This is an incomplete bibliography of my writings, public lectures etc 1973-2020 including citations, reviews, comments. I have been mostly an academic economist who by choice or circumstance over 47 years has had to venture also into science, philosophy, public policy, law, jurisprudence, practical politics, history, international relations, military strategy, financial theory, accounting, management, journalism, literary criticism, psychology, psychoanalysis, theology, aesthetics, biography, children’s fables, etc. If anything unites the seemingly diverse work recorded below it is that I have tried to acquire a grasp of the nature of human reason and then apply this comprehension in practical contexts as simply and clearly as possible. Hence I have ended up following the path of Aristotle, as described in modern times (via Wittgenstein and John Wisdom) by Renford Bambrough. The 2004 public lecture in England, “Science, Religion, Art & the Necessity of Freedom”, also my 2017 “Is ‘Cambridge Philosophy’ dead, in Cambridge? Can it be resurrected, there? Case Study: Renford Bambrough (& Subroto Roy) preceded by decades Cheryl Misak’s thesis on Wittgenstein being linked with Peirce via Ramsey…”
may explain and illustrate all this best. A friend has been kind enough to call me an Academician, which I probably am, though one who really needs his own Academy because the incompetence, greed and mendacity encountered too often in the modern professoriat is dispiriting.
Besides writings and publications printed on paper, there are writings or items not printed on paper — as new media break space, cost and other constraints of traditional publishing. A little repetition and overlap has occurred too. Also in a few cases, e.g., Aldous Huxley’s essay on DH Lawrence, nothing has been done except discover and republish. Several databases have been created and released in the public interest, as have been some rare maps. There is also some biographical and autobiographical material. Several inconsequential errors remain in the text, which shall take time to be rectified as documents come to be rediscovered and collated.
1973
1. “Behavioural study of mus musculus”, Haileybury College, Supervised by J de C Ford-Robertson MA (Oxon). (Due to be published here 2010).
2. “Chemistry at Advanced & Special Level: Student Notes 1972-73” (Due to be published here 2010).
3. “Biology at Advanced & Special Level: Student Notes 1972-73”, (Due to be published here 2010).
4. “Physics at Advanced Level: Student Notes 1972-73”, (Due to be published here 2010).
5. “Revolution: theoria and praxis”, London, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
6. “Gandhi vs Marx”, London, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
1974
7. “Relevance of downward money-wage rigidity to the problem of maintaining full-employment in the classical and Keynesian models of income determination”, London School of Economics, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
8. “Testing aircraft fuels at Shell Finland”.
1975
9. “Oxford Street experiences: down and out in London town”.
10. “SE Region Bulk Distribution Survey”, Unilever, Basingstoke.
11. “Four London poems”, in JCM Paton (ed) New Writing (London, Great Portland Street: International Students House). (Due to be republished here 2010)
12. “On economic growth models and modellers”, London School of Economics, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
1976
13. “World money: system or anarchy?”, lecture to Professor ACL Day’s seminar, London School of Economics, Economics Department, April. (Due to be published here 2010).
14. “A beginner’s guide to some recent developments in monetary theory”, lecture to Professor FH Hahn’s seminar, Cambridge University Economics Department, November 17 (Due to be published here 2010). See also “Announcement of My “Hahn Seminar”, published here June 14 2008.
1977
15. “Inflation and unemployment: a survey”, mimeo, Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge. (Due to be published here 2010).
16. “On short run theories of dual economies”, Cambridge University Economics Department “substantial piece of work” required of first year Research Students. Examiner: DMG Newbery, FBA. (Due to be published here 2010).
1978
17. “Pure theory of developing economies 1 and 2”, Delhi School of Economics mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
18. “Introduction to some market outcomes under uncertainty”, Delhi School of Economics mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
19. “On money and development”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo, September. (Due to be published here 2010)
20. “Notes on the Newbery-Stiglitz model of sharecropping”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo November. (Due to be published here 2010).
1979
21. “A theory of rights and economic justice”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
22. “Monetary theory and economic development”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
23. “Foundations of the case against ‘development planning’”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge, mimeo, November. (Due to be published here 2010).
1979-1989
24. Correspondence with Renford Bambrough (1926-1999), philosopher of St John’s College, Cambridge (Due to be published here 2010).
1980
25. “Models before the monetarist storm”, New Statesman letters
26. “Disciplining rulers and experts”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
1981
27. “On liberty & economic growth: preface to a philosophy for India”, Cambridge University doctoral thesis, supervisor FH Hahn, FBA; examiners CJ Bliss, FBA; TW Hutchison, FBA (Due to be published here 2010). 27a Response of FA Hayek on a partial draft February 18 1981. 27b Response of Peter Bauer, 1982. 27c Response of Theodore W Schultz, 1983. 27d. Response of Frank Hahn 1985.
1982
28. “Knowledge and freedom in economic theory Parts 1 and 2”, Centre for Study of Public Choice, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University, Working Papers.
29. “Economic Theory and Development Economics”. Lecture to American Economic Association, New York, Dec 1982. Panel: RM Solow, HB Chenery, T Weisskopf, P Streeten, G Rosen, S Roy. Published in 29a.
1983
29a “Economic Theory and Development Economics: A Comment”. World Development, 1983. [Citation: Stavros Thefanides “Metamorphosis of Development Economics”, World Development 1988.]
30. “The Political Economy of Trade Policy (Comment on J. Michael Finger)”, Washington DC: Cato Journal, Winter 1983/84. See also 000 “Risk-aversion explains resistance to freer trade”, 2008.
1984
31. “Considerations on Utility, Benevolence and Taxation”, History of Political Economy, 1984. 31a Response of Professor Sir John Hicks May 1 1984.
[Citations: P. Hennipman, “A Tale of Two Schools”, De Economist 1987, “A New Look at the Ordinalist Revolution”, J. Econ. Lit. Mar 1988; P. Rappoport, “Reply to Professor Hennipman”, J. Econ. Lit. Mar 1988; Eugene Smolensky et al “An Application of A Dynamic Cost-of-Living Index to the Evaluation of Changes in Social Welfare”, J. Post-Keynesian Econ.IX.3. 1987.]
32. Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India, London: Institute of Economic Affairs, London 1984.
[Citations: Lead editorial of The Times of London May 29 1984, “India’s economy”, Times letters June 16 1984. John Toye “Political Economy & Analysis of Indian Development”, Modern Asian Studies, 22, 1, 1988; John Toye, Dilemmas of Development; D. Wilson, “Privatization of Asia”, The Banker Sep. 1984 etc]. See also 370 “Silver Jubilee of ‘Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India’” 2009.
33. Review of Utilitarianism and Beyond, Amartya Sen & Bernard Williams (eds) Public Choice.
34. Review of Limits of Utilitarianism, HB Miller & WH Williams (eds.), Public Choice.
35. Deendayal Upadhyaya lecture “On Government and the Individual in India” (one of four invited lecturers), Washington DC, October 1984.
1987
36. (with one other) “Does the Theory of Logical Types Inform the Theory of Communication?”, Journal of Genetic Psychology., 148 (4), Dec. 1987 [Citation:
37. “Irrelevance of Foreign Aid”, India International Centre Quarterly, Winter 1987.
38. Review of Development Planning by Sukhamoy Chakravarty for Economic Affairs, London 1987.
1988
39. (with Seiji Naya and Pearl Imada) “Introduction” to Lessons in Development: A Comparative Study of Asia and Latin America. San Francisco: Inst. of Economic Growth.
40. “A note on the welfare economics of regional cooperation”, lecture to Asia-Latin America conference, East West Center Honolulu, published 2009.
1989
41. Philosophy of Economics: On the Scope of Reason in Economic Inquiry, London & New York: Routledge (International Library of Philosophy) 1989, paperback 1991. Internet edition 2007. [Reviews & Citations: Research in Economics, 1992; De Economist 1991 & 1992; Manch.Sch. Econ.Studs. 59, 1991; Ethics 101.88 Jul. 1991; Kyklos 43.4 1990; Soc. Science Q. 71.880. Dec.1990; Can. Phil. Rev. 1990; J. Econ. Hist. Sep. 1990; Econ. & Phil. Fall 1990; Econ. Affairs June-July 1990; TLS May 1990; Choice March 1990; J. App.Phil. 1994, M. Blaug: Methodology of Economics, 2nd ed., Cambridge, 1992; Hist. Methods. 27.3, 1994; J. of Inst. & Theoretical Econ.,1994; Jahrbucker fur Nationaleconomie 1994, 573:574. Mark A Lutz in Economics for the Common Good, London: Routledge, 1999, et al]. See also 339 “Apropos Philosophy of Economics”, Comments of Sidney Hook, KJ Arrow, Milton Friedman, TW Schultz, SS Alexander, Max Black, Renford Bambrough, John Gray et al.
42. Foreword to Essays on the Political Economy by James M. Buchanan, Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press 1989.
43. “Modern Political Economy of India”, edited by Subroto Roy & William E James, Hawaii mimeo May 21 1989. This published for the first time a November 1955 memorandum to the Government of India by Milton Friedman. See also 43a, 53.
43a. Preface to “Milton Friedman’s extempore comments at the 1989 Hawaii conference: on India, Israel, Palestine, the USA, Debt and its uses, Erhardt abolishing exchange controls, Etc”, May 22 1989, published here for the first time October 31 2008.
44. Milton Friedman’s defence of my work in 1989.
45. Theodore W. Schultz’s defence of Philosophy of Economics
1990
46. “Letter to Judge Evelyn Lance: On A Case Study in Private International Law” (Due to be published here in 2010).
47-49. Selections from advisory work on economic policy etc for Rajiv Gandhi, Leader of the Opposition in the Parliament of India, published in 47a-49a.
1991
41b Philosophy of Economics: On the Scope of Reason in Economic Inquiry, Paperback edition.
50. “Conversations and correspondence with Rajiv Gandhi during the Gulf war, January 1991” (Due to be published here 2010).
47a. A Memo to Rajiv I: Stronger Secular Middle”, The Statesman, Jul 31 1991.
48a “A Memo to Rajiv II: Saving India’s Prestige”, The Statesman, Aug 1 1991.
49a “A Memo to Rajiv III: Salvation in Penny Capitalism”, The Statesman, Aug 2 1991 47b-49b “Three Memoranda to Rajiv Gandhi 1990-91”, 2007 republication here.
51. “Constitution for a Second Indian Republic”, The Saturday Statesman, April 20 1991. Republished here 2009.
52. “On the Art of Government: Experts, Party, Cabinet and Bureaucracy”, New Delhi mimeo March 25 1991, published here July 00 2009.
1992
53. Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s Edited and with an Introduction by Subroto Roy & William E. James New Delhi, London, Newbury Park: Sage: 1992. Citation: Milton and Rose Friedman Two Lucky People (Chicago 1998), pp. 268-269.
54. Foundations of Pakistan’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s Edited and with an Introduction by William E. James & Subroto Roy, Hawaii MS 1989, Sage: 1992, Karachi: Oxford 1993.
Reviews of 53 & 54 include: Bus. Today, Mar-Apr 1992; Political Studies March 1995; Econ Times 21 March 1993; Pakistan Development Review 1992. Hindustan Times 11 July 1992. Pacific Affairs 1993; Hindu 21 March 1993, 15 June 1993; Pakistan News International 12 June 1993. Book Reviews March 1993; Deccan Herald 2 May 1993; Pol.Econ.J. Ind. 1992. Fin Express 13 September 1992; Statesman 16 Jan. 1993. J. Royal Soc Asian Aff. 1994, J. Contemporary Asia, 1994 etc.
55. “Fundamental Problems of the Economies of India and Pakistan”, World Bank, Washington, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
56.“The Road to Stagflation: The Coming Dirigisme in America, or, America, beware thy economists!, or Zen and Clintonomics,” Washington DC, Broad Branch Terrace, mimeo, November 17.
1993
57. “Exchange-rates and manufactured exports of South Asia”, IMF Washington DC mimeo. Published in part in 2007-2008 as 58-62:
58. “Path of the Indian Rupee 1947-1993”, 2008.
59. “Path of the Pakistan Rupee 1947-1993”, 2008.
60. “Path of the Sri Lankan Rupee 1948-1993”, 2008.
61. “Path of the Bangladesh Taka 1972-1993”, 2008.
62. “India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh Manufactured Exports, IMF Washington DC mimeo”, published 2007.
63. “Economic Assessment of US-India Merchandise Trade”, Arlington, Virginia, mimeo, published in slight part in Indo-US Trade & Economic Cooperation, ICRIER New Delhi, 1995, and in whole 2007.
64. “Towards an Economic Solution for Kashmir”, mimeo, Arlington, Virginia, circulated in Washington DC 1993-1995, cf 82, 111 infra. Comment of Selig Harrison.
1994
65. “Comment on Indonesia”, in The Political Economy of Policy Reform edited by John Williamson, Washington, DC: Institute for International Economics.
66a “Gold reserves & the gold price in anticipation of Central Bank behaviour”, Greenwich, Connecticut, mimeo. 67b. “Portfolio optimization and foreign currency exposure hedging” Greenwich, Connecticut mimeo.
1995
68. “On the logic and commonsense of debt and payments crises: How to avoid another Mexico in India and Pakistan”, Scarsdale, NY, mimeo, May 1.
69. “Policies for Young India”, Scarsdale, NY, pp. 350, manuscript.
1996
70. US Supreme Court documents, published in part in 2008 as “Become a US Supreme Court Justice!” 70a, 70b (Due to be published in full here in 2010 as Roy vs University of Hawaii, 1989- including the expert testimonies of Milton Friedman and Theodore W Schultz.).
71. “Key problems of macroeconomic management facing the new Indian Government”, May 17. Scarsdale, New York, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
72. “Preventing a collapse of the rupee”, IIT Kharagpur lecture July 16 1996.
73. “The Economist’s Representation of Technological Knowledge”, Vishvesvaraya lecture to the Institution of Engineers, September 15 1996, IIT Kharagpur.
1997
74. “Union and State Budgets in India”, lecture at the World Bank, Washington DC, May 00.
75. “State Budgets in India”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo, June 6.
1998
76. “Transparency and Economic Policy-Making: An address to the Asia-Pacific Public Relations Conference” (panel on Transparency chaired by CR Irani) Jan 30 1998, published here 2008.
77. Theodore W. Schultz 1902-1998, Feb 25.
78. “The Economic View of Human Resources”, address to a regional conference on human resources, IIT Kharagpur.
79. “Management accounting”, lecture at Lal Bahadur Shastri Academy, Mussourie,
80a “The Original Reformer”, Outlook letters, Jan 23 1998
81. “Recent Developments in Modern Finance”, IIM Bangalore Review, 10, 1 & 2, Jan.-Jun 1998. Reprinted as “From the Management Guru’s Classroom”: 81a “An introduction to derivatives”, Business Standard/Financial Times, Bombay 18 Apr 1999; 81b “Options in the future, Apr 25 1999; 81c “What is hedging?”, May 2 1999; 81d “Teaching computers to think”, May 9 1999.
82. “Towards an Economic Solution for Kashmir”, Jun 22 1998, lecture at Heritage Foundation, Washington DC. Cf 111 Dec 2005.
83. “Sixteen Currencies for India: A Reverse Euro Model for Monetary & Fiscal Efficacy”, Lecture at the Institute of Economic Affairs, London, June 29 1998. Due to be published here 2010.
84. “Fable of the Fox, the Farmer, and the Would-Be Tailors”, October (Published here July 27 2009).
85. “A Common Man’s Guide to Pricing Financial Derivatives”, Lecture to “National Seminar on Derivatives”, Xavier Labour Research Institute, Jamshedpur, Dec. 16 1998. See 98.
1999
86. “An Analysis of Pakistan’s War-Winning Strategy: Are We Ready for This?”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo, published in part as 86a.“Was a Pakistani Grand Strategy Discerned in Time by India?” New Delhi: Security & Political Risk Analysis Bulletin, July 1999, Kargil issue. See also 000
80b. “The Original Reformer”, Outlook letters, Sep 13 1999.
2000
87. “On Freedom & the Scientific Point of View”, SN Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Feb 17 2000. Cf 100 below.
88. “Liberalism and Indian economic policy”, lecture at IIM Calcutta, Indian Liberal Group Meetings Devlali, Hyderabad; also Keynote address to UGC Seminar Guntur, March 30 2002. (Due to be published here 2010).
89. “Towards a Highly Transparent Fiscal & Monetary Framework for India’s Union & State Governments”, Invited address to Conference of State Finance Secretaries, Reserve Bank of India, Bombay, April 29, 2000. Published 2008.
90. “On the Economics of Information Technology”, two lectures at the Indian Institute of Information Technology, Bangalore, Nov 10-11, 2000.
91. Review of A New World by Amit Chaudhuri in Literary Criterion, Mysore.
2001
92. Review of AD Shroff: Titan of Finance and Free Enterprise by Sucheta Dalal, Freedom First., January.
93. “Encounter with Rajiv Gandhi: On the Origins of the 1991 Economic Reform”, Freedom First, October. See also 93a in 2005 and 93b in 2007.
94. “A General Theory of Globalization & Modern Terrorism with Special Reference to September 11”, a keynote address to the Council for Asian Liberals & Democrats, Manila, Philippines, 16 Nov. 2001. Published as 91a.
95. “The Case for and against The Satanic Verses: Diatribe and Dialectic as Art”, Dec 22 republished in print 95a The Statesman Festival Volume, 2006.
2002
94a “A General Theory of Globalization & Modern Terrorism with Special Reference to September 11”, in September 11 & Political Freedom in Asia, eds. Johannen, Smith & Gomez, Singapore 2002.
2002-2010
96. “Recording vivid dreams: Freud’s advice in exploring the Unconscious Mind” (Due to be published here in 2010).
2003
97. “Key principles of government accounting and audit”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo.
98. “Derivative pricing & other topics in financial theory: a student’s complete lecture notes” (Due to be published here in 2010).
2004
99. TV Interview by BBC, Oxford, after May 2004 General Election in India.
100. “Collapse of the Global Conversation”, International Institute for Asian Studies, Leiden, Netherlands, Jul 2004.
101. “Science, Religion, Art & the Necessity of Freedom”, a public lecture, University of Buckingham, UK, August 24 2004. Published here 2007.
2005
93a Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform (this was the full story; it appeared in print for the first time in The Statesman Festival Volume 2007).
102. “Can India become an economic superpower (or will there be a monetary meltdown)?” Cardiff University Institute of Applied Macroeconomics Monetary Economics Seminar, April 13, Institute of Economic Affairs, London, April 27, Reserve Bank of India, Bombay, Chief Economist’s Seminar on Monetary Economics, May 5.
103. Margaret Thatcher’s Revolution: How it Happened and What it Meant, Edited and with an Introduction by Subroto Roy & John Clarke, London & New York: Continuum, 2005; paperback 2006; French translation by Florian Bay, 2007.
104. “Iqbal & Jinnah vs Rahmat Ali in Pakistan’s Creation”, Dawn, Karachi, Sep 3.
105. “The Mitrokhin Archives II from an Indian Perspective: A Review Article”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 11 .
106. “After the Verdict”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 20.
107. “US Espionage Failures”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 26
108. “Waffle But No Models of Monetary Policy”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 30.
109. “On Hindus and Muslims”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Nov 6.
110. “Assessing Vajpayee: Hindutva True and False”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Nov 13-14″.
111. “Fiction from the India Economic Summit”, The Statesman, Front Page, Nov 29.
112. “Solving Kashmir: On an Application of Reason”, The Statesman Editorial Page
I. “Give the Hurriyat et al Indian Green Cards”, Dec 1
II. “Choice of Nationality under Full Information”, Dec 2
III. “Of Flags and Consulates in Gilgit etc”, Dec 3.
2006
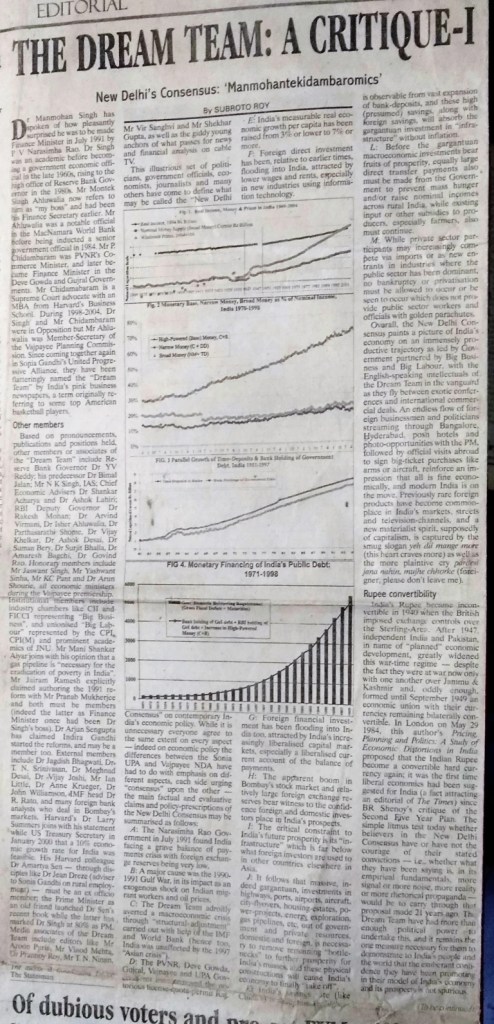
113. “The Dream Team: A Critique”, The Statesman Editorial Page
I : New Delhi’s Consensus (Manmohantekidambaromics), Jan 6
II: Money, Convertibility, Inflationary Deficit Financing, Jan 7
III: Rule of Law, Transparency, Government Accounting, Jan 8.
