninan, Mr Vir Sanghvi and Mr Shekhar Gupta, as well as the giddy young anchors of what passes for news and financial analysis on cable TV.
This illustrious set of politicians, government officials, economists, journalists and many others have come to define what may be called the “New Delhi Consensus” on contemporary India’s economic policy. While it is unnecessary everyone agree to the same extent on every aspect — indeed on economic policy the differences between the Sonia UPA and Vajpayee NDA have had to do with emphasis on different aspects, each side urging “consensus” upon the other — the main factual and evaluative claims and policy-prescriptions of the New Delhi Consensus may be summarised as follows:
A: “The Narasimha Rao Government in July 1991 found India facing a grave balance of payments crisis with foreign exchange reserves being very low.”
B: “A major cause was the 1990-1991 Gulf War, in its impact as an exogenous shock on Indian migrant workers and oil prices.”
C: “The Dream Team averted a macroeconomic crisis through “structural adjustment” carried out with help of the IMF and World Bank; hence too, India was unaffected by the 1997 ‘Asian crisis'”.
D: “The PVNR, Deve Gowda, Gujral and Vajpayee Governments removed the notorious license-quota-permit Raj.”
E: “India’s measurable real economic growth per capita has been raised from 3% or lower to 7% or more.”
F: “Foreign direct investment has been, relative to earlier times, flooding into India, attracted by lower wages and rents, especially in new industries using information technology.”
G: “Foreign financial investment has been flooding into India too, attracted by India’s increasingly liberalised capital markets, especially a liberalised current account of the balance of payments.”
H: “The apparent boom in Bombay’s stock market and relatively large foreign exchange reserves bear witness to the confidence foreign and domestic investors place in India’s prospects.”
I: “The critical constraint to India’s future prosperity is its “infrastructure” which is far below what foreign investors are used to in other countries elsewhere in Asia.”
J: “It follows that massive, indeed gargantuan, investments in highways, ports, airports, aircraft, city-flyovers, housing-estates, power-projects, energy exploration, gas pipelines, etc, out of government and private resources, domestic and foreign, is necessary to remove remaining “bottlenecks” to further prosperity for India’s masses, and these physical constructions will cause India’s economy to finally ‘take off’.”
K: “India’s savings rate (like China’s) is exceptionally high as is observable from vast expansion of bank-deposits, and these high (presumed) savings, along with foreign savings, will absorb the gargantuan investment in “infrastructure” without inflation.”
L: “Before the gargantuan macroeconomic investments bear the fruits of prosperity, equally large direct transfer payments also must be made from the Government to prevent mass hunger and/or raise nominal incomes across rural India, while existing input or other subsidies to producers, especially farmers, also must continue.”
M: “While private sector participants may increasingly compete via imports or as new entrants in industries where the public sector has been dominant, no bankruptcy or privatisation must be allowed to occur or be seen to occur which does not provide public sector workers and officials with golden parachutes.”
Overall, the New Delhi Consensus paints a picture of India’s economy on an immensely productive trajectory as led by Government partnered by Big Business and Big Labour, with the English-speaking intellectuals of the Dream Team in the vanguard as they fly between exotic conferences and international commercial deals. An endless flow of foreign businessmen and politicians streaming through Bangalore, Hyderabad, five-star hotels or photo-opportunities with the PM, followed by official visits abroad to sign big-ticket purchases like arms or aircraft, reinforce an impression that all is fine economically, and modern India is on the move. Previously rare foreign products have become commonplace in India’s markets, streets and television-channels, and a new materialist spirit, supposedly of capitalism, is captured by the smug slogan yeh dil mange more (this heart craves more) as well as the more plaintive cry pardesi jana nahin, mujhe chhorke (foreigner, please don’t leave me).
2. Money, Convertibility, Inflationary Deficit Financing
India’s Rupee became inconvertible in 1942 when the British imposed exchange controls over the Sterling-Area. After 1947 independent India and Pakistan, in name of “planned” economic development, greatly widened this war-time regime – despite the fact they were at war now only with one another over Jammu & Kashmir and, oddly enough, formed an economic union until 1951 with their currencies remaining freely convertible with each other.