114. “Unaccountable Delhi: India’s Separation of Powers’ Doctrine”, The Statesman, Jan 13.
115. “Communists and Constitutions”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 22.
116. “Diplomatic Wisdom”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 31.
117. “Mendacity & the Government Budget Constraint”, The Statesman, Front Page Feb 3.
118. “Of Graven Images”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb5.
119. “Separation of Powers, Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Pages Feb 12-13.
120. “Public Debt, Government Fantasy”, The Statesman, Front Page Editorial Comment, Feb 22.
121. “War or Peace Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 23-24.
122. “Can You Handle This Brief, Mr Chidambaram?” The Statesman, Front Page Feb 26.
123. “A Downpayment On the Taj Mahal Anyone?”, The Statesman, Front Page Comment on the Budget 2006-2007, Mar 1.
124. “Atoms for Peace (or War)”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Mar 5.
125. “Imperialism Redux: Business, Energy, Weapons & Foreign Policy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Mar 14.
126. “Logic of Democracy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Mar 30.
127. “Towards an Energy Policy”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 2.
128. “Iran’s Nationalism”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 6.
129. “A Modern Military”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 16.
130. “On Money & Banking”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 23.
131. “Lessons for India from Nepal’s Revolution”, The Statesman, Front Page Apr 26.
132. “Revisionist Flattery (Inder Malhotra’s Indira Gandhi: A Review Article)”, The Sunday Statesman, May 7.
133. “Modern World History”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, May 7.
134. “Argumentative Indians: A Conversation with Professor Amartya Sen on Philosophy, Identity and Islam,” The Sunday Statesman, May 14 2006. “A Philosophical Conversation between Professor Sen and Dr Roy”, 2008. Translated into Bengali by AA and published in 00.
135. “The Politics of Dr Singh”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, May 21.
136. “Corporate Governance & the Principal-Agent Problem”, lecture at a conference on corporate governance, Kolkata May 31. Published here 2008.
137. “Pakistan’s Allies Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jun 4-5.
138. “Law, Justice and J&K Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 2, The Statesman Editorial Page Jul 3.
139. “The Greatest Pashtun (Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan)”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 16.
140. “Understanding Pakistan Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 30, The Statesman Editorial Page Jul 31.
141. “Indian Money and Credit”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 6.
142. “India’s Moon Mission”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 13.
143. “Jaswant’s Journeyings: A Review Article”, The Sunday Statesman Magazine, Aug 27.
144. “Our Energy Interests, Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 27, The Statesman Editorial Page Aug 28.
145. “Is Balochistan Doomed?”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Sep 3 2006.
146. “Racism New and Old”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Sep 8 2006
147. “Political Economy of India’s Energy Policy”, address to KAF-TERI conference, Goa Oct 7, published in 147a.
148. “New Foreign Policy? Seven phases of Indian foreign policy may be identifiable since Nehru”, Parts 1-2, The Sunday Statesman, Oct 8, The Statesman Oct 9.
149. “Justice & Afzal: There is a difference between law and equity (or natural justice). The power of pardon is an equitable power. Commuting a death-sentence is a partial pardon”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Oct 14
150. “Non-existent liberals (On a Liberal Party for India)”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Oct 22.
151. “History of Jammu & Kashmir Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Oct 29, The Statesman Oct 30, Editorial Page.
152. “American Democracy: Does America need a Prime Minister and a longer-lived Legislature?”, The Sunday Statesman Nov 5.
153. “Milton Friedman A Man of Reason 1912-2006”, The Statesman Perspective Page, Nov 22.
154. “Postscript to Milton Friedman Mahalanobis’s Plan (The Mahalanobis-Nehru “Second Plan”) The Statesman Front Page Nov 22.
155. “Mob Violence and Psychology”, Dec 10, The Statesman, Editorial Page.
156. “What To Tell Musharraf: Peace Is Impossible Without Non-Aggressive Pakistani Intentions”, The Statesman Editorial Page Dec 15.
157. “Land, Liberty and Value: Government must act in good faith treating all citizens equally – not favouring organised business lobbies and organised labour over an unorganised peasantry”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Dec 31.
2007
158. “Hypocrisy of the CPI-M: Political Collapse In Bengal: A Mid-Term Election/Referendum Is Necessary”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 9.
159. “On Land-Grabbing: Dr Singh’s India, Buddhadeb’s Bengal, Modi’s Gujarat have notorious US, Soviet and Chinese examples to follow ~ distracting from the country’s real economic problems,” The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Jan 14.
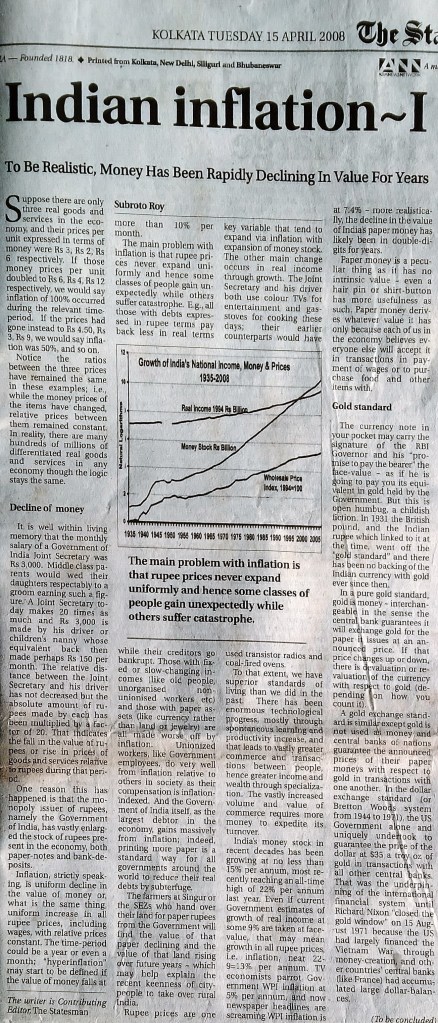
160. “India’s Macroeconomics: Real growth has steadily occurred because India has shared the world’s technological progress. But bad fiscal, monetary policies over decades have led to monetary weakness and capital flight” The Statesman Editorial Page Jan 20.
161. “Fiscal Instability: Interest payments quickly suck dry every year’s Budget. And rolling over old public debt means that Government Borrowing in fact much exceeds the Fiscal Deficit”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 4.
162. “Our trade and payments Parts 1-2” (“India in World Trade and Payments”),The Sunday Statesman, Feb 11 2007, The Statesman, Feb 12 2007.
163. “Our Policy Process: Self-Styled “Planners” Have Controlled India’s Paper Money For Decades,” The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 20.
164. “Bengal’s Finances”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, Feb 25.
165. “Fallacious Finance: Congress, BJP, CPI-M may be leading India to Hyperinflation” The Statesman Editorial Page Mar 5.
166. “Uttar Pradesh Polity and Finance: A Responsible New Govt May Want To Declare A Financial Emergency” The Statesman Editorial Page, Mar 24
167. “A scam in the making” in The Sunday Statesman Front Page Apr 1 2007, published here in full as “Swindling India”.
168. “Maharashtra’s Money: Those Who Are Part Of The Problem Are Unlikely To Be A Part Of Its Solution”, The Statesman Editorial Page Apr 24.
147a. “Political Economy of Energy Policy” in India and Energy Security edited by Anant Sudarshan and Ligia Noronha, Konrad Adenauer Stiftung, New Delhi 2007.
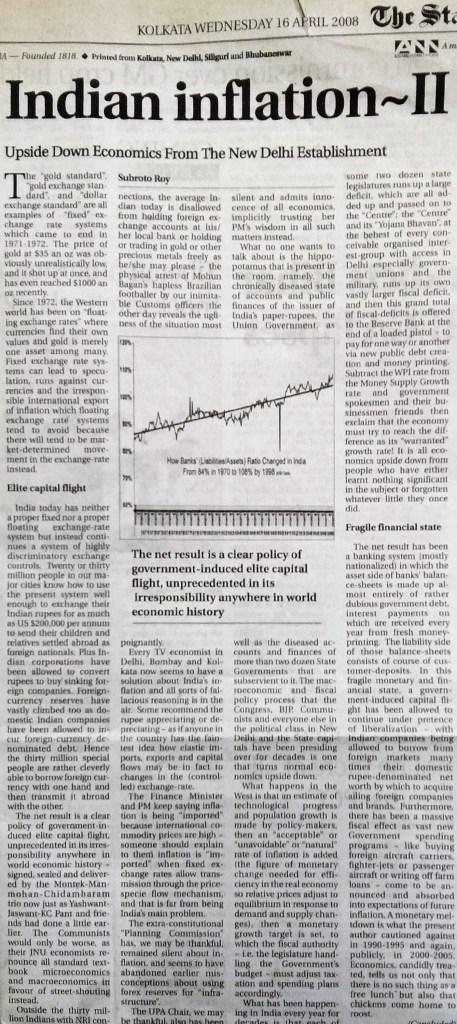
169. “Presidential Qualities: Simplicity, Genuine Achievement Are Desirable; Political Ambition Is Not”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, May 8.
170. “We & Our Neighbours: Pakistanis And Bangladeshis Would Do Well To Learn From Sheikh Abdullah”, The Statesman, Editorial Page May 15.
171. “On Indian Nationhood: From Tamils To Kashmiris And Assamese And Mizos To Sikhs And Goans”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, May 25.
172. A Current Example of the Working of the Unconscious Mind, May 26.
173. Where I would have gone if I was Osama Bin Laden, May 31.
174. “US election ’08:America’s Presidential Campaign Seems Destined To Be Focussed On Iraq”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 1.
175. “Home Team Advantage: On US-Iran talks and Sunni-Shia subtleties: Tehran must transcend its revolution and endorse the principle that the House of Islam has many mansions”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, June 3
176. “Unhealthy Delhi: When will normal political philosophy replace personality cults?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 11.
177. “American Turmoil: A Vice-Presidential Coup – And Now a Grassroots Counterrevolution?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 18
178. “Political Paralysis: India has yet to develop normal conservative, liberal and socialist parties. The Nice-Housing-Effect and a little game-theory may explain the current stagnation”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, June 24.
179. “Has America Lost? War Doctrines Of Kutusov vs Clausewitz May Help Explain Iraq War”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 3.
180. “Lal Masjid ≠ Golden Temple: Wide differences are revealed between contemporary Pakistan and India by these two superficially similar military assaults on armed religious civilians”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page July 15
181. “Political Stonewalling: Only Transparency Can Improve Institutions”, The Statesman, Editorial Page July 20.
182. “Gold standard etc: Fixed versus flexible exchange rates”, July 21.
183. “US Pakistan-India Policy: Delhi & Islamabad Still Look West In Defining Their Relationship”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 27.
184. “Works of DH Lawrence” July 30
185. “An Open Letter to Professor Amartya Sen about Singur etc”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 31.
186. “Martin Buber on Palestine and Israel (with Postscript)”, Aug 4.
187. “Auguste Rodin on Nature, Art, Beauty, Women and Love”, Aug 7.
188. “Saving Pakistan: A Physicist/Political Philosopher May Represent Iqbal’s “Spirit of Modern Times”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 13.
189. Letter to Forbes.com 16 Aug.
190. “Need for Clarity: A poorly drafted treaty driven by business motives is a recipe for international misunderstanding”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 19.
191. “No Marxist MBAs? An amicus curiae brief for the Hon’ble High Court”, The Statesman, FrontPage, Aug 29.
192. On Lawrence, Sep 4.
193. Dalai Lama’s Return: In the tradition of Gandhi, King, Mandela, Sep 11.
194. Of JC Bose, Patrick Geddes & the Leaf-World, Sep 12.
195. “Against Quackery: Manmohan and Sonia have violated Rajiv Gandhi’s intended reforms; the Communists have been appeased or bought; the BJP is incompetent Parts 1-2”, in The Sunday Statesman and The Statesman, Editorial Pages of Sep 23-24.
196. Karl Georg Zinn’s 1994 Review of Philosophy of Economics, Sep 26.
197. DH Lawrence’s Phoenix, Oct 3.
93b. “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform”, Statesman Festival Volume.
198. “Iran, America, Iraq: Bush’s post-Saddam Saddamism — one flip-flop too many?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 16.
199. “Understanding China: The World Needs to Ask China to Find Her True Higher Self”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 22.
200. “India-USA interests: Elements of a serious Indian foreign policy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 30.
201. “China’s India Aggression : German Historians Discover Logic Behind Communist Military Strategy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, Nov 5.
202. Sonia’s Lying Courtier (with Postscript), Nov 25. See also 2014
203. “Surrender or Fight? War is not a cricket match or Bollywood movie. Can India fight China if it must?” The Statesman, Dec 4, Editorial Page.
204. Hutton and Desai: United in Error Dec 14
205. “China’s Commonwealth: Freedom is the Road to Resolving Taiwan, Tibet, Sinkiang”, The Statesman, Dec 17.
2008
206. “Nixon & Mao vs India: How American foreign policy did a U-turn about Communist China’s India aggression. The Government of India should publish its official history of the 1962 war.” The Sunday Statesman, Jan 6, The Statesman Jan 7 Editorial Page.
207. “Lessons from the 1962 War: Beginnings of a solution to the long-standing border problem: there are distinct Tibetan, Chinese and Indian points of view that need to be mutually comprehended”, The Sunday Statesman, January 13 2008.
208. “Our Dismal Politics: Will Independent India Survive Until 2047?”, The Statesman Editorial Page, Feb 1.
209. Median Voter Model of India’s Electorate Feb 7.
210. “Anarchy in Bengal: Intra-Left bandh marks the final unravelling of “Brand Buddha””, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 10.
211. Fifty years since my third birthday: on life and death.
212. “Pakistan’s Kashmir obsession: Sheikh Abdullah Relied In Politics On The French Constitution, Not Islam”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 16.
213. A Note on the Indian Policy Process Feb 21.
214. “Growth & Government Delusion: Progress Comes From Learning, Enterprise, Exchange, Not The Parasitic State”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 22.
215. “How to Budget: Thrift, Not Theft, Needs to Guide Our Public Finances”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 26.
216. “India’s Budget Process (in Theory)”, The Statesman, Front Page Feb 29.
217. “Irresponsible Governance: Congress, BJP, Communists, BSP, Sena Etc Reveal Equally Bad Traits”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 4.
218. “American Politics: Contest Between Obama And Clinton Affects The World”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 11.
219. “China’s India Example: Tibet, Xinjiang May Not Be Assimilated Like Inner Mongolia And Manchuria”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 25.
220. “Taxation of India’s Professional Cricket: A Proposal”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 1.
221. “Two cheers for Pakistan!”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 7.
222. “Indian Inflation: Upside Down Economics From The New Delhi Establishment Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 15-16.
223. “Assessing Manmohan: The Doctor of Deficit Finance should realise the currency is at stake”, The Statesman, Editorial Page Apr 25.
224. John Wisdom, Renford Bambrough: Main Philosophical Works, May 8.
225. “All India wept”: On the death of Rajiv Gandhi, May 21.
226. “China’s force and diplomacy: The need for realism in India” The Statesman, Editorial Page May 31.
227. Serendipity and the China-Tibet-India border problem June 6
228. “Leadership vacuum: Time & Tide Wait For No One In Politics: India Trails Pakistan & Nepal!”, The Statesman Editorial Page June 7.
229. My meeting Jawaharlal Nehru Oct13 1962
230. Manindranath Roy 1891-1958
231. Surendranath Roy 1860-1929
232. The Roys of Behala 1928.
233. Sarat Chandra visits Surendranath Roy 1927
234. Nuksaan-Faida Analysis = Cost-Benefit Analysis in Hindi/Urdu Jun 30
235. One of many reasons John R Hicks was a great economist July 3
236. My father, Indian diplomat, in the Shah’s Tehran 1954-57 July 8
237 Distribution of Govt of India Expenditure (Net of Operational Income) 1995 July 27
238. Growth of Real Income, Money & Prices in India 1869-2008, July 28.
239. Communism from Social Democracy? But not in India or China! July 29
240. Death of Solzhenitsyn, Aug. 3
240a. Tolstoy on Science and Art, Aug 4.
241. “Reddy’s reckoning: Where should India’s real interest rate be relative to the world?” Business Standard Aug 10
242. “Rangarajan Effect”, Business Standard Aug 24
243. My grandfather’s death in Ottawa 50 years ago today Sep 3
244. My books in the Library of Congress and British Library Sep 12
245. On Jimmy Carter & the “India-US Nuclear Deal”, Sep 12
246. My father after presenting his credentials to President Kekkonen of Finland Sep 14 1973.
247. “October 1929? Not!”, Business Standard, Sep 18.
248. “MK Gandhi, SN Roy, MA Jinnah in March 1919: Primary education legislation in a time of protest”
249. 122 sensible American economists Sept 26
250. Govt of India: Please call in the BBC and ask them a question Sep 27
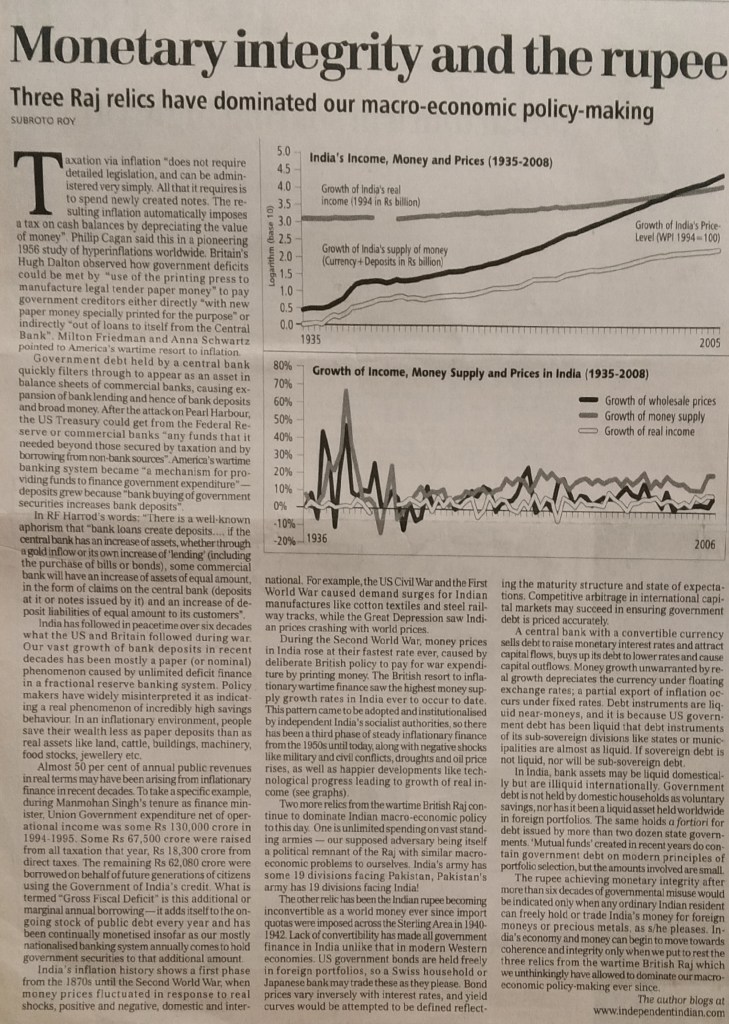
251. “Monetary Integrity and the Rupee: Three British Raj relics have dominated our macroeconomic policy-making” Business Standard Sep 28.
252a. Rabindranath’s daughter writes to her friend my grandmother Oct 5
252b. A Literary Find: Modern Poetry in Bengal, Oct 6.
253. Sarat writes to Manindranath 1931, Oct 12
254. Origins of India’s Constitutional Politics 1913
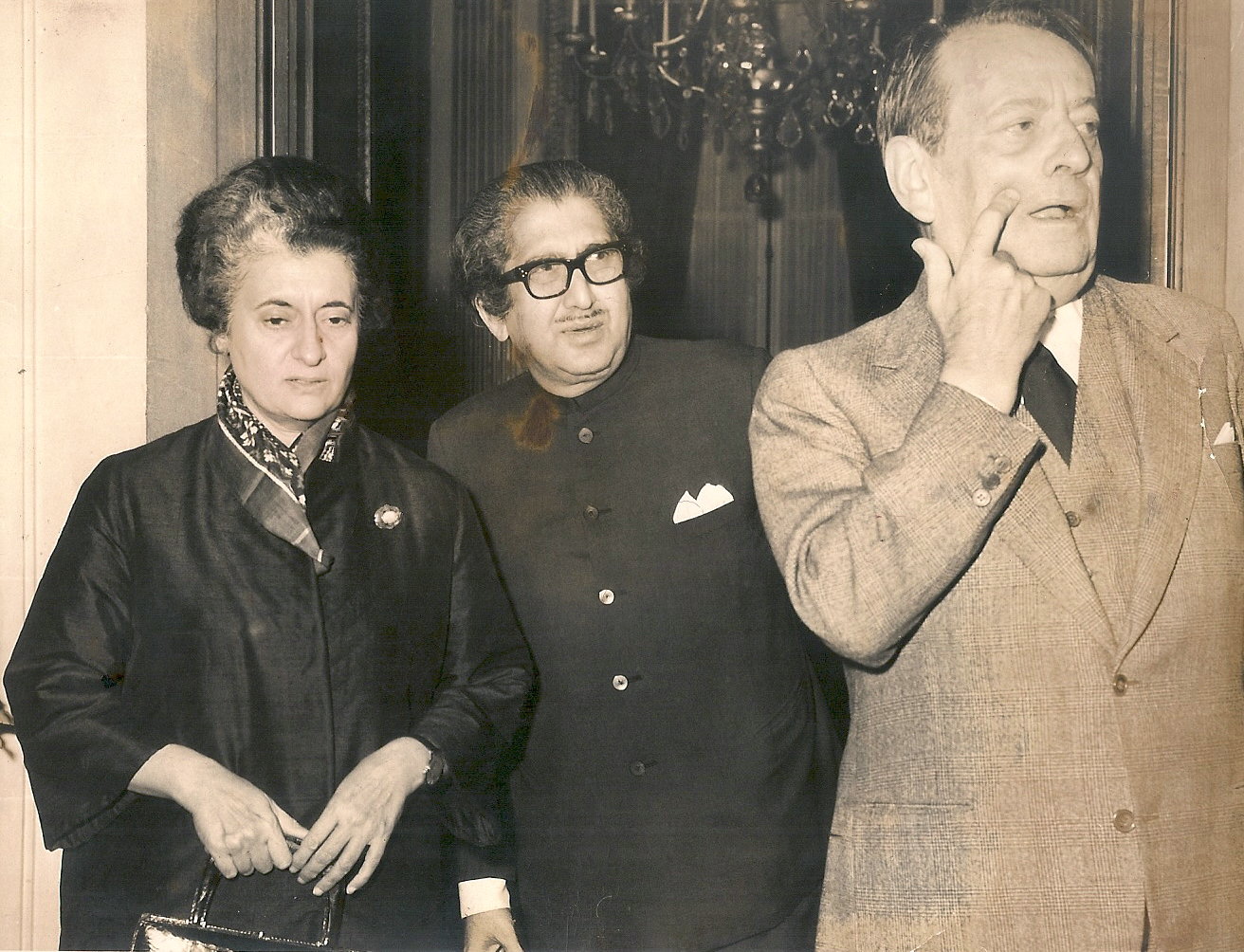
255. Indira Gandhi in Paris, 1971
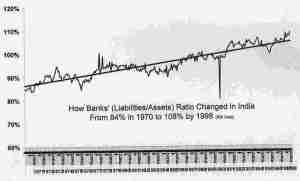
256. How the Liabilities/Assets Ratio of Indian Banks Changed from 84% in 1970 to 108% in 1998, October 20
257a. My Subjective Probabilities on India’s Moon Mission Oct 21
258. Complete History of Mankind’s Moon Missions: An Indian Citizen’s Letter to ISRO’s Chairman, Oct 22.
259. Would not a few million new immigrants solve America’s mortgage crisis? Oct 26
260. “America’s divided economists”, Business Standard Oct 26
261. One tiny prediction about the Obama Administration, Nov 5
262. Rai Bahadur Umbika Churn Rai, 1827-1902, Nov 7 2008
263. Jawaharlal Nehru invites my father to the Mountbatten Farewell Nov 7 2008
70a. “Become a US Supreme Court Justice! (Explorations in the Rule of Law in America) Preface” Nov 9
70b. “Become a US Supreme Court Justice! (Explorations in the Rule of Law in America)” Nov 9.
257b. Neglecting technological progress was the basis of my pessimism about Chandrayaan, Nov 9.
264. Of a new New Delhi myth and the success of the University of Hawaii 1986-1992 Pakistan project Nov 15
265. Pre-Partition Indian Secularism Case-Study: Fuzlul Huq and Manindranath Roy Nov 16
266. Do President-elect Obama’s Pakistan specialists suppose Maulana Azad, Dr Zakir Hussain, Sheikh Abdullah were Pakistanis (or that Sheikh Mujib wanted to remain one)? Nov 18
267. Jews have never been killed in India for being Jews until this sad day, Nov 28.
268. In international law, Pakistan has been the perpetrator, India the victim of aggression in Mumbai, Nov 30.
269. The Indian Revolution, Dec 1.
270. Habeas Corpus: a captured terrorist mass-murderer tells a magistrate he has not been mistreated by Mumbai’s police Dec 3
271. India’s Muslim Voices (Or, Let us be clear the Pakistan-India or Kashmir conflicts have not been Muslim-Hindu conflicts so much as intra-Muslim conflicts about Muslim identity and self-knowledge on the Indian subcontinent), Dec 4
272. “Anger Management” needed? An Oxford DPhil recommends Pakistan launch a nuclear first strike against India within minutes of war, Dec 5.
273. A Quick Comparison Between the September 11 2001 NYC-Washington attacks and the November 26-28 2008 Mumbai Massacres (An Application of the Case-by-Case Philosophical Technique of Wittgenstein, Wisdom and Bambrough), Dec 6
274. Dr Rice finally gets it right (and maybe Mrs Clinton will too) Dec 7
275. Will the Government of India’s new macroeconomic policy dampen or worsen the business-cycle (if such a cycle exists at all)? No one knows! “Where ignorance is bliss, ‘Tis folly to be wise.” Dec 7
276. Pump-priming for car-dealers: Keynes groans in his grave (If evidence was needed of the intellectual dishonesty of New Delhi’s new macroeconomic policy, here it is) Dec 9.
277. Congratulations to Mumbai’s Police: capturing a terrorist, affording him his Habeas Corpus rights, getting him to confess within the Rule of Law, sets a new world standard Dec 10
278. Two cheers — wait, let’s make that one cheer — for America’s Justice Department, Dec 10
279. Will Pakistan accept the bodies of nine dead terrorists who came from Pakistan to Mumbai? If so, let there be a hand-over at the Wagah border, Dec 11.
280. Kasab was a stupid, ignorant, misguided youth, manufactured by Pakistan’s terrorist masterminds into becoming a mass-murdering robot: Mahatma Gandhi’s India should punish him, get him to repent if he wishes, then perhaps rehabilitate him as a potent weapon against Pakistani terrorism Dec 12.
281. Pakistan’s New Delhi Embassy should ask for “Consular Access” to nine dead terrorists in a Mumbai morgue before asking to meet Kasab, Dec 13
282. An Indian Reply to President Zardari: Rewarding Pakistan for bad behaviour leads to schizophrenic relationships Dec 19
283. Is my prediction about Caroline Kennedy becoming US Ambassador to Britain going to be correct? Dec 27
284. Chandrayaan adds a little good cheer! Well done, ISRO!, Dec 28
285. How sad that “Slumdog millionaire” is SO disappointing! Dec 31
289. (with Claude Arpi) “Transparency & history: India’s archives must be opened to world standards” Business Standard New Delhi Dec 31, 2008, published here Jan 1 .
2009
290. A basis of India-Pakistan cooperation on the Mumbai massacres: the ten Pakistani terrorists started off as pirates and the Al-Huseini is a pirate ship Jan 1.
291. India’s “pork-barrel politics” needs a nice (vegetarian) Hindi name! “Teli/oily politics” perhaps? (And are we next going to see a Bill of Rights for Lobbyists?) Jan 3
292. My (armchair) experience of the 1999 Kargil war (Or, “Actionable Intelligence” in the Internet age: How the Kargil effort got a little help from a desktop) Jan 5
293. How Jammu & Kashmir’s Chief Minister Omar Abdullah can become a worthy winner of the Nobel Peace Prize: An Open Letter, Jan 7
294. Could the Satyam/PwC fraud be the visible part of an iceberg? Where are India’s “Generally Accepted Accounting Principles”? Isn’t governance rather poor all over corporate India? Bad public finance may be a root cause Jan 8
295. Satyam does not exist: it is bankrupt, broke, kaput. Which part of this does the new “management team” not get? The assets belong to Satyam’s creditors. Jan 8
296. Jews are massacred in Mumbai and now Jews commit a massacre in Gaza! Jan 9
297. And now for the Great Satyam Whitewash/Cover-Up/Public Subsidy! The wrong Minister appoints the wrong new Board who, probably, will choose the wrong policy Jan 12
298. Letter to Wei Jingsheng Jan 14
299. Memo to the Hon’ble Attorneys General of Pakistan & India: How to jointly prosecute the Mumbai massacre perpetrators most expeditiously Jan 16
300. Satyam and IT-firms in general may be good candidates to become “Labour-Managed” firms Jan 18
301. “Yes we might be able to do that. Perhaps we ought to. But again, perhaps we ought not to, let me think about it…. Most important is Cromwell’s advice: Think it possible we may be mistaken!” Jan 20.
302. RAND’s study of the Mumbai attacks Jan 25
303. Didn’t Dr Obama (the new American President’s late father) once publish an article in Harvard’s Quarterly Journal of Economics? (Or did he?) Jan 25.
304. “A Dialogue in Macroeconomics” 1989 etc: sundry thoughts on US economic policy discourse Jan 30
305. American Voices: A Brief Popular History of the United States in 20 You-Tube Music Videos Feb 5
306. Jaladhar Sen writes to Manindranath at Surendranath’s death, Feb 23
307. Pakistani expansionism: India and the world need to beware of “Non-Resident Pakistanis” ruled by Rahmat Ali’s ghost, Feb 9
308. My American years Part One 1980-90: battles for academic integrity & freedom Feb 11.
309. Thanks and well done Minister Rehman Malik and the Govt of Pakistan Feb 12
310. Can President Obama resist the financial zombies (let alone slay them)? His economists need to consult Dr Anna J Schwartz Feb 14
311. A Brief History of Gilgit, Feb 18
312. Memo to UCLA Geographers: Commonsense suggests Mr Bin Laden is far away from the subcontinent Feb 20
313. The BBC gets its history and geography deliberately wrong again Feb 21
314. Bengal Legislative Council 1921, Feb 28
315. Carmichael visits Surendranath, 1916, Mar 1
316. Memo to GoI CLB: India discovered the Zero, and 51% of Zero is still Zero Mar 10
317. An Academic Database of Doctoral & Other Postgraduate Research Done at UK Universities on India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Other Asian Countries Over 100 Years, Mar 13
318. Pakistan’s progress, Mar 18
319. Risk-aversion explains resistance to free trade, Mar 19
320. India’s incredibly volatile inflation rate! Mar 20
321. Is “Vicky, Cristina, Barcelona” referring to an emasculation of (elite) American society?, Mar 21
322. Just how much intellectual fraud can Delhi produce? Mar 26
323. India is not a monarchy! We urgently need to universalize the French concept of “citoyen”! Mar 28
324. Could this be the real state of some of our higher education institutions? Mar 29
325. Progress! The BBC retracts its prevarication! Mar 30
326. Aldous Huxley’s Essay “DH Lawrence” Mar 31
327. Waffle not institutional reform is what (I predict) the “G-20 summit” will produce, April 1
328. Did a full cricket team of Indian bureaucrats follow our PM into 10 Downing Street? Count for yourself! April 3
329. Will someone please teach the BJP’s gerontocracy some Economics 101 on an emergency basis? April 5
330. The BBC needs to determine exactly where it thinks Pakistan is!, April 5
331. Alfred Lyall on Christians, Muslims, India, China, Etc, 1908, April 6
332. An eminent economist of India passes away April 9
333. Democracy Database for the Largest Electorate Ever Seen in World History, April 12
334. Memo to the Election Commission of India April 14 2009, 9 AM, April 14
335. Caveat emptor! Satyam is taken over, April 14
336. India’s 2009 General Elections: Candidates, Parties, Symbols for Polls on 16-30 April Phases 1,2,3, April 15
337. On the general theory of expertise in democracy: reflections on what emerges from the American “torture memos” today, April 18
338. India’s 2009 General Elections: 467 constituencies (out of 543) for which candidates have been announced as of 1700hrs April 21, April 21
339. Apropos Philosophy of Economics, Comments of Sidney Hook, KJ Arrow, Milton Friedman, TW Schultz, SS Alexander, Max Black, Renford Bambrough, John Gray et al., April 22.
340. India’s 2009 General Elections: Names of all 543 Constituencies of the 15th Lok Sabha, April 22.
341. India’s 2009 General Elections: How 4125 State Assembly Constituencies comprise the 543 new Lok Sabha Constituencies, April 23.
342. Why has America’s “torture debate” yet to mention the obvious? Viz., sadism and racism, April 24
343. India’s 2009 General Elections: the advice of the late “George Eliot” (Mary Ann Evans, 1819-1880) to India’s voting public, April 24.
344. India’s 2009 General Elections: Delimitation and the Different Lists of 543 Lok Sabha Constituencies in 2009 and 2004, April 25
345. Is “Slumdog Millionaire” the single worst Best Picture ever?
346. India’s 2009 General Elections: Result of Delimitation — Old (2004) and New (2009) Lok Sabha and Assembly Constituencies, April 26
347. India’s 2009 General Elections: 7019 Candidates in 485 (out of 543) Constituencies announced as of April 26 noon April 26
348. What is Christine Fair referring to? Would the MEA kindly seek to address what she has claimed asap? April 27
349. Politics can be so entertaining  Manmohan versus Sonia on the poor old CPI(M)!, April 28
Manmohan versus Sonia on the poor old CPI(M)!, April 28
350. A Dozen Grown-Up Questions for Sonia Gandhi, Manmohan Singh, LK Advani, Sharad Pawar, Km Mayawati and Anyone Else Dreaming of Becoming/Deciding India’s PM After the 2009 General Elections, April 28
351. India’s 2009 General Elections: How drastically will the vote-share of political parties change from 2004? May 2
352. India’s 2009 General Elections: And now finally, all 8,070 Candidates across all 543 Lok Sabha Constituencies, May 5
353. India’s 2009 General Elections: The Mapping of Votes into Assembly Segments Won into Parliamentary Seats Won in the 2004 Election, May 7
354. Will Messrs Advani, Rajnath Singh & Modi ride into the sunset if the BJP comes to be trounced? (Corrected), May 10
355. India’s 2009 General Elections: 543 Matrices to Help Ordinary Citizens Audit the Election Commission’s Vote-Tallies May 12
356. Well done Sonia-Rahul! Two hours before polls close today, I am willing to predict a big victory for you (but, please, try to get your economics right, and also, you must get Dr Singh a Lok Sabha seat if he is to be PM) May 13
357. Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee must dissolve the West Bengal Assembly if he is an honest democrat: Please try to follow Gerard Schröder’s example even slightly! May 16
358. India’s 2009 General Elections: Provisional Results from the EC as of 1400 hours Indian Standard Time May 16
359. Memo to the Hon’ble President of India: It is Sonia Gandhi, not Manmohan Singh, who should be invited to our equivalent of the “Kissing Hands” Ceremony May 16
360. Time for heads to roll in the BJP/RSS and CPI(M)!, May 17.
361. Inviting a new Prime Minister of India to form a Government: Procedure Right and Wrong May 18
362. Starting with Procedural Error: Why has the “Cabinet” of the 14th Lok Sabha been meeting today AFTER the results of the Elections to the 15th Lok Sabha have been declared?! May 18
363. Why has the Sonia Congress done something that the Congress under Nehru-Indira-Rajiv would not have done, namely, exaggerate the power of the Rajya Sabha and diminish the power of the Lok Sabha? May 21
364. Shouldn’t Dr Singh’s Cabinet begin with a small apology to the President of India for discourtesy? May we have reviews and reforms of protocols and practices to be followed at Rashtrapati Bhavan and elsewhere? May 23
365. Parliament’s sovereignty has been diminished by the Executive: A record for future generations to know May 25
366. How tightly will organised Big Business be able to control economic policies this time? May 26
367. Why does India not have a Parliament ten days after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected? Nehru and Rajiv would both have been appalled May 27
368. Eleven days and counting after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected and still no Parliament of India! (But we do have 79 Ministers — might that be a world record?) May 28
369. Note to Posterity: 79 Ministers in office but no 15th Lok Sabha until June 1 2009! May 29
370. Silver Jubilee of Pricing, Planning & Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India May 29
371. How to Design a Better Cabinet for the Government of India May 29
372. Parliament is supposed to control the Government, not be bullied or intimidated by it: Will Rahul Gandhi be able to lead the Backbenches in the 15th Lok Sabha? June 1
373. Mistaken Macroeconomics: An Open Letter to Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh, June 12
374. Why did Manmohan Singh and LK Advani apologise to one another? Is Indian politics essentially collusive, not competitive, aiming only to preserve and promote the post-1947 Dilli Raj at the expense of the whole of India? We seem to have no Churchillian repartee (except perhaps from Bihar occasionally) June 18
375. Are Iran’s Revolutionaries now Reactionaries? George Orwell would have understood. A fresh poll may be the only answer Are Iran’s Revolutionaries now Reactionaries? George Orwell would have understood. A fresh poll may be the only answer June 22
376. My March 25 1991 memo to Rajiv (which never reached him) is something the present Government seems to have followed: all for the best of course! July 12
377. Disquietude about France’s behaviour towards India on July 14 2009 July 14
378. Does the Govt. of India assume “foreign investors and analysts” are a key constituency for Indian economic policy-making? If so, why so? Have Govt. economists “learnt nothing, forgotten everything”? Some Bastille Day thoughts July 14
379. Letter to the GoI’s seniormost technical economist, May 21.July 19
380. Excuse me but young Kasab in fact confessed many months ago, immediately after he was captured – he deserves 20 or 30 years in an Indian prison, and a chance to become a model prisoner who will stand against the very terrorists who sent him on his vile mission July 20
381. Finally, three months late, the GoI responds to American and Pakistani allegations about Balochistan July 24
382. Thoughts, words, deeds: My work 1973-2010
2012
383. Life of my father 1915-2012
384. India’s Money” in the Cayman Financial Review, July 2012
386. 5 December 2012 interview by Mr Paranjoy Guha Thakurta, on Lok Sabha TV, the channel of India’s Lower House of Parliament, broadcast for the first time on 9 December 2012 on Lok Sabha TV, is here and here in two parts.
387. Interview by GDI Impuls banking quarterly of Zürich published on 6 Dec 2012 is here.
388. My interview by Ragini Bhuyan of Delhi’s Sunday Guardian published on 16 Dec 2012 is here.
2013
391. Critical assessment dated 19 August 2013 of Raghuram Rajan is here (Live Mint 19 Aug) and here
392. “Did Jagdish Bhagwati “originate”, “pioneer”, “intellectually father” India’s 1991 economic reform? Did Manmohan Singh? Or did I, through my encounter with Rajiv Gandhi, just as Siddhartha Shankar Ray told Manmohan & his aides in Sep 1993 in Washington? Judge the evidence for yourself. And why has Amartya Sen misdescribed his work? India’s right path forward today remains what I said in my 3 Dec 2012 Delhi lecture! 23 August 2013 here
393. My Recent Works, Interviews etc on India’s Money, Public Finance, Banking, Trade, BoP, Land, etc (an incomplete list) Nov 23, 2013
2014
394. 1) My 13 Sep 2019 Advice to PM Modi’s Adviser: Let PM address each State Legislature, get all India Govt Accounting & Public Decision Making to have integrity (2) 16 May 2014 Advice from Rajiv Gandhi’s Adviser to Narendra Modi: Do not populate the “Planning Commission” with worthies, scrap it, integrate its assets with the Treasury. And get the nationalised banks & RBI out of the Treasury. Tell them to read my 3 Dec 2012 Delhi lecture with care. Clean Government Accounting & Audit is the Key to Clean Public Finances & a Proper Indian Currency for the First Time Ever May 16, 2014.