On May 29 1984, the present author’s Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India proposed in London that the Indian Rupee become a convertible hard currency again — the first time liberal economics had been suggested for India since BR Shenoy’s critique of the Second Five Year Plan (a fact attracting an editorial of The Times). The simple litmus test whether believers in the New Delhi Consensus have or have not the courage of their stated convictions – i.e., whether what they have been saying is, in its empirical fundamentals, more signal or noise, more reality or rhetorical propaganda – would be to carry through that proposal made 21 years ago. The Dream Team have had more than enough political power to undertake this, and it remains the one measure necessary for them to demonstrate to India’s people and the world that the exuberant confidence they have been promoting in their model of India’s economy and its prospects is not spurious.
What does convertibility entail? For a decade now, India has had limited ease of availability of foreign exchange for traders, students and tourists. Indeed some senior Government monetary economists believe there is convertibility already except forex dealers are being allowed “one-way” and not “two-way” quotes! That is wrong. The Government since 1942 has requisitioned at the border all foreign exchange earned by exporters or received as loans or investment — allocating these first to pay interest and amortisation on the country’s foreign debt, then to make its own weapons and other purchases abroad, then to release by ration what remains to private traders, students, tourists et al. Current account liberalisation has meant the last of these categories has been relaxed, especially by removal of some import quotas. What a convertible Rupee would mean is far more profound. It would allow any citizen to hold and save an Indian money that was exchangeable freely (i.e. without Government hindrance) into moneys of other countries. Full convertibility would mean all the paper money, bank deposits and rupee-denominated nominal assets held by ordinary people in India becomes, overnight, exchangeable without hindrance into dollars, yens, pounds or euros held anywhere (although not of course at the “one-way” rates quoted today).
Now money is a most peculiar human institution. Paper money is intrinsically worthless but all of India’s 1,000 million people (from street children onwards) have need to hold it temporarily to expedite their individual transactions of buying and selling real goods and services. Money also acts as a repository of value over time and unit of account or measure of economic value. While demand to hold such intrinsically worthless paper is universal, its supply is a Government monopoly. Because Government accepts obligations owed to it in terms of the fiat money it has itself issued, the otherwise worthless paper comes to possess value in exchange. Because Government controls its supply, money also can be abused easily enough as a technique of invisible taxation via inflation.
With convertibility in India, the quantity of currency and other paper assets like public debt instruments representing fiscal decisions of India’s Union and State Governments, will have to start to compete with those produced by other governments. Just as India’s long-jumpers and tennis-players must compete with the world’s best if they are to establish and sustain their athletic reputations, so India’s fiscal and monetary decisions (i.e. about government spending and revenues, interest-rates and money supply growth) will have to start competing in the world’s financial markets with those of the EU, USA, Japan, Switzerland, ASEAN etc.
The average family in rural Madhya Pradesh who may wish, for whatever personal reason, to liquidate rupee-denominated assets and buy instead Canadian, Swiss or Japanese Government debt, or mutual fund shares in New York, Frankfurt or Singapore, would not be hindered by India’s Government from doing so. They would become as free as the swankiest NRI jet-setters have been for years (like many members of the New Delhi Consensus and their grown children abroad). Scores of millions of ordinary Indians unconnected with Big Business or Big Labour, neither among the 18 million people in government nor the 12 million in the organised private sector, would become free to hold any portfolio of assets they chose in global markets (small as any given individual portfolio may be in value). Like all those glamorous NRIs, every Indian would be able to hold dollar or Swiss Franc deposit accounts at the local neighbourhood bank. Hawala operators worldwide would become redundant. Ordinary citizens could choose to hold foreign shares, real-estate or travellers’ cheques as assets just as they now choose jewellery before a wedding. The Indian Rupee, after more than 65 years, would once again become as good as all the proverbial gold in Fort Knox.
When added up, the new demand of India’s anonymous masses to hold foreign rather than Rupee-denominated assets will certainly make the Rupee decline in price in world markets. But — if the implicit model of India’s economy promoted by the Dream Team is based on correctly ascertained empirical facts — foreign and domestic investor confidence should suffice for countervailing tendencies to keep India’s financial and banking system stable under convertibility. Not only would India’s people be able to use and save a currency of integrity, the allocation of real resources would also improve in efficiency as distortions would be reduced in the signalling function of domestic relative prices compared to world relative prices. An honest Rupee freely priced in world markets at, say, 90 per dollar, would cause very different real microeconomic decisions of Government and private producers and consumers (e.g., with respect to weapons’ purchases or domestic transportation, given petroleum and jet fuel imports) than a semi-artificial Rupee at 45 per dollar which forcibly an inconvertible asset in global markets. A fully convertible Rupee will cause economic and political decisions in the country more consistent with word realities.