396. Much as I might love Russia, England, France, America, I despise their spies & local agents affecting poor India’s policies: Memo to PM Modi, Mr Jaitley, Mr Doval & the new Govt. of India: Beware of Delhi’s sleeper agents, lobbyists & other dalals
397. “Haksar, Manmohan and Sonia” August 7, 2014 New Indian Express http://t.co/bRnQI1hrwy
2015
399. Delhi can never be improved — until the rest of India improves! February 13, 2015
400. Pakistan’s & India’s Illusions of Power (Psychosis vs Vanity) March 3, 2015
401. How the India-Bangladesh Enclaves Problem Was Jump-Started in 2007 Towards its 2015 Solution: A Case Study of Academic Impact on Policy June 8, 2015
402. On being reunited with Arrow Hahn after a dozen years July 3, 2015
403. Fixing Washington: On Improving Institutional Design in the United States November 24, 2016
404. Modi & Monetary Theory: Economic Consequences of the Prime Minister of India December 9, 2016.
405. Physics & Reasoning (An Ongoing Tract) by Subroto Roy DRAFT 01.12.2017 September 26, 2017
406. Is “Cambridge Philosophy” dead, in Cambridge? Can it be resurrected, there? Case Study: Renford Bambrough (& Subroto Roy) preceded by decades Cheryl Misak’s thesis on Wittgenstein being linked with Peirce via Ramsey… October 27, 2017
407. S N Roy hears from Lytton: A 1922 case of British imperial racism in Indian governance (with lessons for today) [Draft text 12 August 2018] February 8, 2018
408. Solving a Problem of State Tyranny: Director General Siddhanta Das: Have Forest Service Officers been threatening ordinary citizens, seizing their property, then threatening them with arrest if they complain? If so, how many cases of wrongful seizure and wrongful imprisonment have WCCB caused among India’s villagers and forest dwellers since 1994? There is immediate need for an Ombudsman to independently review all cases in each of your Five Zones! May 4,
409. Critique of Monetary Ideas of Manmohan & Modi: the Roy Model explaining to Bimal Jalan, Nirmala Sitharaman, RBI etc what it is they are doing (Drafts 4 August, 7 August 2019; 27 August, 28 August, 30 August, 31 August, 1 September 2019) August 4, 2019
410. 1 May 2020 Statement of Dr. Subroto Roy, Economist & Citizen, Proposing PM Narendra Modi & Home Minister Amit Shah Apologize to India’s People, Create Remedy, and Resign to Do Prayaschit/Atonement; 9 May: A New Cabinet for President Kovind May 1, 2020
See also:
M1. Map of Asia c. 1900
M2. Map of Chinese Empire c. 1900
M3. Map of Sinkiang, Tibet and Neighbours 1944
M4. China’s Secretly Built 1957 Road Through India’s Aksai Chin
M5. Map of Kashmir to Sinkiang 1944
M6. Map of India-Tibet-China-Mongolia 1959
M7. Map of India, Afghanistan, Russia, China, 1897
M8. Map of Xinjiang/Sinkiang/E Turkestan
M9. Map of Bombay/Mumbai 1909
M10-M13. Himalayan Expedition, West Sikkim 1970 – 1,2,3,4
Thoughts, words, deeds
My work 1973-2014
Subroto Roy
This is an incomplete bibliography of my writings, public lectures etc 1973-2014 including citations, reviews, comments. I have been mostly an academic economist who by choice or circumstance over 41 years has had to venture also into science, philosophy, public policy, law, jurisprudence, practical politics, history, international relations, military strategy, financial theory, accounting, management, journalism, literary criticism, psychology, psychoanalysis, theology, aesthetics, biography, children’s fables, etc. If anything unites the seemingly diverse work recorded below it is that I have tried to acquire a grasp of the nature of human reason and then apply this comprehension in practical contexts as simply and clearly as possible. Hence I have ended up following the path of Aristotle, as described in modern times (via Wittgenstein and John Wisdom) by Renford Bambrough. The 2004 public lecture in England, “Science, Religion, Art & the Necessity of Freedom”, may explain and illustrate all this best. A friend has been kind enough to call me an Academician, which I probably am, though one who really needs his own Academy because the incompetence, greed and mendacity encountered too often in the modern professoriat is dispiriting.
Besides writings and publications printed on paper, there are writings or items not printed on paper — as new media break space, cost and other constraints of traditional publishing. A little repetition and overlap has occurred too. Also in a few cases, e.g., Aldous Huxley’s essay on DH Lawrence, nothing has been done except discover and republish. Several databases have been created and released in the public interest, as have been some rare maps. There is also some biographical and autobiographical material. Several inconsequential errors remain in the text, which shall take time to be rectified as documents come to be rediscovered and collated.
1973
1. “Behavioural study of mus musculus”, Haileybury College, Supervised by J de C Ford-Robertson MA (Oxon). (Due to be published here 2010).
2. “Chemistry at Advanced & Special Level: Student Notes 1972-73” (Due to be published here 2010).
3. “Biology at Advanced & Special Level: Student Notes 1972-73”, (Due to be published here 2010).
4. “Physics at Advanced Level: Student Notes 1972-73”, (Due to be published here 2010).
5. “Revolution: theoria and praxis”, London, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
6. “Gandhi vs Marx”, London, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
1974
7. “Relevance of downward money-wage rigidity to the problem of maintaining full-employment in the classical and Keynesian models of income determination”, London School of Economics, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
8. “Testing aircraft fuels at Shell Finland”.
1975
9. “Oxford Street experiences: down and out in London town”.
10. “SE Region Bulk Distribution Survey”, Unilever, Basingstoke.
11. “Four London poems”, in JCM Paton (ed) New Writing (London, Great Portland Street: International Students House). (Due to be republished here 2010)
12. “On economic growth models and modellers”, London School of Economics, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
1976
13. “World money: system or anarchy?”, lecture to Professor ACL Day’s seminar, London School of Economics, Economics Department, April. (Due to be published here 2010).
14. “A beginner’s guide to some recent developments in monetary theory”, lecture to Professor FH Hahn’s seminar, Cambridge University Economics Department, November 17 (Due to be published here 2010). See also “Announcement of My “Hahn Seminar”, published here June 14 2008.
1977
15. “Inflation and unemployment: a survey”, mimeo, Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge. (Due to be published here 2010).
16. “On short run theories of dual economies”, Cambridge University Economics Department “substantial piece of work” required of first year Research Students. Examiner: DMG Newbery, FBA. (Due to be published here 2010).
1978
17. “Pure theory of developing economies 1 and 2”, Delhi School of Economics mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
18. “Introduction to some market outcomes under uncertainty”, Delhi School of Economics mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
19. “On money and development”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo, September. (Due to be published here 2010)
20. “Notes on the Newbery-Stiglitz model of sharecropping”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo November. (Due to be published here 2010).
1979
21. “A theory of rights and economic justice”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
22. “Monetary theory and economic development”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
23. “Foundations of the case against ‘development planning’”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge, mimeo, November. (Due to be published here 2010).
1979-1989
24. Correspondence with Renford Bambrough (1926-1999), philosopher of St John’s College, Cambridge (Due to be published here 2010).
1980
25. “Models before the monetarist storm”, New Statesman letters
26. “Disciplining rulers and experts”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
1981
27. “On liberty & economic growth: preface to a philosophy for India”, Cambridge University doctoral thesis, supervisor FH Hahn, FBA; examiners CJ Bliss, FBA; TW Hutchison, FBA (Due to be published here 2010). 27a Response of FA Hayek on a partial draft February 18 1981. 27b Response of Peter Bauer, 1982. 27c Response of Theodore W Schultz, 1983. 27d. Response of Frank Hahn 1985.
1982
28. “Knowledge and freedom in economic theory Parts 1 and 2”, Centre for Study of Public Choice, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University, Working Papers.
29. “Economic Theory and Development Economics”. Lecture to American Economic Association, New York, Dec 1982. Panel: RM Solow, HB Chenery, T Weisskopf, P Streeten, G Rosen, S Roy. Published in 29a.
1983
29a “Economic Theory and Development Economics: A Comment”. World Development, 1983. [Citation: Stavros Thefanides “Metamorphosis of Development Economics”, World Development 1988.]
30. “The Political Economy of Trade Policy (Comment on J. Michael Finger)”, Washington DC: Cato Journal, Winter 1983/84. See also “Did Donald Trump & Bernie Sanders get their Trade Policy from my 1983 Cato talk?” 2009/2017.
1984
31. “Considerations on Utility, Benevolence and Taxation”, History of Political Economy, 1984. 31a Response of Professor Sir John Hicks May 1 1984.
[Citations: P. Hennipman, “A Tale of Two Schools”, De Economist 1987, “A New Look at the Ordinalist Revolution”, J. Econ. Lit. Mar 1988; P. Rappoport, “Reply to Professor Hennipman”, J. Econ. Lit. Mar 1988; Eugene Smolensky et al “An Application of A Dynamic Cost-of-Living Index to the Evaluation of Changes in Social Welfare”, J. Post-Keynesian Econ.IX.3. 1987.]
32. Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India, London: Institute of Economic Affairs, London 1984.
[Citations: Lead editorial of The Times of London May 29 1984, “India’s economy”, Times letters June 16 1984. John Toye “Political Economy & Analysis of Indian Development”, Modern Asian Studies, 22, 1, 1988; John Toye, Dilemmas of Development; D. Wilson, “Privatization of Asia”, The Banker Sep. 1984 etc]. See also 370 “Silver Jubilee of ‘Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India’” 2009.
33. Review of Utilitarianism and Beyond, Amartya Sen & Bernard Williams (eds) Public Choice.
34. Review of Limits of Utilitarianism, HB Miller & WH Williams (eds.), Public Choice.
35. Deendayal lecture (one of four invited lecturers), Washington DC, May October “On Government and the Individual in India”
1987
36. (with one other) “Does the Theory of Logical Types Inform the Theory of Communication?”, Journal of Genetic Psychology., 148 (4), Dec. 1987 [Citation:
37. “Irrelevance of Foreign Aid”, India International Centre Quarterly, Winter 1987.
38. Review of Development Planning by Sukhamoy Chakravarty for Economic Affairs, London 1987.
1988
39. (with Seiji Naya and Pearl Imada) “Introduction” to Lessons in Development: A Comparative Study of Asia and Latin America. San Francisco: Inst. of Economic Growth.
40. “A note on the welfare economics of regional cooperation”, lecture to Asia-Latin America conference, East West Center Honolulu, published 2009.
1989
41. Philosophy of Economics: On the Scope of Reason in Economic Inquiry, London & New York: Routledge (International Library of Philosophy) 1989, paperback 1991. Internet edition 2007. [Reviews & Citations: Research in Economics, 1992; De Economist 1991 & 1992; Manch.Sch. Econ.Studs. 59, 1991; Ethics 101.88 Jul. 1991; Kyklos 43.4 1990; Soc. Science Q. 71.880. Dec.1990; Can. Phil. Rev. 1990; J. Econ. Hist. Sep. 1990; Econ. & Phil. Fall 1990; Econ. Affairs June-July 1990; TLS May 1990; Choice March 1990; J. App.Phil. 1994, M. Blaug: Methodology of Economics, 2nd ed., Cambridge, 1992; Hist. Methods. 27.3, 1994; J. of Inst. & Theoretical Econ.,1994; Jahrbucker fur Nationaleconomie 1994, 573:574. Mark A Lutz in Economics for the Common Good, London: Routledge, 1999, et al]. See also 339 “Apropos Philosophy of Economics”, Comments of Sidney Hook, KJ Arrow, Milton Friedman, TW Schultz, SS Alexander, Max Black, Renford Bambrough, John Gray et al.
42. Foreword to Essays on the Political Economy by James M. Buchanan, Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press 1989.
43. “Modern Political Economy of India”, edited by Subroto Roy & William E James, Hawaii mimeo May 21 1989. This published for the first time a November 1955 memorandum to the Government of India by Milton Friedman. See also 43a, 53.
43a. Preface to “Milton Friedman’s extempore comments at the 1989 Hawaii conference: on India, Israel, Palestine, the USA, Debt and its uses, Erhardt abolishing exchange controls, Etc”, May 22 1989, published here for the first time October 31 2008.
44. Milton Friedman’s defence of my work in 1989.
45. Theodore W. Schultz’s defence of Philosophy of Economics
1990
46. “Letter to Judge Evelyn Lance: On A Case Study in Private International Law” (Due to be published here in 2010).
47-49. Selections from advisory work on economic policy etc for Rajiv Gandhi, Leader of the Opposition in the Parliament of India, published in 47a-49a.
1991
41b Philosophy of Economics: On the Scope of Reason in Economic Inquiry, Paperback edition.
50. “Conversations and correspondence with Rajiv Gandhi during the Gulf war, January 1991” (Due to be published here 2010).
47a. A Memo to Rajiv I: Stronger Secular Middle”, The Statesman, Jul 31 1991.
48a “A Memo to Rajiv II: Saving India’s Prestige”, The Statesman, Aug 1 1991.
49a “A Memo to Rajiv III: Salvation in Penny Capitalism”, The Statesman, Aug 2 1991 47b-49b “Three Memoranda to Rajiv Gandhi 1990-91”, 2007 republication here.
51. “Constitution for a Second Indian Republic”, The Saturday Statesman, April 20 1991. Republished here 2009.
52. “On the Art of Government: Experts, Party, Cabinet and Bureaucracy”, New Delhi mimeo March 25 1991, published here July 00 2009.
1992
53. Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s Edited and with an Introduction by Subroto Roy & William E. James New Delhi, London, Newbury Park: Sage: 1992. Citation: Milton and Rose Friedman Two Lucky People (Chicago 1998), pp. 268-269.
54. Foundations of Pakistan’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s Edited and with an Introduction by William E. James & Subroto Roy, Hawaii MS 1989, Sage: 1992, Karachi: Oxford 1993.
Reviews of 53 & 54 include: Bus. Today, Mar-Apr 1992; Political Studies March 1995; Econ Times 21 March 1993; Pakistan Development Review 1992. Hindustan Times 11 July 1992. Pacific Affairs 1993; Hindu 21 March 1993, 15 June 1993; Pakistan News International 12 June 1993. Book Reviews March 1993; Deccan Herald 2 May 1993; Pol.Econ.J. Ind. 1992. Fin Express 13 September 1992; Statesman 16 Jan. 1993. J. Royal Soc Asian Aff. 1994, J. Contemporary Asia, 1994 etc.
55. “Fundamental Problems of the Economies of India and Pakistan”, World Bank, Washington, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
56.“The Road to Stagflation: The Coming Dirigisme in America, or, America, beware thy economists!, or Zen and Clintonomics,” Washington DC, Broad Branch Terrace, mimeo, November 17.
1993
57. “Exchange-rates and manufactured exports of South Asia”, IMF Washington DC mimeo. Published in part in 2007-2008 as 58-62:
58. “Path of the Indian Rupee 1947-1993”, 2008.
59. “Path of the Pakistan Rupee 1947-1993”, 2008.
60. “Path of the Sri Lankan Rupee 1948-1993”, 2008.
61. “Path of the Bangladesh Taka 1972-1993”, 2008.
62. “India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh Manufactured Exports, IMF Washington DC mimeo”, published 2007.
63. “Economic Assessment of US-India Merchandise Trade”, Arlington, Virginia, mimeo, published in slight part in Indo-US Trade & Economic Cooperation, ICRIER New Delhi, 1995, and in whole 2007.
64. “Towards an Economic Solution for Kashmir”, mimeo, Arlington, Virginia, circulated in Washington DC 1993-1995, cf 82, 111 infra. Comment of Selig Harrison.
1994
65. “Comment on Indonesia”, in The Political Economy of Policy Reform edited by John Williamson, Washington, DC: Institute for International Economics.
66a “Gold reserves & the gold price in anticipation of Central Bank behaviour”, Greenwich, Connecticut, mimeo. 67b. “Portfolio optimization and foreign currency exposure hedging” Greenwich, Connecticut mimeo.
1995
68. “On the logic and commonsense of debt and payments crises: How to avoid another Mexico in India and Pakistan”, Scarsdale, NY, mimeo, May 1.
69. “Policies for Young India”, Scarsdale, NY, pp. 350, manuscript.
1996
70. US Supreme Court documents, published in part in 2008 as “Become a US Supreme Court Justice!” 70a, 70b (Due to be published in full here in 2010 as Roy vs University of Hawaii, 1989- including the expert testimonies of Milton Friedman and Theodore W Schultz.).
71. “Key problems of macroeconomic management facing the new Indian Government”, May 17. Scarsdale, New York, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
72. “Preventing a collapse of the rupee”, IIT Kharagpur lecture July 16 1996.
73. “The Economist’s Representation of Technological Knowledge”, Vishvesvaraya lecture to the Institution of Engineers, September 15 1996, IIT Kharagpur.
1997
74. “Union and State Budgets in India”, lecture at the World Bank, Washington DC, May 00.
75. “State Budgets in India”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo, June 6.
1998
76. “Transparency and Economic Policy-Making: An address to the Asia-Pacific Public Relations Conference” (panel on Transparency chaired by CR Irani) Jan 30 1998, published here 2008.
77. Theodore W. Schultz 1902-1998, Feb 25.
78. “The Economic View of Human Resources”, address to a regional conference on human resources, IIT Kharagpur.
79. “Management accounting”, lecture at Lal Bahadur Shastri Academy, Mussourie,
80a “The Original Reformer”, Outlook letters, Jan 23 1998
81. “Recent Developments in Modern Finance”, IIM Bangalore Review, 10, 1 & 2, Jan.-Jun 1998. Reprinted as “From the Management Guru’s Classroom”: 81a “An introduction to derivatives”, Business Standard/Financial Times, Bombay 18 Apr 1999; 81b “Options in the future, Apr 25 1999; 81c “What is hedging?”, May 2 1999; 81d “Teaching computers to think”, May 9 1999.
82. “Towards an Economic Solution for Kashmir”, Jun 22 1998, lecture at Heritage Foundation, Washington DC. Cf 111 Dec 2005.
83. “Sixteen Currencies for India: A Reverse Euro Model for Monetary & Fiscal Efficacy”, Lecture at the Institute of Economic Affairs, London, June 29 1998. Due to be published here 2010.
84. “Fable of the Fox, the Farmer, and the Would-Be Tailors”, October (Published here July 27 2009).
85. “A Common Man’s Guide to Pricing Financial Derivatives”, Lecture to “National Seminar on Derivatives”, Xavier Labour Research Institute, Jamshedpur, Dec. 16 1998. See 98.
1999
86. “An Analysis of Pakistan’s War-Winning Strategy: Are We Ready for This?”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo, published in part as 86a.“Was a Pakistani Grand Strategy Discerned in Time by India?” New Delhi: Security & Political Risk Analysis Bulletin, July 1999, Kargil issue. See also 000
80b. “The Original Reformer”, Outlook letters, Sep 13 1999.
2000
87. “On Freedom & the Scientific Point of View”, SN Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Feb 17 2000. Cf 100 below.
88. “Liberalism and Indian economic policy”, lecture at IIM Calcutta, Indian Liberal Group Meetings Devlali, Hyderabad; also Keynote address to UGC Seminar Guntur, March 30 2002. (Due to be published here 2010).
89. “Towards a Highly Transparent Fiscal & Monetary Framework for India’s Union & State Governments”, Invited address to Conference of State Finance Secretaries, Reserve Bank of India, Bombay, April 29, 2000. Published 2008.
90. “On the Economics of Information Technology”, two lectures at the Indian Institute of Information Technology, Bangalore, Nov 10-11, 2000.
91. Review of A New World by Amit Chaudhuri in Literary Criterion, Mysore.
2001
92. Review of AD Shroff: Titan of Finance and Free Enterprise by Sucheta Dalal, Freedom First., January.
93. “Encounter with Rajiv Gandhi: On the Origins of the 1991 Economic Reform”, Freedom First, October. See also 93a in 2005 and 93b in 2007.
94. “A General Theory of Globalization & Modern Terrorism with Special Reference to September 11”, a keynote address to the Council for Asian Liberals & Democrats, Manila, Philippines, 16 Nov. 2001. Published as 91a.
95. “The Case for and against The Satanic Verses: Diatribe and Dialectic as Art”, Dec 22 republished in print 95a The Statesman Festival Volume, 2006.
2002
94a “A General Theory of Globalization & Modern Terrorism with Special Reference to September 11”, in September 11 & Political Freedom in Asia, eds. Johannen, Smith & Gomez, Singapore 2002.
2002-2010
96. “Recording vivid dreams: Freud’s advice in exploring the Unconscious Mind” (Due to be published here in 2010).
2003
97. “Key principles of government accounting and audit”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo.
98. “Derivative pricing & other topics in financial theory: a student’s complete lecture notes” (Due to be published here in 2010).
2004
99. TV Interview by BBC, Oxford, after May 2004 General Election in India.
100. “Collapse of the Global Conversation”, International Institute for Asian Studies, Leiden, Netherlands, Jul 2004.
101. “Science, Religion, Art & the Necessity of Freedom”, a public lecture, University of Buckingham, UK, August 24 2004. Published here 2007.
2005
93a Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform (this was the full story; it appeared in print for the first time in The Statesman Festival Volume 2007).
102. “Can India become an economic superpower (or will there be a monetary meltdown)?” Cardiff University Institute of Applied Macroeconomics Monetary Economics Seminar, April 13, Institute of Economic Affairs, London, April 27, Reserve Bank of India, Bombay, Chief Economist’s Seminar on Monetary Economics, May 5.
103. Margaret Thatcher’s Revolution: How it Happened and What it Meant, Edited and with an Introduction by Subroto Roy & John Clarke, London & New York: Continuum, 2005; paperback 2006; French translation by Florian Bay, 2007.
104. “Iqbal & Jinnah vs Rahmat Ali in Pakistan’s Creation”, Dawn, Karachi, Sep 3.
105. “The Mitrokhin Archives II from an Indian Perspective: A Review Article”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 11 .
106. “After the Verdict”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 20.
107. “US Espionage Failures”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 26
108. “Waffle But No Models of Monetary Policy”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 30.
109. “On Hindus and Muslims”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Nov 6.
110. “Assessing Vajpayee: Hindutva True and False”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Nov 13-14″.
111. “Fiction from the India Economic Summit”, The Statesman, Front Page, Nov 29.
112. “Solving Kashmir: On an Application of Reason”, The Statesman Editorial Page
I. “Give the Hurriyat et al Indian Green Cards”, Dec 1
II. “Choice of Nationality under Full Information”, Dec 2
III. “Of Flags and Consulates in Gilgit etc”, Dec 3.
2006
113. “The Dream Team: A Critique”, The Statesman Editorial Page
I : New Delhi’s Consensus (Manmohantekidambaromics), Jan 6
II: Money, Convertibility, Inflationary Deficit Financing, Jan 7
III: Rule of Law, Transparency, Government Accounting, Jan 8.
114. “Unaccountable Delhi: India’s Separation of Powers’ Doctrine”, The Statesman, Jan 13.
115. “Communists and Constitutions”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 22.
116. “Diplomatic Wisdom”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 31.
117. “Mendacity & the Government Budget Constraint”, The Statesman, Front Page Feb 3.
118. “Of Graven Images”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb5.
119. “Separation of Powers, Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Pages Feb 12-13.
120. “Public Debt, Government Fantasy”, The Statesman, Front Page Editorial Comment, Feb 22.
121. “War or Peace Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 23-24.
122. “Can You Handle This Brief, Mr Chidambaram?” The Statesman, Front Page Feb 26.
123. “A Downpayment On the Taj Mahal Anyone?”, The Statesman, Front Page Comment on the Budget 2006-2007, Mar 1.
124. “Atoms for Peace (or War)”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Mar 5.
125. “Imperialism Redux: Business, Energy, Weapons & Foreign Policy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Mar 14.
126. “Logic of Democracy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Mar 30.
127. “Towards an Energy Policy”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 2.
128. “Iran’s Nationalism”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 6.
129. “A Modern Military”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 16.
130. “On Money & Banking”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 23.
131. “Lessons for India from Nepal’s Revolution”, The Statesman, Front Page Apr 26.
132. “Revisionist Flattery (Inder Malhotra’s Indira Gandhi: A Review Article)”, The Sunday Statesman, May 7.
133. “Modern World History”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, May 7.
134. “Argumentative Indians: A Conversation with Professor Amartya Sen on Philosophy, Identity and Islam,” The Sunday Statesman, May 14 2006. “A Philosophical Conversation between Professor Sen and Dr Roy”, 2008. Translated into Bengali by AA and published in 00.
135. “The Politics of Dr Singh”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, May 21.
136. “Corporate Governance & the Principal-Agent Problem”, lecture at a conference on corporate governance, Kolkata May 31. Published here 2008.
137. “Pakistan’s Allies Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jun 4-5.
138. “Law, Justice and J&K Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 2, The Statesman Editorial Page Jul 3.
139. “The Greatest Pashtun (Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan)”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 16.
140. “Understanding Pakistan Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 30, The Statesman Editorial Page Jul 31.
141. “Indian Money and Credit”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 6.
142. “India’s Moon Mission”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 13.
143. “Jaswant’s Journeyings: A Review Article”, The Sunday Statesman Magazine, Aug 27.
144. “Our Energy Interests, Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 27, The Statesman Editorial Page Aug 28.
145. “Is Balochistan Doomed?”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Sep 3 2006.
146. “Racism New and Old”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Sep 8 2006
147. “Political Economy of India’s Energy Policy”, address to KAF-TERI conference, Goa Oct 7, published in 147a.
148. “New Foreign Policy? Seven phases of Indian foreign policy may be identifiable since Nehru”, Parts 1-2, The Sunday Statesman, Oct 8, The Statesman Oct 9.
149. “Justice & Afzal: There is a difference between law and equity (or natural justice). The power of pardon is an equitable power. Commuting a death-sentence is a partial pardon”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Oct 14
150. “Non-existent liberals (On a Liberal Party for India)”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Oct 22.
151. “History of Jammu & Kashmir Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Oct 29, The Statesman Oct 30, Editorial Page.
152. “American Democracy: Does America need a Prime Minister and a longer-lived Legislature?”, The Sunday Statesman Nov 5.
153. “Milton Friedman A Man of Reason 1912-2006”, The Statesman Perspective Page, Nov 22.
154. “Postscript to Milton Friedman Mahalanobis’s Plan (The Mahalanobis-Nehru “Second Plan”) The Statesman Front Page Nov 22.
155. “Mob Violence and Psychology”, Dec 10, The Statesman, Editorial Page.
156. “What To Tell Musharraf: Peace Is Impossible Without Non-Aggressive Pakistani Intentions”, The Statesman Editorial Page Dec 15.
157. “Land, Liberty and Value: Government must act in good faith treating all citizens equally – not favouring organised business lobbies and organised labour over an unorganised peasantry”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Dec 31.
2007
158. “Hypocrisy of the CPI-M: Political Collapse In Bengal: A Mid-Term Election/Referendum Is Necessary”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 9.
159. “On Land-Grabbing: Dr Singh’s India, Buddhadeb’s Bengal, Modi’s Gujarat have notorious US, Soviet and Chinese examples to follow ~ distracting from the country’s real economic problems,” The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Jan 14.
160. “India’s Macroeconomics: Real growth has steadily occurred because India has shared the world’s technological progress. But bad fiscal, monetary policies over decades have led to monetary weakness and capital flight” The Statesman Editorial Page Jan 20.
161. “Fiscal Instability: Interest payments quickly suck dry every year’s Budget. And rolling over old public debt means that Government Borrowing in fact much exceeds the Fiscal Deficit”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 4.
162. “Our trade and payments Parts 1-2” (“India in World Trade and Payments”),The Sunday Statesman, Feb 11 2007, The Statesman, Feb 12 2007.
163. “Our Policy Process: Self-Styled “Planners” Have Controlled India’s Paper Money For Decades,” The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 20.
164. “Bengal’s Finances”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, Feb 25.
165. “Fallacious Finance: Congress, BJP, CPI-M may be leading India to Hyperinflation” The Statesman Editorial Page Mar 5.
166. “Uttar Pradesh Polity and Finance: A Responsible New Govt May Want To Declare A Financial Emergency” The Statesman Editorial Page, Mar 24
167. “A scam in the making” in The Sunday Statesman Front Page Apr 1 2007, published here in full as “Swindling India”.
168. “Maharashtra’s Money: Those Who Are Part Of The Problem Are Unlikely To Be A Part Of Its Solution”, The Statesman Editorial Page Apr 24.
147a. “Political Economy of Energy Policy” in India and Energy Security edited by Anant Sudarshan and Ligia Noronha, Konrad Adenauer Stiftung, New Delhi 2007.
169. “Presidential Qualities: Simplicity, Genuine Achievement Are Desirable; Political Ambition Is Not”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, May 8.
170. “We & Our Neighbours: Pakistanis And Bangladeshis Would Do Well To Learn From Sheikh Abdullah”, The Statesman, Editorial Page May 15.
171. “On Indian Nationhood: From Tamils To Kashmiris And Assamese And Mizos To Sikhs And Goans”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, May 25.
172. A Current Example of the Working of the Unconscious Mind, May 26.
173. Where I would have gone if I was Osama Bin Laden, May 31.
174. “US election ’08:America’s Presidential Campaign Seems Destined To Be Focussed On Iraq”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 1.
175. “Home Team Advantage: On US-Iran talks and Sunni-Shia subtleties: Tehran must transcend its revolution and endorse the principle that the House of Islam has many mansions”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, June 3
176. “Unhealthy Delhi: When will normal political philosophy replace personality cults?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 11.
177. “American Turmoil: A Vice-Presidential Coup – And Now a Grassroots Counterrevolution?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 18
178. “Political Paralysis: India has yet to develop normal conservative, liberal and socialist parties. The Nice-Housing-Effect and a little game-theory may explain the current stagnation”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, June 24.
179. “Has America Lost? War Doctrines Of Kutusov vs Clausewitz May Help Explain Iraq War”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 3.
180. “Lal Masjid ≠ Golden Temple: Wide differences are revealed between contemporary Pakistan and India by these two superficially similar military assaults on armed religious civilians”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page July 15
181. “Political Stonewalling: Only Transparency Can Improve Institutions”, The Statesman, Editorial Page July 20.
182. “Gold standard etc: Fixed versus flexible exchange rates”, July 21.
183. “US Pakistan-India Policy: Delhi & Islamabad Still Look West In Defining Their Relationship”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 27.
184. “Works of DH Lawrence” July 30
185. “An Open Letter to Professor Amartya Sen about Singur etc”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 31.
186. “Martin Buber on Palestine and Israel (with Postscript)”, Aug 4.
187. “Auguste Rodin on Nature, Art, Beauty, Women and Love”, Aug 7.
188. “Saving Pakistan: A Physicist/Political Philosopher May Represent Iqbal’s “Spirit of Modern Times”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 13.
189. Letter to Forbes.com 16 Aug.
190. “Need for Clarity: A poorly drafted treaty driven by business motives is a recipe for international misunderstanding”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 19.
191. “No Marxist MBAs? An amicus curiae brief for the Hon’ble High Court”, The Statesman, FrontPage, Aug 29.
192. On Lawrence, Sep 4.
193. Dalai Lama’s Return: In the tradition of Gandhi, King, Mandela, Sep 11.
194. Of JC Bose, Patrick Geddes & the Leaf-World, Sep 12.
195. “Against Quackery: Manmohan and Sonia have violated Rajiv Gandhi’s intended reforms; the Communists have been appeased or bought; the BJP is incompetent Parts 1-2”, in The Sunday Statesman and The Statesman, Editorial Pages of Sep 23-24.
196. Karl Georg Zinn’s 1994 Review of Philosophy of Economics, Sep 26.
197. DH Lawrence’s Phoenix, Oct 3.
93b. “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform”, Statesman Festival Volume.
198. “Iran, America, Iraq: Bush’s post-Saddam Saddamism — one flip-flop too many?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 16.
199. “Understanding China: The World Needs to Ask China to Find Her True Higher Self”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 22.
200. “India-USA interests: Elements of a serious Indian foreign policy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 30.
201. “China’s India Aggression : German Historians Discover Logic Behind Communist Military Strategy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, Nov 5.
202. Sonia’s Lying Courtier (with Postscript), Nov 25. See also 2014
203. “Surrender or Fight? War is not a cricket match or Bollywood movie. Can India fight China if it must?” The Statesman, Dec 4, Editorial Page.
204. Hutton and Desai: United in Error Dec 14
205. “China’s Commonwealth: Freedom is the Road to Resolving Taiwan, Tibet, Sinkiang”, The Statesman, Dec 17.
2008
206. “Nixon & Mao vs India: How American foreign policy did a U-turn about Communist China’s India aggression. The Government of India should publish its official history of the 1962 war.” The Sunday Statesman, Jan 6, The Statesman Jan 7 Editorial Page.
207. “Lessons from the 1962 War: Beginnings of a solution to the long-standing border problem: there are distinct Tibetan, Chinese and Indian points of view that need to be mutually comprehended”, The Sunday Statesman, January 13 2008.
208. “Our Dismal Politics: Will Independent India Survive Until 2047?”, The Statesman Editorial Page, Feb 1.
209. Median Voter Model of India’s Electorate Feb 7.
210. “Anarchy in Bengal: Intra-Left bandh marks the final unravelling of “Brand Buddha””, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 10.
211. Fifty years since my third birthday: on life and death.
212. “Pakistan’s Kashmir obsession: Sheikh Abdullah Relied In Politics On The French Constitution, Not Islam”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 16.
213. A Note on the Indian Policy Process Feb 21.
214. “Growth & Government Delusion: Progress Comes From Learning, Enterprise, Exchange, Not The Parasitic State”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 22.
215. “How to Budget: Thrift, Not Theft, Needs to Guide Our Public Finances”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 26.
216. “India’s Budget Process (in Theory)”, The Statesman, Front Page Feb 29.
217. “Irresponsible Governance: Congress, BJP, Communists, BSP, Sena Etc Reveal Equally Bad Traits”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 4.
218. “American Politics: Contest Between Obama And Clinton Affects The World”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 11.
219. “China’s India Example: Tibet, Xinjiang May Not Be Assimilated Like Inner Mongolia And Manchuria”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 25.
220. “Taxation of India’s Professional Cricket: A Proposal”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 1.
221. “Two cheers for Pakistan!”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 7.
222. “Indian Inflation: Upside Down Economics From The New Delhi Establishment Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 15-16.
223. “Assessing Manmohan: The Doctor of Deficit Finance should realise the currency is at stake”, The Statesman, Editorial Page Apr 25.
224. John Wisdom, Renford Bambrough: Main Philosophical Works, May 8.
225. “All India wept”: On the death of Rajiv Gandhi, May 21.
226. “China’s force and diplomacy: The need for realism in India” The Statesman, Editorial Page May 31.
227. Serendipity and the China-Tibet-India border problem June 6
228. “Leadership vacuum: Time & Tide Wait For No One In Politics: India Trails Pakistan & Nepal!”, The Statesman Editorial Page June 7.
229. My meeting Jawaharlal Nehru Oct13 1962
230. Manindranath Roy 1891-1958
231. Surendranath Roy 1860-1929
232. The Roys of Behala 1928.
233. Sarat Chandra visits Surendranath Roy 1927
234. Nuksaan-Faida Analysis = Cost-Benefit Analysis in Hindi/Urdu Jun 30
235. One of many reasons John R Hicks was a great economist July 3
236. My father, Indian diplomat, in the Shah’s Tehran 1954-57 July 8
237 Distribution of Govt of India Expenditure (Net of Operational Income) 1995 July 27
238. Growth of Real Income, Money & Prices in India 1869-2008, July 28.
239. Communism from Social Democracy? But not in India or China! July 29
240. Death of Solzhenitsyn, Aug. 3
240a. Tolstoy on Science and Art, Aug 4.
241. “Reddy’s reckoning: Where should India’s real interest rate be relative to the world?” Business Standard Aug 10
242. “Rangarajan Effect”, Business Standard Aug 24
243. My grandfather’s death in Ottawa 50 years ago today Sep 3
244. My books in the Library of Congress and British Library Sep 12
245. On Jimmy Carter & the “India-US Nuclear Deal”, Sep 12
246. My father after presenting his credentials to President Kekkonen of Finland Sep 14 1973.
247. “October 1929? Not!”, Business Standard, Sep 18.
248. “MK Gandhi, SN Roy, MA Jinnah in March 1919: Primary education legislation in a time of protest”
249. 122 sensible American economists Sept 26
250. Govt of India: Please call in the BBC and ask them a question Sep 27
251. “Monetary Integrity and the Rupee: Three British Raj relics have dominated our macroeconomic policy-making” Business Standard Sep 28.
252a. Rabindranath’s daughter writes to her friend my grandmother Oct 5
252b. A Literary Find: Modern Poetry in Bengal, Oct 6.
253. Sarat writes to Manindranath 1931, Oct 12
254. Origins of India’s Constitutional Politics 1913
255. Indira Gandhi in Paris, 1971
256. How the Liabilities/Assets Ratio of Indian Banks Changed from 84% in 1970 to 108% in 1998, October 20
257a. My Subjective Probabilities on India’s Moon Mission Oct 21
258. Complete History of Mankind’s Moon Missions: An Indian Citizen’s Letter to ISRO’s Chairman, Oct 22.
259. Would not a few million new immigrants solve America’s mortgage crisis? Oct 26
260. “America’s divided economists”, Business Standard Oct 26
261. One tiny prediction about the Obama Administration, Nov 5
262. Rai Bahadur Umbika Churn Rai, 1827-1902, Nov 7 2008
263. Jawaharlal Nehru invites my father to the Mountbatten Farewell Nov 7 2008
70a. “Become a US Supreme Court Justice! (Explorations in the Rule of Law in America) Preface” Nov 9
70b. “Become a US Supreme Court Justice! (Explorations in the Rule of Law in America)” Nov 9.
257b. Neglecting technological progress was the basis of my pessimism about Chandrayaan, Nov 9.
264. Of a new New Delhi myth and the success of the University of Hawaii 1986-1992 Pakistan project Nov 15
265. Pre-Partition Indian Secularism Case-Study: Fuzlul Huq and Manindranath Roy Nov 16
266. Do President-elect Obama’s Pakistan specialists suppose Maulana Azad, Dr Zakir Hussain, Sheikh Abdullah were Pakistanis (or that Sheikh Mujib wanted to remain one)? Nov 18
267. Jews have never been killed in India for being Jews until this sad day, Nov 28.
268. In international law, Pakistan has been the perpetrator, India the victim of aggression in Mumbai, Nov 30.
269. The Indian Revolution, Dec 1.
270. Habeas Corpus: a captured terrorist mass-murderer tells a magistrate he has not been mistreated by Mumbai’s police Dec 3
271. India’s Muslim Voices (Or, Let us be clear the Pakistan-India or Kashmir conflicts have not been Muslim-Hindu conflicts so much as intra-Muslim conflicts about Muslim identity and self-knowledge on the Indian subcontinent), Dec 4
272. “Anger Management” needed? An Oxford DPhil recommends Pakistan launch a nuclear first strike against India within minutes of war, Dec 5.
273. A Quick Comparison Between the September 11 2001 NYC-Washington attacks and the November 26-28 2008 Mumbai Massacres (An Application of the Case-by-Case Philosophical Technique of Wittgenstein, Wisdom and Bambrough), Dec 6
274. Dr Rice finally gets it right (and maybe Mrs Clinton will too) Dec 7
275. Will the Government of India’s new macroeconomic policy dampen or worsen the business-cycle (if such a cycle exists at all)? No one knows! “Where ignorance is bliss, ‘Tis folly to be wise.” Dec 7
276. Pump-priming for car-dealers: Keynes groans in his grave (If evidence was needed of the intellectual dishonesty of New Delhi’s new macroeconomic policy, here it is) Dec 9.
277. Congratulations to Mumbai’s Police: capturing a terrorist, affording him his Habeas Corpus rights, getting him to confess within the Rule of Law, sets a new world standard Dec 10
278. Two cheers — wait, let’s make that one cheer — for America’s Justice Department, Dec 10
279. Will Pakistan accept the bodies of nine dead terrorists who came from Pakistan to Mumbai? If so, let there be a hand-over at the Wagah border, Dec 11.
280. Kasab was a stupid, ignorant, misguided youth, manufactured by Pakistan’s terrorist masterminds into becoming a mass-murdering robot: Mahatma Gandhi’s India should punish him, get him to repent if he wishes, then perhaps rehabilitate him as a potent weapon against Pakistani terrorism Dec 12.
281. Pakistan’s New Delhi Embassy should ask for “Consular Access” to nine dead terrorists in a Mumbai morgue before asking to meet Kasab, Dec 13
282. An Indian Reply to President Zardari: Rewarding Pakistan for bad behaviour leads to schizophrenic relationships Dec 19
283. Is my prediction about Caroline Kennedy becoming US Ambassador to Britain going to be correct? Dec 27
284. Chandrayaan adds a little good cheer! Well done, ISRO!, Dec 28
285. How sad that “Slumdog millionaire” is SO disappointing! Dec 31
289. (with Claude Arpi) “Transparency & history: India’s archives must be opened to world standards” Business Standard New Delhi Dec 31, 2008, published here Jan 1 .
2009
290. A basis of India-Pakistan cooperation on the Mumbai massacres: the ten Pakistani terrorists started off as pirates and the Al-Huseini is a pirate ship Jan 1.