Why the Rupee is not going to be made convertible in the foreseeable future – or why, in India’s present fiscal circumstances if it was, it would be imprudent to do so – is because, contrary to the immense optimism promoted by the Dream Team about their own deeds since 1991, they have in fact been causing India’s monetary economy to skate on the thinnest of thin ice. Put another way, a house of cards has been constructed whose cornerstone constitutes that most unscientific anti-economic of assumptions, the “free lunch”: that something can be had for nothing, that real growth in average consumption levels of the masses of ordinary households of rural and urban India can meaningfully come about by nominal paper-money creation accompanied by verbal exhortation, hocus-pocus or abracadabra from policy-makers and their friends in Big Business, Big Labour and the media. (Lest half-remembered inanities about “orthodox economics” come to be mouthed, Maynard Keynes’s 1936 book was about specific circumstances in Western economies during the Depression and it is unwise to extend its presumptions to unintended situations.)
3. Rajiv Gandhi and Perestroika Project
On 25 May 2002, India’s newspapers reported “PV Narasimha Rao and Manmohan Singh lost their place in Congress history as architects of economic reforms as the Congress High Command sponsored an amendment to a resolution that had laid credit at the duo’s door. The motion was moved by…. Digvijay Singh asserting that the reforms were a brainchild of the late Rajiv Gandhi and that the Rao-Singh combine had simply nudged the process forward.”
Now Rajiv Gandhi was an airline-pilot and knew no economics. But the origins of the 1991 reform did come about because of an encounter he had, as Opposition Leader and Congress President from September 1990 onwards, with a “perestroika” project for India’s political economy occurring at an American university since 1986 (viz., The Statesman Editorial Page July 31-August 2 1991, now republished here; Freedom First October 2001). In being less than candid in acknowledging the origins of the reform, the Dream Team may have failed to describe accurately the main symptoms of illness that afflicted India before 1991, and have consequently failed to diagnose and prescribe for it correctly ever since.
The Government of India, like many others, has been sorely tempted to finance its extravagant expenditures by abusing its monopoly over paper-money creation. The British taught us how to do this, and in 1941-43 caused the highest inflation rates ever seen in India as a result. Fig. 1 shows this, and also that real growth in India follows as expected the trend-rate of technological progress (having little to do with government policy). Independent India has continually financed budget- deficits by money creation in a process similar to what the British and Americans did in wartime. This became most conspicuous after Indira Gandhi’s bank and insurance nationalisations of 1969-1970. Indeed, among current policy-makers, Pranab Mukherjee, Manmohan Singh, Arjun Sengupta, Montek Singh Ahluwalia, Bimal Jalan, NK Singh, Amaresh Bagchi and Shankar Acharya, were among those governing such macroeconomic processes before 1991 — albeit in absence of the equations that illustrate their nature. Why the Rupee cannot be made an honest, internationally convertible, stable money held with confidence by all Indians today, is because the Dream Team have continued with the same macroeconomics ever since. The personal and political ambitions of the tiniest super-elite that the New Delhi Consensus represent (both personal and political) have depended precisely on gargantuan unending deficit-financing backed by unlimited printing of paper-money, and hence the continuing destruction of the integrity of India’s banking system. A convertible Rupee would allow India’s ordinary people to choose to hold other stores of value available in the world today, like gold or monies issued by foreign governments, and thus force an end to such processes.
Two recent articles in The Statesman (Perspective Page 30 October 2005, Front Page 29 November 2005) outlined India’s financial repression and negative real interest rates (which suffice to explain the present stock market boom the way athletes perform better on steroids), and also how deficits get financed by money creation accompanied by wishful projections of economic growth in an upside down imitation of how macroeconomic policy gets done in the West.