291. India’s “pork-barrel politics” needs a nice (vegetarian) Hindi name! “Teli/oily politics” perhaps? (And are we next going to see a Bill of Rights for Lobbyists?) Jan 3
292. My (armchair) experience of the 1999 Kargil war (Or, “Actionable Intelligence” in the Internet age: How the Kargil effort got a little help from a desktop) Jan 5
293. How Jammu & Kashmir’s Chief Minister Omar Abdullah can become a worthy winner of the Nobel Peace Prize: An Open Letter, Jan 7
294. Could the Satyam/PwC fraud be the visible part of an iceberg? Where are India’s “Generally Accepted Accounting Principles”? Isn’t governance rather poor all over corporate India? Bad public finance may be a root cause Jan 8
295. Satyam does not exist: it is bankrupt, broke, kaput. Which part of this does the new “management team” not get? The assets belong to Satyam’s creditors. Jan 8
296. Jews are massacred in Mumbai and now Jews commit a massacre in Gaza! Jan 9
297. And now for the Great Satyam Whitewash/Cover-Up/Public Subsidy! The wrong Minister appoints the wrong new Board who, probably, will choose the wrong policy Jan 12
298. Letter to Wei Jingsheng Jan 14
299. Memo to the Hon’ble Attorneys General of Pakistan & India: How to jointly prosecute the Mumbai massacre perpetrators most expeditiously Jan 16
300. Satyam and IT-firms in general may be good candidates to become “Labour-Managed” firms Jan 18
301. “Yes we might be able to do that. Perhaps we ought to. But again, perhaps we ought not to, let me think about it…. Most important is Cromwell’s advice: Think it possible we may be mistaken!” Jan 20.
302. RAND’s study of the Mumbai attacks Jan 25
303. Didn’t Dr Obama (the new American President’s late father) once publish an article in Harvard’s Quarterly Journal of Economics? (Or did he?) Jan 25.
304. “A Dialogue in Macroeconomics” 1989 etc: sundry thoughts on US economic policy discourse Jan 30
305. American Voices: A Brief Popular History of the United States in 20 You-Tube Music Videos Feb 5
306. Jaladhar Sen writes to Manindranath at Surendranath’s death, Feb 23
307. Pakistani expansionism: India and the world need to beware of “Non-Resident Pakistanis” ruled by Rahmat Ali’s ghost, Feb 9
308. My American years Part One 1980-90: battles for academic integrity & freedom Feb 11.
309. Thanks and well done Minister Rehman Malik and the Govt of Pakistan Feb 12
310. Can President Obama resist the financial zombies (let alone slay them)? His economists need to consult Dr Anna J Schwartz Feb 14
311. A Brief History of Gilgit, Feb 18
312. Memo to UCLA Geographers: Commonsense suggests Mr Bin Laden is far away from the subcontinent Feb 20
313. The BBC gets its history and geography deliberately wrong again Feb 21
314. Bengal Legislative Council 1921, Feb 28
315. Carmichael visits Surendranath, 1916, Mar 1
316. Memo to GoI CLB: India discovered the Zero, and 51% of Zero is still Zero Mar 10
317. An Academic Database of Doctoral & Other Postgraduate Research Done at UK Universities on India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Other Asian Countries Over 100 Years, Mar 13
318. Pakistan’s progress, Mar 18
319. Risk-aversion explains resistance to free trade, Mar 19
320. India’s incredibly volatile inflation rate! Mar 20
321. Is “Vicky, Cristina, Barcelona” referring to an emasculation of (elite) American society?, Mar 21
322. Just how much intellectual fraud can Delhi produce? Mar 26
323. India is not a monarchy! We urgently need to universalize the French concept of “citoyen”! Mar 28
324. Could this be the real state of some of our higher education institutions? Mar 29
325. Progress! The BBC retracts its prevarication! Mar 30
326. Aldous Huxley’s Essay “DH Lawrence” Mar 31
327. Waffle not institutional reform is what (I predict) the “G-20 summit” will produce, April 1
328. Did a full cricket team of Indian bureaucrats follow our PM into 10 Downing Street? Count for yourself! April 3
329. Will someone please teach the BJP’s gerontocracy some Economics 101 on an emergency basis? April 5
330. The BBC needs to determine exactly where it thinks Pakistan is!, April 5
331. Alfred Lyall on Christians, Muslims, India, China, Etc, 1908, April 6
332. An eminent economist of India passes away April 9
333. Democracy Database for the Largest Electorate Ever Seen in World History, April 12
334. Memo to the Election Commission of India April 14 2009, 9 AM, April 14
335. Caveat emptor! Satyam is taken over, April 14
336. India’s 2009 General Elections: Candidates, Parties, Symbols for Polls on 16-30 April Phases 1,2,3, April 15
337. On the general theory of expertise in democracy: reflections on what emerges from the American “torture memos” today, April 18
338. India’s 2009 General Elections: 467 constituencies (out of 543) for which candidates have been announced as of 1700hrs April 21, April 21
339. Apropos Philosophy of Economics, Comments of Sidney Hook, KJ Arrow, Milton Friedman, TW Schultz, SS Alexander, Max Black, Renford Bambrough, John Gray et al., April 22.
340. India’s 2009 General Elections: Names of all 543 Constituencies of the 15th Lok Sabha, April 22.
341. India’s 2009 General Elections: How 4125 State Assembly Constituencies comprise the 543 new Lok Sabha Constituencies, April 23.
342. Why has America’s “torture debate” yet to mention the obvious? Viz., sadism and racism, April 24
343. India’s 2009 General Elections: the advice of the late “George Eliot” (Mary Ann Evans, 1819-1880) to India’s voting public, April 24.
344. India’s 2009 General Elections: Delimitation and the Different Lists of 543 Lok Sabha Constituencies in 2009 and 2004, April 25
345. Is “Slumdog Millionaire” the single worst Best Picture ever?
346. India’s 2009 General Elections: Result of Delimitation — Old (2004) and New (2009) Lok Sabha and Assembly Constituencies, April 26
347. India’s 2009 General Elections: 7019 Candidates in 485 (out of 543) Constituencies announced as of April 26 noon April 26
348. What is Christine Fair referring to? Would the MEA kindly seek to address what she has claimed asap? April 27
349. Politics can be so entertaining 🙂 Manmohan versus Sonia on the poor old CPI(M)!, April 28
350. A Dozen Grown-Up Questions for Sonia Gandhi, Manmohan Singh, LK Advani, Sharad Pawar, Km Mayawati and Anyone Else Dreaming of Becoming/Deciding India’s PM After the 2009 General Elections, April 28
351. India’s 2009 General Elections: How drastically will the vote-share of political parties change from 2004? May 2
352. India’s 2009 General Elections: And now finally, all 8,070 Candidates across all 543 Lok Sabha Constituencies, May 5
353. India’s 2009 General Elections: The Mapping of Votes into Assembly Segments Won into Parliamentary Seats Won in the 2004 Election, May 7
354. Will Messrs Advani, Rajnath Singh & Modi ride into the sunset if the BJP comes to be trounced? (Corrected), May 10
355. India’s 2009 General Elections: 543 Matrices to Help Ordinary Citizens Audit the Election Commission’s Vote-Tallies May 12
356. Well done Sonia-Rahul! Two hours before polls close today, I am willing to predict a big victory for you (but, please, try to get your economics right, and also, you must get Dr Singh a Lok Sabha seat if he is to be PM) May 13
357. Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee must dissolve the West Bengal Assembly if he is an honest democrat: Please try to follow Gerard Schröder’s example even slightly! May 16
358. India’s 2009 General Elections: Provisional Results from the EC as of 1400 hours Indian Standard Time May 16
359. Memo to the Hon’ble President of India: It is Sonia Gandhi, not Manmohan Singh, who should be invited to our equivalent of the “Kissing Hands” Ceremony May 16
360. Time for heads to roll in the BJP/RSS and CPI(M)!, May 17.
361. Inviting a new Prime Minister of India to form a Government: Procedure Right and Wrong May 18
362. Starting with Procedural Error: Why has the “Cabinet” of the 14th Lok Sabha been meeting today AFTER the results of the Elections to the 15th Lok Sabha have been declared?! May 18
363. Why has the Sonia Congress done something that the Congress under Nehru-Indira-Rajiv would not have done, namely, exaggerate the power of the Rajya Sabha and diminish the power of the Lok Sabha? May 21
364. Shouldn’t Dr Singh’s Cabinet begin with a small apology to the President of India for discourtesy? May we have reviews and reforms of protocols and practices to be followed at Rashtrapati Bhavan and elsewhere? May 23
365. Parliament’s sovereignty has been diminished by the Executive: A record for future generations to know May 25
366. How tightly will organised Big Business be able to control economic policies this time? May 26
367. Why does India not have a Parliament ten days after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected? Nehru and Rajiv would both have been appalled May 27
368. Eleven days and counting after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected and still no Parliament of India! (But we do have 79 Ministers — might that be a world record?) May 28
369. Note to Posterity: 79 Ministers in office but no 15th Lok Sabha until June 1 2009! May 29
370. Silver Jubilee of Pricing, Planning & Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India May 29
371. How to Design a Better Cabinet for the Government of India May 29
372. Parliament is supposed to control the Government, not be bullied or intimidated by it: Will Rahul Gandhi be able to lead the Backbenches in the 15th Lok Sabha? June 1
373. Mistaken Macroeconomics: An Open Letter to Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh, June 12
374. Why did Manmohan Singh and LK Advani apologise to one another? Is Indian politics essentially collusive, not competitive, aiming only to preserve and promote the post-1947 Dilli Raj at the expense of the whole of India? We seem to have no Churchillian repartee (except perhaps from Bihar occasionally) June 18
375. Are Iran’s Revolutionaries now Reactionaries? George Orwell would have understood. A fresh poll may be the only answer Are Iran’s Revolutionaries now Reactionaries? George Orwell would have understood. A fresh poll may be the only answer June 22
376. My March 25 1991 memo to Rajiv (which never reached him) is something the present Government seems to have followed: all for the best of course! July 12
377. Disquietude about France’s behaviour towards India on July 14 2009 July 14
378. Does the Govt. of India assume “foreign investors and analysts” are a key constituency for Indian economic policy-making? If so, why so? Have Govt. economists “learnt nothing, forgotten everything”? Some Bastille Day thoughts July 14
379. Letter to the GoI’s seniormost technical economist, May 21.July 19
380. Excuse me but young Kasab in fact confessed many months ago, immediately after he was captured – he deserves 20 or 30 years in an Indian prison, and a chance to become a model prisoner who will stand against the very terrorists who sent him on his vile mission July 20
381. Finally, three months late, the GoI responds to American and Pakistani allegations about Balochistan July 24
382. Thoughts, words, deeds: My work 1973-2010
2012
383. Life of my father 1915-2012
384. India’s Money” in the Cayman Financial Review, July 2012
385. Towards Making the Indian Rupee a Hard Currency of the World Economy: An analysis from British times until the present day, lecture at India International Centre, Delhi, 3 Dec 2012
386. 5 December 2012 interview by Mr Paranjoy Guha Thakurta, on Lok Sabha TV, the channel of India’s Lower House of Parliament, broadcast for the first time on 9 December 2012 on Lok Sabha TV, is here and here in two parts.
387. Interview by GDI Impuls banking quarterly of Zürich published on 6 Dec 2012 is here.
388. My interview by Ragini Bhuyan of Delhi’s Sunday Guardian published on 16 Dec 2012 is here.
2013
389. “I have a student called Suby Roy…”: Reflections on Frank Hahn (1925-2013), my master in economic theory
390. Cambridge Economics & the Disputation in India’s Economic Policy, Revised 15 July 2013
391. Critical assessment dated 19 August 2013 of Raghuram Rajan is here (Live Mint 19 Aug) and here
392. 23 August 2013 of Professors Jagdish Bhagwati & Amartya Sen and Dr Manmohan Singh is here…
2014
393. “Mrs Irani’s New Job”/”Task Cut Out For Smriti Irani” June 16, 2014http://www.newindianexpress.com/opinion/Task-Cut-Out-for-Smriti-Irani/2014/06/16/article2282316.ece
394. Much as I might love Russia, England, France, America, I despise their spies & local agents affecting poor India’s policies: Memo to PM Modi, Mr Jaitley, Mr Doval & the new Govt. of India: Beware of Delhi’s sleeper agents, lobbyists & other dalals
395. “Haksar, Manmohan and Sonia” August 7, 2014 New Indian Express http://t.co/bRnQI1hrwy
396. Free India’s Foreign Policy & Economy in One Chart: Weapons Imports 1950-2013 by Country of Origin
See also:
My Recent Works, Interviews etc on India’s Money, Public Finance, Banking, Trade, BoP, etc (an incomplete list)
My Seventy-One Articles, Notes Etc on Kashmir, Pakistan, & of course, India (plus my undelivered Lahore lectures)
My Ten Articles on China, Tibet, Xinjiang, Taiwan in relation to India
M1. Map of Asia c. 1900
M2. Map of Chinese Empire c. 1900
M3. Map of Sinkiang, Tibet and Neighbours 1944
M4. China’s Secretly Built 1957 Road Through India’s Aksai Chin
M5. Map of Kashmir to Sinkiang 1944
M6. Map of India-Tibet-China-Mongolia 1959
M7. Map of India, Afghanistan, Russia, China, 1897
M8. Map of Xinjiang/Sinkiang/E Turkestan
M9. Map of Bombay/Mumbai 1909
M10-M13. Himalayan Expedition, West Sikkim 1970 – 1,2,3,4
2010 version:
This an incomplete bibliography of my writings, public lectures etc 1973-2010 including citations, reviews, comments. I have been mostly an academic economist who by choice or circumstance over 36 years has had to venture also into science, philosophy, public policy, law, jurisprudence, practical politics, history, international relations, military strategy, financial theory, accounting, management, journalism, literary criticism, psychology, psychoanalysis, theology, aesthetics, biography, children’s fables, etc. If anything unites the seemingly diverse work recorded below it is that I have tried to acquire a grasp of the nature of human reason and then apply this comprehension in practical contexts as simply and clearly as possible. Hence I have ended up following the path of Aristotle, as described in modern times (via Wittgenstein and John Wisdom) by Renford Bambrough. The 2004 public lecture in England, “Science, Religion, Art & the Necessity of Freedom”, may explain and illustrate all this best. A friend has been kind enough to call me an Academician, which I probably am, though one who really needs his own Academy because the incompetence, greed and mendacity encountered too often in the modern professoriat is dispiriting.
1-289 refer mostly to writings and publications printed on paper; 290-382 refer to writings or items not printed on paper — as new media break space, cost and other constraints of traditional publishing, a little repetition and overlap has occurred too. Also in a few cases, e.g., Aldous Huxley’s essay on DH Lawrence, nothing has been done except discover and republish. Several databases have been created and released in the public interest, as have been some rare maps. There is also some biographical and autobiographical material. Several inconsequential errors remain in the text, which shall take time to be rectified as documents come to be rediscovered and collated.
1973
1. “Behavioural study of mus musculus”, Haileybury College, Supervised by J de C Ford-Robertson MA (Oxon). (Due to be published here 2010).
2. “Chemistry at Advanced & Special Level: Student Notes 1972-73” (Due to be published here 2010).
3. “Biology at Advanced & Special Level: Student Notes 1972-73”, (Due to be published here 2010).
4. “Physics at Advanced Level: Student Notes 1972-73”, (Due to be published here 2010).
5. “Revolution: theoria and praxis”, London, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
6. “Gandhi vs Marx”, London, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
1974
7. “Relevance of downward money-wage rigidity to the problem of maintaining full-employment in the classical and Keynesian models of income determination”, London School of Economics, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
8. “Testing aircraft fuels at Shell Finland”.
1975
9. “Oxford Street experiences: down and out in London town”.
10. “SE Region Bulk Distribution Survey”, Unilever, Basingstoke.
11. “Four London poems”, in JCM Paton (ed) New Writing (London, Great Portland Street: International Students House). (Due to be republished here 2010)
12. “On economic growth models and modellers”, London School of Economics, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
1976
13. “World money: system or anarchy?”, lecture to Professor ACL Day’s seminar, London School of Economics, Economics Department, April. (Due to be published here 2010).
14. “A beginner’s guide to some recent developments in monetary theory”, lecture to Professor FH Hahn’s seminar, Cambridge University Economics Department, November 17 (Due to be published here 2010). See also “Announcement of My “Hahn Seminar”, published here June 14 2008.
1977
15. “Inflation and unemployment: a survey”, mimeo, Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge. (Due to be published here 2010).
16. “On short run theories of dual economies”, Cambridge University Economics Department “substantial piece of work” required of first year Research Students. Examiner: DMG Newbery, FBA. (Due to be published here 2010).
1978
17. “Pure theory of developing economies 1 and 2”, Delhi School of Economics mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
18. “Introduction to some market outcomes under uncertainty”, Delhi School of Economics mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
19. “On money and development”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo, September. (Due to be published here 2010)
20. “Notes on the Newbery-Stiglitz model of sharecropping”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo November. (Due to be published here 2010).
1979
21. “A theory of rights and economic justice”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
22. “Monetary theory and economic development”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
23. “Foundations of the case against ‘development planning’”, Corpus Christi College Cambridge, mimeo, November. (Due to be published here 2010).
1979-1989
24. Correspondence with Renford Bambrough (1926-1999), philosopher of St John’s College, Cambridge (Due to be published here 2010).
1980
25. “Models before the monetarist storm”, New Statesman letters
26. “Disciplining rulers and experts”, Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
1981
27. “On liberty & economic growth: preface to a philosophy for India”, Cambridge University doctoral thesis, supervisor FH Hahn, FBA; examiners CJ Bliss, FBA; TW Hutchison, FBA (Due to be published here 2010). 27a Response of FA Hayek on a partial draft February 18 1981. 27b Response of Peter Bauer, 1982. 27c Response of Theodore W Schultz, 1983. 27d. Response of Frank Hahn 1985.
1982
28. “Knowledge and freedom in economic theory Parts 1 and 2”, Centre for Study of Public Choice, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University, Working Papers.
29. “Economic Theory and Development Economics”. Lecture to American Economic Association, New York, Dec 1982. Panel: RM Solow, HB Chenery, T Weisskopf, P Streeten, G Rosen, S Roy. Published in 29a.
1983
29a “Economic Theory and Development Economics: A Comment”. World Development, 1983. [Citation: Stavros Thefanides “Metamorphosis of Development Economics”, World Development 1988.]
30. “The Political Economy of Trade Policy (Comment on J. Michael Finger)”, Washington DC: Cato Journal, Winter 1983/84. See also 000 “Risk-aversion explains resistance to freer trade”, 2008.
1984
31. “Considerations on Utility, Benevolence and Taxation”, History of Political Economy, 1984. 31a Response of Professor Sir John Hicks May 1 1984.
[Citations: P. Hennipman, “A Tale of Two Schools”, De Economist 1987, “A New Look at the Ordinalist Revolution”, J. Econ. Lit. Mar 1988; P. Rappoport, “Reply to Professor Hennipman”, J. Econ. Lit. Mar 1988; Eugene Smolensky et al “An Application of A Dynamic Cost-of-Living Index to the Evaluation of Changes in Social Welfare”, J. Post-Keynesian Econ.IX.3. 1987.]
32. Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India, London: Institute of Economic Affairs, London 1984.
[Citations: Lead editorial of The Times of London May 29 1984, “India’s economy”, Times letters June 16 1984. John Toye “Political Economy & Analysis of Indian Development”, Modern Asian Studies, 22, 1, 1988; John Toye, Dilemmas of Development; D. Wilson, “Privatization of Asia”, The Banker Sep. 1984 etc]. See also 370 “Silver Jubilee of ‘Pricing, Planning and Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India’” 2009.
33. Review of Utilitarianism and Beyond, Amartya Sen & Bernard Williams (eds) Public Choice.
34. Review of Limits of Utilitarianism, HB Miller & WH Williams (eds.), Public Choice.
35. Deendayal lecture (one of four invited lecturers), Washington DC, May.
1987
36. (with one other) “Does the Theory of Logical Types Inform the Theory of Communication?”, Journal of Genetic Psychology., 148 (4), Dec. 1987 [Citation:
37. “Irrelevance of Foreign Aid”, India International Centre Quarterly, Winter 1987.
38. Review of Development Planning by Sukhamoy Chakravarty for Economic Affairs, London 1987.
1988
39. (with two others) “Introduction” to Lessons in Development: A Comparative Study of Asia and Latin America. San Francisco: Inst. of Economic Growth.
40. “A note on the welfare economics of regional cooperation”, lecture to Asia-Latin America conference, East West Center Honolulu, published 2009.
1989
41. Philosophy of Economics: On the Scope of Reason in Economic Inquiry, London & New York: Routledge (International Library of Philosophy) 1989, paperback 1991. Internet edition 2007. [Reviews & Citations: Research in Economics, 1992; De Economist 1991 & 1992; Manch.Sch. Econ.Studs. 59, 1991; Ethics 101.88 Jul. 1991; Kyklos 43.4 1990; Soc. Science Q. 71.880. Dec.1990; Can. Phil. Rev. 1990; J. Econ. Hist. Sep. 1990; Econ. & Phil. Fall 1990; Econ. Affairs June-July 1990; TLS May 1990; Choice March 1990; J. App.Phil. 1994, M. Blaug: Methodology of Economics, 2nd ed., Cambridge, 1992; Hist. Methods. 27.3, 1994; J. of Inst. & Theoretical Econ.,1994; Jahrbucker fur Nationaleconomie 1994, 573:574. Mark A Lutz in Economics for the Common Good, London: Routledge, 1999, et al]. See also 339 “Apropos Philosophy of Economics”, Comments of Sidney Hook, KJ Arrow, Milton Friedman, TW Schultz, SS Alexander, Max Black, Renford Bambrough, John Gray et al.
42. Foreword to Essays on the Political Economy by James M. Buchanan, Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press 1989.
43. “Modern Political Economy of India”, edited by Subroto Roy & William E James, Hawaii mimeo May 21 1989. This published for the first time a November 1955 memorandum to the Government of India by Milton Friedman. See also 43a, 53.
43a. Preface to “Milton Friedman’s extempore comments at the 1989 Hawaii conference: on India, Israel, Palestine, the USA, Debt and its uses, Erhardt abolishing exchange controls, Etc”, May 22 1989, published here for the first time October 31 2008.
44. Milton Friedman’s defence of my work in 1989.
45. Theodore W. Schultz’s defence of Philosophy of Economics
1990
46. “Letter to Judge Evelyn Lance: On A Case Study in Private International Law” (Due to be published here in 2010).
47-49. Selections from advisory work on economic policy etc for Rajiv Gandhi, Leader of the Opposition in the Parliament of India, published in 47a-49a.
1991
41b Philosophy of Economics: On the Scope of Reason in Economic Inquiry, Paperback edition.
50. “Conversations and correspondence with Rajiv Gandhi during the Gulf war, January 1991” (Due to be published here 2010).
47a. A Memo to Rajiv I: Stronger Secular Middle”, The Statesman, Jul 31 1991.
48a “A Memo to Rajiv II: Saving India’s Prestige”, The Statesman, Aug 1 1991.
49a “A Memo to Rajiv III: Salvation in Penny Capitalism”, The Statesman, Aug 2 1991 47b-49b “Three Memoranda to Rajiv Gandhi 1990-91”, 2007 republication here.
51. “Constitution for a Second Indian Republic”, The Saturday Statesman, April 20 1991. Republished here 2009.
52. “On the Art of Government: Experts, Party, Cabinet and Bureaucracy”, New Delhi mimeo March 25 1991, published here July 00 2009.
1992
53. Foundations of India’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s Edited and with an Introduction by Subroto Roy & William E. James New Delhi, London, Newbury Park: Sage: 1992. Citation: Milton and Rose Friedman Two Lucky People (Chicago 1998), pp. 268-269.
54. Foundations of Pakistan’s Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s Edited and with an Introduction by William E. James & Subroto Roy, Hawaii MS 1989, Sage: 1992, Karachi: Oxford 1993.
Reviews of 53 & 54 include: Bus. Today, Mar-Apr 1992; Political Studies March 1995; Econ Times 21 March 1993; Pakistan Development Review 1992. Hindustan Times 11 July 1992. Pacific Affairs 1993; Hindu 21 March 1993, 15 June 1993; Pakistan News International 12 June 1993. Book Reviews March 1993; Deccan Herald 2 May 1993; Pol.Econ.J. Ind. 1992. Fin Express 13 September 1992; Statesman 16 Jan. 1993. J. Royal Soc Asian Aff. 1994, J. Contemporary Asia, 1994 etc.
55. “Fundamental Problems of the Economies of India and Pakistan”, World Bank, Washington, mimeo (Due to be published here 2010).
56.“The Road to Stagflation: The Coming Dirigisme in America, or, America, beware thy economists!, or Zen and Clintonomics,” Washington DC, Broad Branch Terrace, mimeo, November 17.
1993
57. “Exchange-rates and manufactured exports of South Asia”, IMF Washington DC mimeo. Published in part in 2007-2008 as 58-62:
58. “Path of the Indian Rupee 1947-1993”, 2008.
59. “Path of the Pakistan Rupee 1947-1993”, 2008.
60. “Path of the Sri Lankan Rupee 1948-1993”, 2008.
61. “Path of the Bangladesh Taka 1972-1993”, 2008.
62. “India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh Manufactured Exports, IMF Washington DC mimeo”, published 2007.
63. “Economic Assessment of US-India Merchandise Trade”, Arlington, Virginia, mimeo, published in slight part in Indo-US Trade & Economic Cooperation, ICRIER New Delhi, 1995, and in whole 2007.
64. “Towards an Economic Solution for Kashmir”, mimeo, Arlington, Virginia, circulated in Washington DC 1993-1995, cf 82, 111 infra. Comment of Selig Harrison.
1994
65. “Comment on Indonesia”, in The Political Economy of Policy Reform edited by John Williamson, Washington, DC: Institute for International Economics.
66a “Gold reserves & the gold price in anticipation of Central Bank behaviour”, Greenwich, Connecticut, mimeo. 67b. “Portfolio optimization and foreign currency exposure hedging” Greenwich, Connecticut mimeo.
1995
68. “On the logic and commonsense of debt and payments crises: How to avoid another Mexico in India and Pakistan”, Scarsdale, NY, mimeo, May 1.
69. “Policies for Young India”, Scarsdale, NY, pp. 350, manuscript.
1996
70. US Supreme Court documents, published in part in 2008 as “Become a US Supreme Court Justice!” 70a, 70b (Due to be published in full here in 2010 as Roy vs University of Hawaii, 1989- including the expert testimonies of Milton Friedman and Theodore W Schultz.).
71. “Key problems of macroeconomic management facing the new Indian Government”, May 17. Scarsdale, New York, mimeo. (Due to be published here 2010).
72. “Preventing a collapse of the rupee”, IIT Kharagpur lecture July 16 1996.
73. “The Economist’s Representation of Technological Knowledge”, Vishleshlaya lecture to the Institution of Engineers, September 15 1996, IIT Kharagpur.
1997
74. “Union and State Budgets in India”, lecture at the World Bank, Washington DC, May 00.
75. “State Budgets in India”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo, June 6.
1998
76. “Transparency and Economic Policy-Making: An address to the Asia-Pacific Public Relations Conference” (panel on Transparency chaired by CR Irani) Jan 30 1998, published here 2008.
77. Theodore W. Schultz 1902-1998, Feb 25.
78. “The Economic View of Human Resources”, address to a regional conference on human resources, IIT Kharagpur.
79. “Management accounting”, lecture at Lal Bahadur Shastri Academy, Mussourie,
80a “The Original Reformer”, Outlook letters, Jan 23 1998
81. “Recent Developments in Modern Finance”, IIM Bangalore Review, 10, 1 & 2, Jan.-Jun 1998. Reprinted as “From the Management Guru’s Classroom”: 81a “An introduction to derivatives”, Business Standard/Financial Times, Bombay 18 Apr 1999; 81b “Options in the future, Apr 25 1999; 81c “What is hedging?”, May 2 1999; 81d “Teaching computers to think”, May 9 1999.
82. “Towards an Economic Solution for Kashmir”, Jun 22 1998, lecture at Heritage Foundation, Washington DC. Cf 111 Dec 2005.
83. “Sixteen Currencies for India: A Reverse Euro Model for Monetary & Fiscal Efficacy”, Lecture at the Institute of Economic Affairs, London, June 29 1998. Due to be published here 2010.
84. “Fable of the Fox, the Farmer, and the Would-Be Tailors”, October (Published here July 27 2009).
85. “A Common Man’s Guide to Pricing Financial Derivatives”, Lecture to “National Seminar on Derivatives”, Xavier Labour Research Institute, Jamshedpur, Dec. 16 1998. See 98.
1999
86. “An Analysis of Pakistan’s War-Winning Strategy: Are We Ready for This?”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo, published in part as 86a.“Was a Pakistani Grand Strategy Discerned in Time by India?” New Delhi: Security & Political Risk Analysis Bulletin, July 1999, Kargil issue. See also 000
80b. “The Original Reformer”, Outlook letters, Sep 13 1999.
2000
87. “On Freedom & the Scientific Point of View”, SN Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Feb 17 2000. Cf 100 below.
88. “Liberalism and Indian economic policy”, lecture at IIM Calcutta, Indian Liberal Group Meetings Devlali, Hyderabad; also Keynote address to UGC Seminar Guntur, March 30 2002. (Due to be published here 2010).
89. “Towards a Highly Transparent Fiscal & Monetary Framework for India’s Union & State Governments”, Invited address to Conference of State Finance Secretaries, Reserve Bank of India, Bombay, April 29, 2000. Published 2008.
90. “On the Economics of Information Technology”, two lectures at the Indian Institute of Information Technology, Bangalore, Nov 10-11, 2000.
91. Review of A New World by Amit Chaudhuri in Literary Criterion, Mysore.
2001
92. Review of AD Shroff: Titan of Finance and Free Enterprise by Sucheta Dalal, Freedom First., January.
93. “Encounter with Rajiv Gandhi: On the Origins of the 1991 Economic Reform”, Freedom First, October. See also 93a in 2005 and 93b in 2007.
94. “A General Theory of Globalization & Modern Terrorism with Special Reference to September 11”, a keynote address to the Council for Asian Liberals & Democrats, Manila, Philippines, 16 Nov. 2001. Published as 91a.
95. “The Case for and against The Satanic Verses: Diatribe and Dialectic as Art”, Dec 22 republished in print 95a The Statesman Festival Volume, 2006.
2002
94a “A General Theory of Globalization & Modern Terrorism with Special Reference to September 11”, in September 11 & Political Freedom in Asia, eds. Johannen, Smith & Gomez, Singapore 2002.
2002-2010
96. “Recording vivid dreams: Freud’s advice in exploring the Unconscious Mind” (Due to be published here in 2010).
2003
97. “Key principles of government accounting and audit”, IIT Kharagpur mimeo.
98. “Derivative pricing & other topics in financial theory: a student’s complete lecture notes” (Due to be published here in 2010).
2004
99. “Collapse of the Global Conversation”, International Institute for Asian Studies, Leiden, Netherlands, Jul 2004.
100. “Science, Religion, Art & the Necessity of Freedom”, a public lecture, University of Buckingham, UK, August 24 2004. Published here 2007.
2005
93a Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform (this was the full story; it appeared in print for the first time in The Statesman Festival Volume 2007).
101. “Can India become an economic superpower (or will there be a monetary meltdown)?” Cardiff University Institute of Applied Macroeconomics Monetary Economics Seminar, April 13, Institute of Economic Affairs, London, April 27, Reserve Bank of India, Bombay, Chief Economist’s Seminar on Monetary Economics, May 5.
102. Margaret Thatcher’s Revolution: How it Happened and What it Meant, Edited and with an Introduction by Subroto Roy & John Clarke, London & New York: Continuum, 2005; paperback 2006; French translation by Florian Bay, 2007.
103. “Iqbal & Jinnah vs Rahmat Ali in Pakistan’s Creation”, Dawn, Karachi, Sep 3.
104. “The Mitrokhin Archives II from an Indian Perspective: A Review Article”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 11 .
105. “After the Verdict”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 20.
106. “US Espionage Failures”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 26
107. “Waffle But No Models of Monetary Policy”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Oct 30.
108. “On Hindus and Muslims”, The Statesman, Perspective Page, Nov 6.
109. “Assessing Vajpayee: Hindutva True and False”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Nov 13-14″.
110. “Fiction from the India Economic Summit”, The Statesman, Front Page, Nov 29.
111. “Solving Kashmir: On an Application of Reason”, The Statesman Editorial Page
I. “Give the Hurriyat et al Indian Green Cards”, Dec 1
II. “Choice of Nationality under Full Information”, Dec 2
III. “Of Flags and Consulates in Gilgit etc”, Dec 3.
2006
112. “The Dream Team: A Critique”, The Statesman Editorial Page
I : New Delhi’s Consensus (Manmohantekidambaromics), Jan 6
II: Money, Convertibility, Inflationary Deficit Financing, Jan 7
III: Rule of Law, Transparency, Government Accounting, Jan 8.
113. “Unaccountable Delhi: India’s Separation of Powers’ Doctrine”, The Statesman, Jan 13.
114. “Communists and Constitutions”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 22.
115. “Diplomatic Wisdom”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 31.
116. “Mendacity & the Government Budget Constraint”, The Statesman, Front Page Feb 3.
117. “Of Graven Images”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb5.
118. “Separation of Powers, Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Pages Feb 12-13.
119. “Public Debt, Government Fantasy”, The Statesman, Front Page Editorial Comment, Feb 22.
120. “War or Peace Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 23-24.
121. “Can You Handle This Brief, Mr Chidambaram?” The Statesman, Front Page Feb 26.
122. “A Downpayment On the Taj Mahal Anyone?”, The Statesman, Front Page Comment on the Budget 2006-2007, Mar 1.
123. “Atoms for Peace (or War)”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Mar 5.
124. “Imperialism Redux: Business, Energy, Weapons & Foreign Policy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Mar 14.
125. “Logic of Democracy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Mar 30.
126. “Towards an Energy Policy”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 2.
127. “Iran’s Nationalism”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 6.
128. “A Modern Military”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 16.
129. “On Money & Banking”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Apr 23.
130. “Lessons for India from Nepal’s Revolution”, The Statesman, Front Page Apr 26.
131. “Revisionist Flattery (Inder Malhotra’s Indira Gandhi: A Review Article)”, The Sunday Statesman, May 7.
132. “Modern World History”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, May 7.
133. “Argumentative Indians: A Conversation with Professor Amartya Sen on Philosophy, Identity and Islam,” The Sunday Statesman, May 14 2006. “A Philosophical Conversation between Professor Sen and Dr Roy”, 2008. Translated into Bengali by AA and published in 00.
134. “The Politics of Dr Singh”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, May 21.
135. “Corporate Governance & the Principal-Agent Problem”, lecture at a conference on corporate governance, Kolkata May 31. Published here 2008.
136. “Pakistan’s Allies Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jun 4-5.
137. “Law, Justice and J&K Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 2, The Statesman Editorial Page Jul 3.
138. “The Greatest Pashtun (Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan)”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 16.
139. “Understanding Pakistan Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Jul 30, The Statesman Editorial Page Jul 31.
140. “Indian Money and Credit”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 6.
141. “India’s Moon Mission”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 13.
142. “Jaswant’s Journeyings: A Review Article”, The Sunday Statesman Magazine, Aug 27.
143. “Our Energy Interests, Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 27, The Statesman Editorial Page Aug 28.
144. “Is Balochistan Doomed?”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Sep 3 2006.
145. “Racism New and Old”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Sep 8 2006
146. “Political Economy of India’s Energy Policy”, address to KAF-TERI conference, Goa Oct 7, published in 146a.
147. “New Foreign Policy? Seven phases of Indian foreign policy may be identifiable since Nehru”, Parts 1-2, The Sunday Statesman, Oct 8, The Statesman Oct 9.
148. “Justice & Afzal: There is a difference between law and equity (or natural justice). The power of pardon is an equitable power. Commuting a death-sentence is a partial pardon”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Oct 14
149. “Non-existent liberals (On a Liberal Party for India)”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Oct 22.
150. “History of Jammu & Kashmir Parts 1-2”, The Sunday Statesman, Oct 29, The Statesman Oct 30, Editorial Page.
151. “American Democracy: Does America need a Prime Minister and a longer-lived Legislature?”, The Sunday Statesman Nov 5.
152. “Milton Friedman A Man of Reason 1912-2006”, The Statesman Perspective Page, Nov 22.
153. “Postscript to Milton Friedman Mahalanobis’s Plan (The Mahalanobis-Nehru “Second Plan”) The Statesman Front Page Nov 22.
154. “Mob Violence and Psychology”, Dec 10, The Statesman, Editorial Page.
155. “What To Tell Musharraf: Peace Is Impossible Without Non-Aggressive Pakistani Intentions”, The Statesman Editorial Page Dec 15.
156. “Land, Liberty and Value: Government must act in good faith treating all citizens equally – not favouring organised business lobbies and organised labour over an unorganised peasantry”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page Dec 31.
2007
157. “Hypocrisy of the CPI-M: Political Collapse In Bengal: A Mid-Term Election/Referendum Is Necessary”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Jan 9.
158. “On Land-Grabbing: Dr Singh’s India, Buddhadeb’s Bengal, Modi’s Gujarat have notorious US, Soviet and Chinese examples to follow ~ distracting from the country’s real economic problems,” The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page Jan 14.
159. “India’s Macroeconomics: Real growth has steadily occurred because India has shared the world’s technological progress. But bad fiscal, monetary policies over decades have led to monetary weakness and capital flight” The Statesman Editorial Page Jan 20.
160. “Fiscal Instability: Interest payments quickly suck dry every year’s Budget. And rolling over old public debt means that Government Borrowing in fact much exceeds the Fiscal Deficit”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 4.
161. “Our trade and payments Parts 1-2” (“India in World Trade and Payments”),The Sunday Statesman, Feb 11 2007, The Statesman, Feb 12 2007.
162. “Our Policy Process: Self-Styled “Planners” Have Controlled India’s Paper Money For Decades,” The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 20.
163. “Bengal’s Finances”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, Feb 25.
164. “Fallacious Finance: Congress, BJP, CPI-M may be leading India to Hyperinflation” The Statesman Editorial Page Mar 5.
165. “Uttar Pradesh Polity and Finance: A Responsible New Govt May Want To Declare A Financial Emergency” The Statesman Editorial Page, Mar 24
166. “A scam in the making” in The Sunday Statesman Front Page Apr 1 2007, published here in full as “Swindling India”.
167. “Maharashtra’s Money: Those Who Are Part Of The Problem Are Unlikely To Be A Part Of Its Solution”, The Statesman Editorial Page Apr 24.
146a. “Political Economy of Energy Policy” in India and Energy Security edited by Anant Sudarshan and Ligia Noronha, Konrad Adenauer Stiftung, New Delhi 2007.
168. “Presidential Qualities: Simplicity, Genuine Achievement Are Desirable; Political Ambition Is Not”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, May 8.
169. “We & Our Neighbours: Pakistanis And Bangladeshis Would Do Well To Learn From Sheikh Abdullah”, The Statesman, Editorial Page May 15.
170. “On Indian Nationhood: From Tamils To Kashmiris And Assamese And Mizos To Sikhs And Goans”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, May 25.
171. A Current Example of the Working of the Unconscious Mind, May 26.
172. Where I would have gone if I was Osama Bin Laden, May 31.
173. “US election ’08:America’s Presidential Campaign Seems Destined To Be Focussed On Iraq”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 1.
174. “Home Team Advantage: On US-Iran talks and Sunni-Shia subtleties: Tehran must transcend its revolution and endorse the principle that the House of Islam has many mansions”, The Sunday Statesman Editorial Page, June 3
175. “Unhealthy Delhi: When will normal political philosophy replace personality cults?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 11.
176. “American Turmoil: A Vice-Presidential Coup – And Now a Grassroots Counterrevolution?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, June 18
177. “Political Paralysis: India has yet to develop normal conservative, liberal and socialist parties. The Nice-Housing-Effect and a little game-theory may explain the current stagnation”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, June 24.
177. “Has America Lost? War Doctrines Of Kutusov vs Clausewitz May Help Explain Iraq War”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 3.
178. “Lal Masjid ≠ Golden Temple: Wide differences are revealed between contemporary Pakistan and India by these two superficially similar military assaults on armed religious civilians”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page July 15
179 “Political Stonewalling: Only Transparency Can Improve Institutions”, The Statesman, Editorial Page July 20.
180. “Gold standard etc: Fixed versus flexible exchange rates”, July 21.
181. “US Pakistan-India Policy: Delhi & Islamabad Still Look West In Defining Their Relationship”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 27.
182. “Works of DH Lawrence” July 30
183. “An Open Letter to Professor Amartya Sen about Singur etc”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, July 31.
184. “Martin Buber on Palestine and Israel (with Postscript)”, Aug 4.
185. “Auguste Rodin on Nature, Art, Beauty, Women and Love”, Aug 7.
186. “Saving Pakistan: A Physicist/Political Philosopher May Represent Iqbal’s “Spirit of Modern Times”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 13.
187. Letter to Forbes.com 16 Aug.
188. “Need for Clarity: A poorly drafted treaty driven by business motives is a recipe for international misunderstanding”, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Aug 19.
189. “No Marxist MBAs? An amicus curiae brief for the Hon’ble High Court”, The Statesman, FrontPage, Aug 29.
190. On Lawrence, Sep 4.
191. Dalai Lama’s Return: In the tradition of Gandhi, King, Mandela, Sep 11.
192. Of JC Bose, Patrick Geddes & the Leaf-World, Sep 12.
193. “Against Quackery: Manmohan and Sonia have violated Rajiv Gandhi’s intended reforms; the Communists have been appeased or bought; the BJP is incompetent Parts 1-2”, in The Sunday Statesman and The Statesman, Editorial Pages of Sep 23-24.
194. Karl Georg Zinn’s 1994 Review of Philosophy of Economics, Sep 26.
195. DH Lawrence’s Phoenix, Oct 3.
93b. “Rajiv Gandhi and the Origins of India’s 1991 Economic Reform”, Statesman Festival Volume.
196. “Iran, America, Iraq: Bush’s post-Saddam Saddamism — one flip-flop too many?”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 16.
197. “Understanding China: The World Needs to Ask China to Find Her True Higher Self”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 22.