“Narrow Money” consists mostly of hand-to-hand currency. “Broad Money” consists of Narrow Money plus bank-deposits. Modern banking is built on “fractional reserves”, i.e. a system of trust where your bank does not literally hold onto deposits you place there but lends these out again – which causes further deposit expansion because no individual banker can tell whether a new deposit received by it is being caused by the depositor having himself borrowed. As a general rule, bank lending causes further deposit expansion. Why India’s (and China’s) bank deposits have been expanding is not because Indians (or Chinese) are superhuman savers of financial assets in banks but because the Government of India (and China) has for decades compelled (the mostly nationalised) banks to hold vast sums of Government debt on the asset side of their balance-sheets. Thus there has been humongous lending by the banking system to pay for Government expenditures. The Dream Team’s macroeconomics relies entirely on this kind of unending recourse to deficit finance and money creation, causing dry rot to set into banks’ balance sheets (Figs. 2,3, 4). If the Rupee became convertible, those vast holdings of Government debt by banks would become valued at world prices. The crucial question would be how heavily New York, London and Hong Kong financial markets discounted Indian sovereign debt. If upon convertibility, the asset sides of domestic Indian banks get discounted very heavily by world financial markets, their insolvency upon being valued at international prices could trigger catastrophic repercussions throughout India’s economy. Hence the Rupee cannot be made convertible — and all our present inefficiencies and inequities will continue for ever with New Delhi’s rhetorical propaganda alongside. The capital flight of 10 out of 1000 million Indians will continue, leaving everyone else with the internal and foreign public debts to pay.
4. A Different Strategy had Rajiv Not Been Assassinated
Had Rajiv Gandhi not been assassinated and the perestroika project allowed to take its course, a different strategy would have been chosen. Honest money first demands honest Government and political leadership. It would at the outset have been recognised by Government (and through Government by all India’s people) that the asset-liability, income-expenditure and cash-flow positions of every public entity in the country without exception — of the Union Government, every State and local Government, every public undertaking and project – is abysmal. Due to entanglement with government financial loans, labour regulations, subsidies, price controls, protection and favouritism, the same holds for the financial positions of vast numbers of firms in the organised private sector. Superimpose on this dismal scene, the bleak situation of the Rule of Law in the country today – where Courts of Justice from highest to lowest suffer terrible abuse receiving pitiable amounts of public resources despite constituting a third and independent branch of India’s Government (while police forces, despite massive expenditure, remain incompetent, high-handed and brutal). What India has needed ever since 1991 is the Rule of Law, total transparency of public information, and the fiercest enforcement of rigorous accounting and audit standards in every government entity and public institution. It is only when budgets and financial positions become sound that ambitious goals can be achieved.
The Dream Team have instead made a fetish of physical construction of “infrastructure”, in some grandiose make-believe dreamworld which says the people of India wish the country to be a superpower. The Dream Team have failed to properly redefine for India’s masses the appropriate fiscal and monetary relationship between State and citizen – i.e. to demarcate public from private domains, and so enhance citizens’ sense of individual responsibility for their own futures, as well as explain and define what government and public institutions can and cannot do to help people’s lives. Grotesque corruption and inefficiency have thus continued to corrode practically all organs, institutions and undertakings of government. Corruption is the transmutation of publicly owned things into private property, while its mirror image, pollution, is the disposal of private wastes into the public domain. Both become vastly more prevalent where property rights between private and public domains remain ill demarcated. What belongs to the individual citizen and what to sovereign India –their rights and obligations to one another – remains fuzzy. Hence corruption and pollution run amuck. The irrational obsession with “infrastructure” is based on bad economics, and has led to profoundly wrong political and financial directions. The Rupee cannot be made an honest stable money because India’s fiscal and monetary situation remains not merely out of control but beyond New Delhi’s proper comprehension and grasp. If and when the Dream Team choose to wake up to India’s macroeconomic realities, a great deal of serious work will need to be done.
After the Verdict: Why the Executive Needed a Vote of Confidence
October 20, 2005 — drsubrotoroyAFTER THE VERDICT
by
Subroto Roy
First published The Statesman, 20 October 2005, Editorial Page Special Article

The last and only time a Head of State of India “resigned” was when Edward VIII (uncle of the present Queen of England) abdicated in 1936 because he wished to marry Mrs Wallis Simpson, a twice-divorced American, and the British Government under Stanley Baldwin felt this was unacceptable to the public and told him so. To his eternal credit, Edward VIII chose true love over the vainglorious trappings of a constitutional monarchy, gave up the kingship, and went with his new wife into a quiet voluntary life-exile in France as the Duke and Duchess of Windsor. India’s Presidents cannot act in state except upon advice of the Cabinet. That means they cannot even resign from office except upon advice of the Cabinet. A President may tragically die in office in which case the Vice-President would become the acting Head of State but there is no provision or precedent in India for a President to be made to resign except for Edward VIII’s abdication.
Richard Nixon resigned the office of the President of the United States in 1974 and more recently William Jefferson Clinton was brought under a lot of pressure to do so by the legislative impeachment proceedings against him. Nixon resigned (which made Gerald Ford President) because it had become impossible for him to stay in office having been proved to have lied to the people, and Clinton managed to stay on by the skin of his teeth for similar misdeeds. But the American system is different because the Head of State and Head of Government are united in the person of the President.
In our system, the Head of State embodies the sovereignty of India and does nothing more. Mountbatten as the first Governor-General imagined himself much more than that and caused damage to the subcontinent’s polity which has still to be repaired. But the first four Indian Heads of State, C. Rajagopalachari, Dr Rajendra Prasad, Dr S. Radhakrishnan, and Dr Zakir Hussain, were exemplary role-models. Unfortunately since their time the office of the President has suffered some of the shocks too that have been suffered by almost all our institutions. For example, retired Presidents really should vanish most gracefully into quietude to write their memoirs and help raise their grandchildren, yet we have had a former President say that an award received after retirement as President has been his most prized. It is not logically possible for such a thing to happen, since to become President of India is the ultimate honour for any citizen of our country. We elect someone among us to be a constitutional monarch for a period of five years and call that person President. Even if a former Indian President should receive the Nobel Peace Prize afterwards it would not mean his/her having embodied the sovereignty of our Republic was not the ultimate honour.
In our constitutional law, our Head of State cannot choose to resign any more than the sovereignty of India can be made to momentarily come to an end. If, to construct a hypothetical case, a President of India while in office became, heavens forbid, physically or mentally incapable of carrying out the duties of the office, the Government of India as represented by the Union Cabinet may well look to the Vice-President to fulfil the role of the Head of State temporarily but there would be no provision for the President to be made to demit office. The only precedent is that of Edward VIII where his personal love for Mrs Simpson compelled his abdication upon the advice of the Prime Minister.
Bringing ourselves back to Bihar, the Honourable Supreme Court’s finding of unconstitutionality is of grave import. On the positive side, what it indicates yet again is that India’s political institutions, no matter how battered and bloody they become by our self-inflicted wounds, still do work.
Furthermore, for the Honourable Court to have allowed the elections to go forward indicates how fine is the quality of our justice, for the Court has allowed the people of Bihar to speak again, and of course Mr Nitish Kumar and friends have been free to use at the hustings the Court’s finding in their favour. Certainly heads should roll and be seen to roll for all this. The Governor should have gone immediately but has not only not done so, he has let it be known that he was acting under orders himself. If so, the least that should happen is that the party-functionary responsible for this should be sacked.
For some press-commentators to demand that Sonia Gandhi should replace Dr Manmohan Singh reveals an appalling ignorance of constitutional norms; this is not a matter of a “High Command” replacing one acolyte by another as chief minister somewhere – if a Prime Minister resigns, so does the entire Cabinet he has appointed, and a new Government has to be sought to be formed. At the same time it is less than candid for the Leader of the Opposition to demand via the television cameras that the Prime Minister should resign, since the Opposition knows fully well that there is an institution called Parliament which can express its lack of confidence in a Government. And of course it also remains open for the Prime Minister himself to go to Parliament and seek to renew its confidence in his Government when the public confidence has thus come to be shaken.
In fact, the right course of action for the President is to summon the Prime Minister and say something like: “It would appear the Judicial Branch of the Government of India has found the Executive Branch to have breached the Constitution. Reference must now be made to the Legislative Branch, namely, to Parliament, to see if it still has confidence in the Executive. Please ask for a Vote of Confidence in the Lok Sabha as soon as possible.” Of course, Dr Manmohan Singh has been the first Prime Minister in Commonwealth history since Salisbury who has not been himself a member of the Lower House. Curzon had wished to be British prime minister after returning from India but was passed over in 1922 in favour of Baldwin in a decisive demonstration that a prime minister must be a member of the Lower House. That is why Alec Douglas-Home stopped being a member of the House of Lords in order to become British PM in 1963-64. India in the last thirty years has seen parliamentary traditions at the Union and State levels being ruinously weakened (or not even allowed to develop) being replaced all too frequently either by street-fighting or by discretionary bureaucratic decision-making by committee. The present moment is an opportunity for the rot to be stemmed. It may be too optimistic though to believe that it will be taken.