198. “India-USA interests: Elements of a serious Indian foreign policy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Oct 30.
199. “China’s India Aggression : German Historians Discover Logic Behind Communist Military Strategy”, The Statesman, Editorial Page Special Article, Nov 5.
200. Sonia’s Lying Courtier (with Postscript), Nov 25.
201. “Surrender or Fight? War is not a cricket match or Bollywood movie. Can India fight China if it must?” The Statesman, Dec 4, Editorial Page.
202. Hutton and Desai: United in Error Dec 14
203. “China’s Commonwealth: Freedom is the Road to Resolving Taiwan, Tibet, Sinkiang”, The Statesman, Dec 17.
2008
204. “Nixon & Mao vs India: How American foreign policy did a U-turn about Communist China’s India aggression. The Government of India should publish its official history of the 1962 war.” The Sunday Statesman, Jan 6, The Statesman Jan 7 Editorial Page.
205. “Lessons from the 1962 War: Beginnings of a solution to the long-standing border problem: there are distinct Tibetan, Chinese and Indian points of view that need to be mutually comprehended”, The Sunday Statesman, January 13 2008.
206. “Our Dismal Politics: Will Independent India Survive Until 2047?”, The Statesman Editorial Page, Feb 1.
207. Median Voter Model of India’s Electorate Feb 7.
208. “Anarchy in Bengal: Intra-Left bandh marks the final unravelling of “Brand Buddha””, The Sunday Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 10.
209. Fifty years since my third birthday: on life and death.
210. “Pakistan’s Kashmir obsession: Sheikh Abdullah Relied In Politics On The French Constitution, Not Islam”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 16.
211. A Note on the Indian Policy Process Feb 21.
212. “Growth & Government Delusion: Progress Comes From Learning, Enterprise, Exchange, Not The Parasitic State”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 22.
213. “How to Budget: Thrift, Not Theft, Needs to Guide Our Public Finances”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, Feb 26.
214. “India’s Budget Process (in Theory)”, The Statesman, Front Page Feb 29.
215. “Irresponsible Governance: Congress, BJP, Communists, BSP, Sena Etc Reveal Equally Bad Traits”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 4.
216. “American Politics: Contest Between Obama And Clinton Affects The World”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 11.
217. “China’s India Example: Tibet, Xinjiang May Not Be Assimilated Like Inner Mongolia And Manchuria”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, March 25.
218. “Taxation of India’s Professional Cricket: A Proposal”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 1.
219. “Two cheers for Pakistan!”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 7.
220. “Indian Inflation: Upside Down Economics From The New Delhi Establishment Parts 1-2”, The Statesman, Editorial Page, April 15-16.
221. “Assessing Manmohan: The Doctor of Deficit Finance should realise the currency is at stake”, The Statesman, Editorial Page Apr 25.
222. John Wisdom, Renford Bambrough: Main Philosophical Works, May 8.
223. “All India wept”: On the death of Rajiv Gandhi, May 21.
224. “China’s force and diplomacy: The need for realism in India” The Statesman, Editorial Page May 31.
226. Serendipity and the China-Tibet-India border problem June 6
227. “Leadership vacuum: Time & Tide Wait For No One In Politics: India Trails Pakistan & Nepal!”, The Statesman Editorial Page June 7.
228. My meeting Jawaharlal Nehru Oct13 1962
229. Manindranath Roy 1891-1958
230. Surendranath Roy 1860-1929
231. The Roys of Behala 1928.
232. Sarat Chandra visits Surendranath Roy 1927
233. Nuksaan-Faida Analysis = Cost-Benefit Analysis in Hindi/Urdu Jun 30
234. One of many reasons John R Hicks was a great economist July 3
236. My father, Indian diplomat, in the Shah’s Tehran 1954-57 July 8
237 Distribution of Govt of India Expenditure (Net of Operational Income) 1995 July 27
238. Growth of Real Income, Money & Prices in India 1869-2008, July 28.
239. Communism from Social Democracy? But not in India or China! July 29
240. Death of Solzhenitsyn, Aug. 3
240a. Tolstoy on Science and Art, Aug 4.
241. “Reddy`s reckoning: Where should India’s real interest rate be relative to the world?” Business Standard Aug 10
242. “Rangarajan Effect”, Business Standard Aug 24
243. My grandfather’s death in Ottawa 50 years ago today Sep 3
244. My books in the Library of Congress and British Library Sep 12
245. On Jimmy Carter & the “India-US Nuclear Deal”, Sep 12
246. My father after presenting his credentials to President Kekkonen of Finland Sep 14 1973.
247. “October 1929? Not!”, Business Standard, Sep 18.
248. “MK Gandhi, SN Roy, MA Jinnah in March 1919: Primary education legislation in a time of protest”
249. 122 sensible American economists Sept 26
250. Govt of India: Please call in the BBC and ask them a question Sep 27
251. “Monetary Integrity and the Rupee: Three British Raj relics have dominated our macroeconomic policy-making” Business Standard Sep 28.
252a. Rabindranath’s daughter writes to her friend my grandmother Oct 5
252b. A Literary Find: Modern Poetry in Bengal, Oct 6.
253. Sarat writes to Manindranath 1931, Oct 12
254. Origins of India’s Constitutional Politics 1913
255. Indira Gandhi in Paris, 1971
256. How the Liabilities/Assets Ratio of Indian Banks Changed from 84% in 1970 to 108% in 1998, October 20
257a. My Subjective Probabilities on India’s Moon Mission Oct 21
258. Complete History of Mankind’s Moon Missions: An Indian Citizen’s Letter to ISRO’s Chairman, Oct 22.
259. Would not a few million new immigrants solve America’s mortgage crisis? Oct 26
260. “America’s divided economists”, Business Standard Oct 26
261. One tiny prediction about the Obama Administration, Nov 5
262. Rai Bahadur Umbika Churn Rai, 1827-1902, Nov 7 2008
263. Jawaharlal Nehru invites my father to the Mountbatten Farewell Nov 7 2008
70a. “Become a US Supreme Court Justice! (Explorations in the Rule of Law in America) Preface” Nov 9
70b. “Become a US Supreme Court Justice! (Explorations in the Rule of Law in America) Password protected.” Nov 9.
257b. Neglecting technological progress was the basis of my pessimism about Chandrayaan, Nov 9.
264. Of a new New Delhi myth and the success of the University of Hawaii 1986-1992 Pakistan project Nov 15
265. Pre-Partition Indian Secularism Case-Study: Fuzlul Huq and Manindranath Roy Nov 16
266. Do President-elect Obama’s Pakistan specialists suppose Maulana Azad, Dr Zakir Hussain, Sheikh Abdullah were Pakistanis (or that Sheikh Mujib wanted to remain one)? Nov 18
267. Jews have never been killed in India for being Jews until this sad day, Nov 28.
268. In international law, Pakistan has been the perpetrator, India the victim of aggression in Mumbai, Nov 30.
269. The Indian Revolution, Dec 1.
270. Habeas Corpus: a captured terrorist mass-murderer tells a magistrate he has not been mistreated by Mumbai’s police Dec 3
271. India’s Muslim Voices (Or, Let us be clear the Pakistan-India or Kashmir conflicts have not been Muslim-Hindu conflicts so much as intra-Muslim conflicts about Muslim identity and self-knowledge on the Indian subcontinent), Dec 4
272. “Anger Management” needed? An Oxford DPhil recommends Pakistan launch a nuclear first strike against India within minutes of war, Dec 5.
273. A Quick Comparison Between the September 11 2001 NYC-Washington attacks and the November 26-28 2008 Mumbai Massacres (An Application of the Case-by-Case Philosophical Technique of Wittgenstein, Wisdom and Bambrough), Dec 6
274. Dr Rice finally gets it right (and maybe Mrs Clinton will too) Dec 7
275. Will the Government of India’s new macroeconomic policy dampen or worsen the business-cycle (if such a cycle exists at all)? No one knows! “Where ignorance is bliss, ‘Tis folly to be wise.” Dec 7
276. Pump-priming for car-dealers: Keynes groans in his grave (If evidence was needed of the intellectual dishonesty of New Delhi’s new macroeconomic policy, here it is) Dec 9.
277. Congratulations to Mumbai’s Police: capturing a terrorist, affording him his Habeas Corpus rights, getting him to confess within the Rule of Law, sets a new world standard Dec 10
278. Two cheers — wait, let’s make that one cheer — for America’s Justice Department, Dec 10
279. Will Pakistan accept the bodies of nine dead terrorists who came from Pakistan to Mumbai? If so, let there be a hand-over at the Wagah border, Dec 11.
280. Kasab was a stupid, ignorant, misguided youth, manufactured by Pakistan’s terrorist masterminds into becoming a mass-murdering robot: Mahatma Gandhi’s India should punish him, get him to repent if he wishes, then perhaps rehabilitate him as a potent weapon against Pakistani terrorism Dec 12.
281. Pakistan’s New Delhi Embassy should ask for “Consular Access” to nine dead terrorists in a Mumbai morgue before asking to meet Kasab, Dec 13
282. An Indian Reply to President Zardari: Rewarding Pakistan for bad behaviour leads to schizophrenic relationships Dec 19
283. Is my prediction about Caroline Kennedy becoming US Ambassador to Britain going to be correct? Dec 27
284. Chandrayaan adds a little good cheer! Well done, ISRO!, Dec 28
285. How sad that “Slumdog millionaire” is SO disappointing! Dec 31
289. (with Claude Arpi) “Transparency & history: India’s archives must be opened to world standards” Business Standard New Delhi Dec 31, 2008, published here Jan 1 .
2009
290. A basis of India-Pakistan cooperation on the Mumbai massacres: the ten Pakistani terrorists started off as pirates and the Al-Huseini is a pirate ship Jan 1.
291. India’s “pork-barrel politics” needs a nice (vegetarian) Hindi name! “Teli/oily politics” perhaps? (And are we next going to see a Bill of Rights for Lobbyists?) Jan 3
292. My (armchair) experience of the 1999 Kargil war (Or, “Actionable Intelligence” in the Internet age: How the Kargil effort got a little help from a desktop) Jan 5
293. How Jammu & Kashmir’s Chief Minister Omar Abdullah can become a worthy winner of the Nobel Peace Prize: An Open Letter, Jan 7
294. Could the Satyam/PwC fraud be the visible part of an iceberg? Where are India’s “Generally Accepted Accounting Principles”? Isn’t governance rather poor all over corporate India? Bad public finance may be a root cause Jan 8
295. Satyam does not exist: it is bankrupt, broke, kaput. Which part of this does the new “management team” not get? The assets belong to Satyam’s creditors. Jan 8
296. Jews are massacred in Mumbai and now Jews commit a massacre in Gaza! Jan 9
297. And now for the Great Satyam Whitewash/Cover-Up/Public Subsidy! The wrong Minister appoints the wrong new Board who, probably, will choose the wrong policy Jan 12
298. Letter to Wei Jingsheng Jan 14
299. Memo to the Hon’ble Attorneys General of Pakistan & India: How to jointly prosecute the Mumbai massacre perpetrators most expeditiously Jan 16
300. Satyam and IT-firms in general may be good candidates to become “Labour-Managed” firms Jan 18
301. “Yes we might be able to do that. Perhaps we ought to. But again, perhaps we ought not to, let me think about it…. Most important is Cromwell’s advice: Think it possible we may be mistaken!” Jan 20.
302. RAND’s study of the Mumbai attacks Jan 25
303. Didn’t Dr Obama (the new American President’s late father) once publish an article in Harvard’s Quarterly Journal of Economics? (Or did he?) Jan 25.
304. “A Dialogue in Macroeconomics” 1989 etc: sundry thoughts on US economic policy discourse Jan 30
305. American Voices: A Brief Popular History of the United States in 20 You-Tube Music Videos Feb 5
306. Jaladhar Sen writes to Manindranath at Surendranath’s death, Feb 23
307. Pakistani expansionism: India and the world need to beware of “Non-Resident Pakistanis” ruled by Rahmat Ali’s ghost, Feb 9
308. My American years Part One 1980-90: battles for academic integrity & freedom Feb 11.
309. Thanks and well done Minister Rehman Malik and the Govt of Pakistan Feb 12
310. Can President Obama resist the financial zombies (let alone slay them)? His economists need to consult Dr Anna J Schwartz Feb 14
311. A Brief History of Gilgit, Feb 18
312. Memo to UCLA Geographers: Commonsense suggests Mr Bin Laden is far away from the subcontinent Feb 20
313. The BBC gets its history and geography deliberately wrong again Feb 21
314. Bengal Legislative Council 1921, Feb 28
315. Carmichael visits Surendranath, 1916, Mar 1
316. Memo to GoI CLB: India discovered the Zero, and 51% of Zero is still Zero Mar 10
317. An Academic Database of Doctoral & Other Postgraduate Research Done at UK Universities on India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Other Asian Countries Over 100 Years, Mar 13
318. Pakistan’s progress, Mar 18
319. Risk-aversion explains resistance to free trade, Mar 19
320. India’s incredibly volatile inflation rate! Mar 20
321. Is “Vicky, Cristina, Barcelona” referring to an emasculation of (elite) American society?, Mar 21
322. Just how much intellectual fraud can Delhi produce? Mar 26
323. India is not a monarchy! We urgently need to universalize the French concept of “citoyen”! Mar 28
324. Could this be the real state of some of our higher education institutions? Mar 29
325. Progress! The BBC retracts its prevarication! Mar 30
326. Aldous Huxley’s Essay “DH Lawrence” Mar 31
327. Waffle not institutional reform is what (I predict) the “G-20 summit” will produce, April 1
328. Did a full cricket team of Indian bureaucrats follow our PM into 10 Downing Street? Count for yourself! April 3
329. Will someone please teach the BJP’s gerontocracy some Economics 101 on an emergency basis? April 5
330. The BBC needs to determine exactly where it thinks Pakistan is!, April 5
331. Alfred Lyall on Christians, Muslims, India, China, Etc, 1908, April 6
332. An eminent economist of India passes away April 9
333. Democracy Database for the Largest Electorate Ever Seen in World History, April 12
334. Memo to the Election Commission of India April 14 2009, 9 AM, April 14
335. Caveat emptor! Satyam is taken over, April 14
336. India’s 2009 General Elections: Candidates, Parties, Symbols for Polls on 16-30 April Phases 1,2,3, April 15
337. On the general theory of expertise in democracy: reflections on what emerges from the American “torture memos” today, April 18
338. India’s 2009 General Elections: 467 constituencies (out of 543) for which candidates have been announced as of 1700hrs April 21, April 21
339. Apropos Philosophy of Economics, Comments of Sidney Hook, KJ Arrow, Milton Friedman, TW Schultz, SS Alexander, Max Black, Renford Bambrough, John Gray et al., April 22.
340. India’s 2009 General Elections: Names of all 543 Constituencies of the 15th Lok Sabha, April 22.
341. India’s 2009 General Elections: How 4125 State Assembly Constituencies comprise the 543 new Lok Sabha Constituencies, April 23.
342. Why has America’s “torture debate” yet to mention the obvious? Viz., sadism and racism, April 24
343. India’s 2009 General Elections: the advice of the late “George Eliot” (Mary Ann Evans, 1819-1880) to India’s voting public, April 24.
344. India’s 2009 General Elections: Delimitation and the Different Lists of 543 Lok Sabha Constituencies in 2009 and 2004, April 25
345. Is “Slumdog Millionaire” the single worst Best Picture ever?
346. India’s 2009 General Elections: Result of Delimitation — Old (2004) and New (2009) Lok Sabha and Assembly Constituencies, April 26
347. India’s 2009 General Elections: 7019 Candidates in 485 (out of 543) Constituencies announced as of April 26 noon April 26
348. What is Christine Fair referring to? Would the MEA kindly seek to address what she has claimed asap? April 27
349. Politics can be so entertaining 🙂 Manmohan versus Sonia on the poor old CPI(M)!, April 28
350. A Dozen Grown-Up Questions for Sonia Gandhi, Manmohan Singh, LK Advani, Sharad Pawar, Km Mayawati and Anyone Else Dreaming of Becoming/Deciding India’s PM After the 2009 General Elections, April 28
351. India’s 2009 General Elections: How drastically will the vote-share of political parties change from 2004? May 2
352. India’s 2009 General Elections: And now finally, all 8,070 Candidates across all 543 Lok Sabha Constituencies, May 5
353. India’s 2009 General Elections: The Mapping of Votes into Assembly Segments Won into Parliamentary Seats Won in the 2004 Election, May 7
354. Will Messrs Advani, Rajnath Singh & Modi ride into the sunset if the BJP comes to be trounced? (Corrected), May 10
355. India’s 2009 General Elections: 543 Matrices to Help Ordinary Citizens Audit the Election Commission’s Vote-Tallies May 12
356. Well done Sonia-Rahul! Two hours before polls close today, I am willing to predict a big victory for you (but, please, try to get your economics right, and also, you must get Dr Singh a Lok Sabha seat if he is to be PM) May 13
357. Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee must dissolve the West Bengal Assembly if he is an honest democrat: Please try to follow Gerard Schröder’s example even slightly! May 16
358. India’s 2009 General Elections: Provisional Results from the EC as of 1400 hours Indian Standard Time May 16
359. Memo to the Hon’ble President of India: It is Sonia Gandhi, not Manmohan Singh, who should be invited to our equivalent of the “Kissing Hands” Ceremony May 16
360. Time for heads to roll in the BJP/RSS and CPI(M)!, May 17.
361. Inviting a new Prime Minister of India to form a Government: Procedure Right and Wrong May 18
362. Starting with Procedural Error: Why has the “Cabinet” of the 14th Lok Sabha been meeting today AFTER the results of the Elections to the 15th Lok Sabha have been declared?! May 18
363. Why has the Sonia Congress done something that the Congress under Nehru-Indira-Rajiv would not have done, namely, exaggerate the power of the Rajya Sabha and diminish the power of the Lok Sabha? May 21
364. Shouldn’t Dr Singh’s Cabinet begin with a small apology to the President of India for discourtesy? May we have reviews and reforms of protocols and practices to be followed at Rashtrapati Bhavan and elsewhere? May 23
365. Parliament’s sovereignty has been diminished by the Executive: A record for future generations to know May 25
366. How tightly will organised Big Business be able to control economic policies this time? May 26
367. Why does India not have a Parliament ten days after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected? Nehru and Rajiv would both have been appalled May 27
368. Eleven days and counting after the 15th Lok Sabha was elected and still no Parliament of India! (But we do have 79 Ministers — might that be a world record?) May 28
369. Note to Posterity: 79 Ministers in office but no 15th Lok Sabha until June 1 2009! May 29
370. Silver Jubilee of Pricing, Planning & Politics: A Study of Economic Distortions in India May 29
371. How to Design a Better Cabinet for the Government of India May 29
372. Parliament is supposed to control the Government, not be bullied or intimidated by it: Will Rahul Gandhi be able to lead the Backbenches in the 15th Lok Sabha? June 1
373. Mistaken Macroeconomics: An Open Letter to Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh, June 12
374. Why did Manmohan Singh and LK Advani apologise to one another? Is Indian politics essentially collusive, not competitive, aiming only to preserve and promote the post-1947 Dilli Raj at the expense of the whole of India? We seem to have no Churchillian repartee (except perhaps from Bihar occasionally) June 18
375. Are Iran’s Revolutionaries now Reactionaries? George Orwell would have understood. A fresh poll may be the only answer Are Iran’s Revolutionaries now Reactionaries? George Orwell would have understood. A fresh poll may be the only answer June 22
376. My March 25 1991 memo to Rajiv (which never reached him) is something the present Government seems to have followed: all for the best of course! July 12
377. Disquietude about France’s behaviour towards India on July 14 2009 July 14
378. Does the Govt. of India assume “foreign investors and analysts” are a key constituency for Indian economic policy-making? If so, why so? Have Govt. economists “learnt nothing, forgotten everything”? Some Bastille Day thoughts July 14
379. Letter to the GoI’s seniormost technical economist, May 21.July 19
380. Excuse me but young Kasab in fact confessed many months ago, immediately after he was captured – he deserves 20 or 30 years in an Indian prison, and a chance to become a model prisoner who will stand against the very terrorists who sent him on his vile mission July 20
381. Finally, three months late, the GoI responds to American and Pakistani allegations about Balochistan July 24
382. Thoughts, words, deeds: My work 1973-2010
M1. Map of Asia c. 1900
M2. Map of Chinese Empire c. 1900
M3. Map of Sinkiang, Tibet and Neighbours 1944
M4. China’s Secretly Built 1957 Road Through India’s Aksai Chin
M5. Map of Kashmir to Sinkiang 1944
M6. Map of India-Tibet-China-Mongolia 1959
M7. Map of India, Afghanistan, Russia, China, 1897
M8. Map of Xinjiang/Sinkiang/E Turkestan
M9. Map of Bombay/Mumbai 1909
M10-M13. Himalayan Expedition, West Sikkim 1970 – 1,2,3,4